Kainate Receptors
Kainate receptors, or KARs, are ionotropic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter glutamate. They were first identified as a distinct receptor type through their selective activation by the agonist kainate, a drug first isolated from the red alga Digenea simplex. KARs are less understood than AMPA and NMDA receptors, the other ionotropic glutamate receptors. Postsynaptic kainate receptors are involved in excitatory neurotransmission. Presynaptic kainate receptors have been implicated in inhibitory neurotransmission by modulating release of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA through a presynaptic mechanism.
Products for Kainate Receptors
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
BCC5883
PDZ1 Domain inhibitor peptideDisrupts interaction between GluR6 and PSD-95 PDZ1 domain
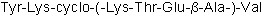
-
BCC6052
UBP 310

-
BCC6572
Kainic acidkainate receptor agonist, selective
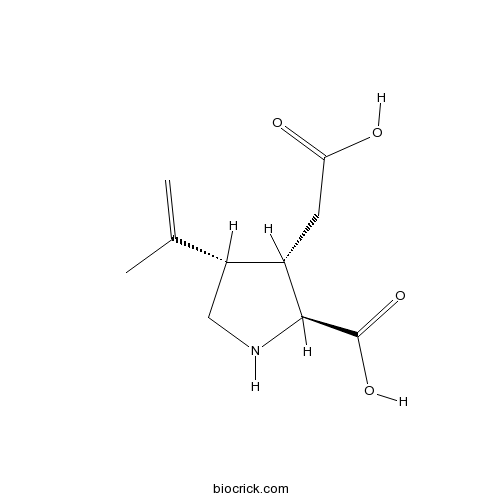
-
BCC6586
Domoic acid
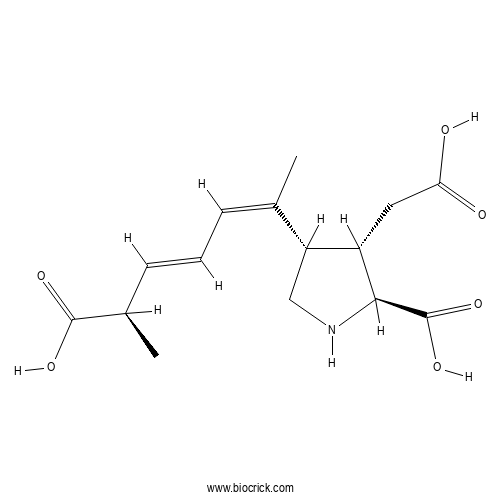
-
BCC6597
(S)-(-)-5-Iodowillardiine
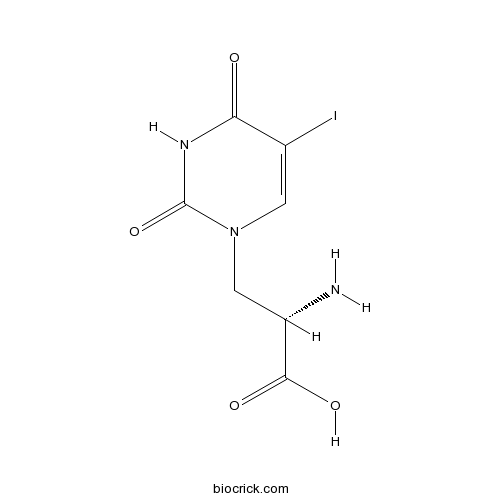
-
BCC6840
SYM 2081Inhibits EAAT2. Also kainate receptor agonist

-
BCC6940
ATPA
-
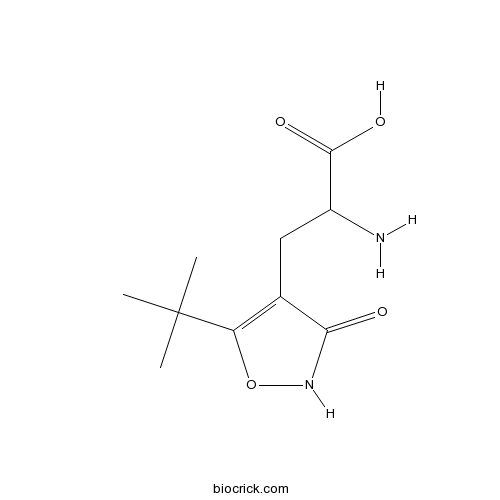
BCC7172
UBP 301
-
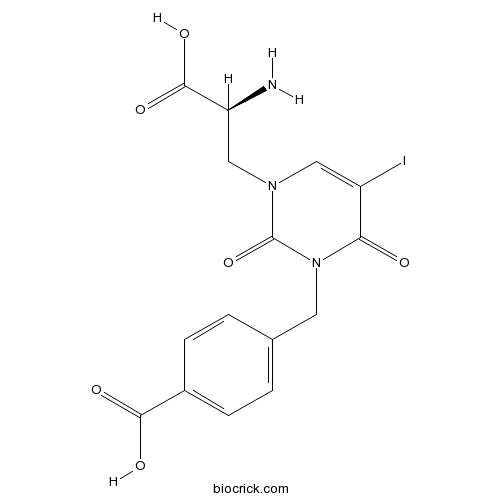
BCC7255
UBP 296
-
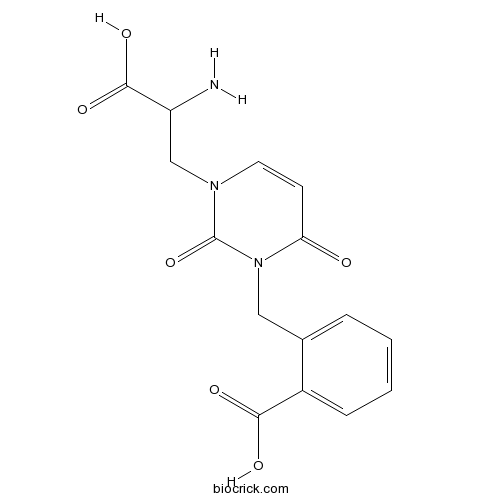
BCC7256
UBP 302
-
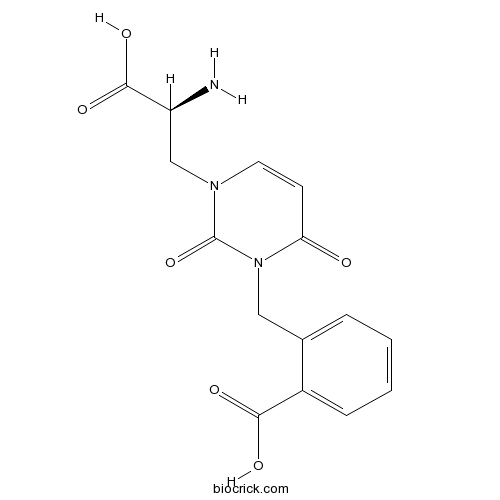
BCC7275
NS 3763
-
BCC7462
ACET



