Kainic acidkainate receptor agonist, selective CAS# 487-79-6 |
- 3,3'-Diindolylmethane
Catalog No.:BCC1306
CAS No.:1968-05-4
- BAM7
Catalog No.:BCC1397
CAS No.:331244-89-4
- Bendamustine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1153
CAS No.:3543-75-7
- Betulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5524
CAS No.:472-15-1
- Brassinolide
Catalog No.:BCC1438
CAS No.:72962-43-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 487-79-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10255 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H15NO4 | M.Wt | 213.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (234.49 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
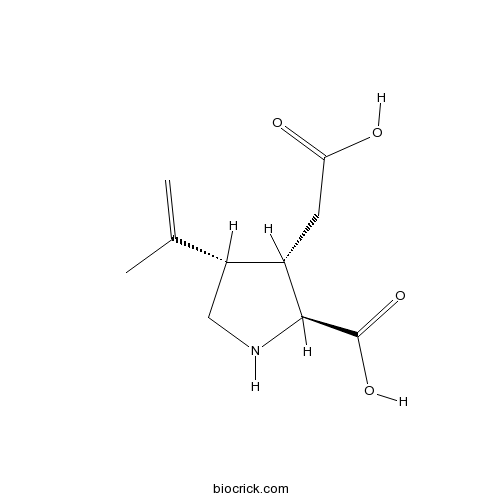
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S)-3-(carboxymethyl)-4-prop-1-en-2-ylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(=C)C1CNC(C1CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VLSMHEGGTFMBBZ-OOZYFLPDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H15NO4/c1-5(2)7-4-11-9(10(14)15)6(7)3-8(12)13/h6-7,9,11H,1,3-4H2,2H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15)/t6-,7+,9-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective agonist at kainate receptors. Potent excitant and neurotoxin. Also available as part of the Kainate Receptor Tocriset™. |

Kainic acid Dilution Calculator

Kainic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6898 mL | 23.4489 mL | 46.8977 mL | 93.7954 mL | 117.2443 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.938 mL | 4.6898 mL | 9.3795 mL | 18.7591 mL | 23.4489 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.469 mL | 2.3449 mL | 4.6898 mL | 9.3795 mL | 11.7244 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0938 mL | 0.469 mL | 0.938 mL | 1.8759 mL | 2.3449 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0469 mL | 0.2345 mL | 0.469 mL | 0.938 mL | 1.1724 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Kainic acid is a selective agonist of kainate receptor [1].
Kainate receptor is an ionotropic receptor that responds to glutamate. Presynaptic kainate receptor modulates GABA release and is involved in inhibitory neurotransmission. Postsynaptic kainate receptor is involved in excitatory neurotransmission.
In aged rats, kainic acid significantly reduced the latency to full clonic-tonic seizures and increased the amount of seizures rats. Also, kainic acid significantly increased the release of norepinephrine (NE), ASP and GLU in aged rats with clonic-tonic seizures [1]. In neonatal rats, intrahippocampal injection of kainic acid (1 μg) significantly induced pyramidal cell death [2]. In adult rats, kainic acid significantly increased the mRNA levels of neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5) in the dorsal horn and in the spinal cord white matter, and increased the mRNA level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the ventral horn. While kainic acid didn’t affect neurotrophin-3 (NT-3). These results suggested that NT-4/5 and BDNF participated in the response of the spinal cord to excitotoxic stimuli induced by kainic acid [3].
References:
[1]. Dawson R Jr, Wallace DR. Kainic acid-induced seizures in aged rats: neurochemical correlates. Brain Res Bull, 1992, 29(3-4): 459-468.
[2]. Cook TM, Crutcher KA. Intrahippocampal injection of kainic acid produces significant pyramidal cell loss in neonatal rats. Neuroscience, 1986, 18(1): 79-92.
[3]. Scarisbrick IA, Isackson PJ, Windebank AJ. Differential expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5 in the adult rat spinal cord: regulation by the glutamate receptor agonist kainic acid. J Neurosci, 1999, 19(18): 7757-7769.
- Hypaphorine
Catalog No.:BCN2775
CAS No.:487-58-1
- Butein
Catalog No.:BCN5592
CAS No.:487-52-5
- Ononetin
Catalog No.:BCC6367
CAS No.:487-49-0
- Phillyrin
Catalog No.:BCN1096
CAS No.:487-41-2
- Phillygenin
Catalog No.:BCN2653
CAS No.:487-39-8
- Pinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5591
CAS No.:487-36-5
- Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3042
CAS No.:487-35-4
- Scopoline
Catalog No.:BCN1942
CAS No.:487-27-4
- Elemicin
Catalog No.:BCN2818
CAS No.:487-11-6
- Citropten
Catalog No.:BCN4831
CAS No.:487-06-9
- Cyclocalopin A
Catalog No.:BCN5587
CAS No.:486430-94-8
- O-Acetylcyclocalopin A
Catalog No.:BCN5586
CAS No.:486430-93-7
- Lindelofine
Catalog No.:BCN2043
CAS No.:487-99-0
- HI TOPK 032
Catalog No.:BCC6225
CAS No.:487020-03-1
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
- SNAP 94847 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7658
CAS No.:487051-12-7
- Curcumol
Catalog No.:BCN5976
CAS No.:4871-97-0
- Heleurine
Catalog No.:BCN1953
CAS No.:488-00-6
- Thesinine
Catalog No.:BCN1990
CAS No.:488-02-8
- 3-Methylcatechol
Catalog No.:BCN3925
CAS No.:488-17-5
- Allitol
Catalog No.:BCN5593
CAS No.:488-44-8
- vibo-Quercitol
Catalog No.:BCN5594
CAS No.:488-76-6
- D-Ribitol-5-phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4838
CAS No.:35320-17-3
- D-arabinitol
Catalog No.:BCN5595
CAS No.:488-82-4
Long-term electrical stimulation at ear and electro-acupuncture at ST36-ST37 attenuated COX-2 in the CA1 of hippocampus in kainic acid-induced epileptic seizure rats.[Pubmed:28352122]
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 28;7(1):472.
Seizures produce brain inflammation, which in turn enhances neuronal excitability. Therefore, anti-inflammation has become a therapeutic strategy for antiepileptic treatment. Cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) plays a critical role in postseizure brain inflammation and neuronal hyperexcitability. Our previous studies have shown that both electrical stimulation (ES) at the ear and electro-acupuncture (EA) at the Zusanli and Shangjuxu acupoints (ST36-ST37) for 6 weeks can reduce mossy fiber sprouting, spike population, and high-frequency hippocampal oscillations in Kainic acid (KA)-induced epileptic seizure rats. This study further investigated the effect of long-term ear ES and EA at ST36-ST37 on the inflammatory response in KA-induced epileptic seizure rats. Both the COX-2 levels in the hippocampus and the number of COX-2 immunoreactive cells in the hippocampal CA1 region were increased after KA-induced epileptic seizures, and these were reduced through the 6-week application of ear ES or EA at ST36-ST37. Thus, long-term ear ES or long-term EA at ST36-ST37 have an anti-inflammatory effect, suggesting that they are beneficial for the treatment of epileptic seizures.
Pregnane X Receptor Not Nuclear Factor-kappa B Up-regulates P-glycoprotein Expression in the Brain of Chronic Epileptic Rats Induced by Kainic Acid.[Pubmed:28303499]
Neurochem Res. 2017 Aug;42(8):2167-2177.
Drug-resistance epilepsy (DRE) is attributed to the brain P-glycoprotein (P-gp) overexpression. We previously reported that nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) played a critical role in regulating P-gp expression at the brain of the acute seizure rats. This study was extended further to investigate the interaction effect of NF-kappaB and pregnane X receptor (PXR) on P-gp expression at the brain of chronic epileptic rats treated with carbamazepine (CBZ). The chronic epileptic models were induced by the micro-injection of Kainic acid (KA) into rats' hippocampus. Subsequently, the successful models were treated with different intervention agents of CBZ; PMA(a non-specific PXR activity inhibitor) or PDTC(a specific NF-kappaB activity inhibitor) respectively. The expression levels of P-gp and its encoded gene mdr1a/b were significantly up-regulated on the brain of KA-induced chronic epilepsy rats or the epilepsy rats treated with CBZ for 1 week, meanwhile with a high expression of PXR. The treatment of PMA dramatically reduced both PXR and P-gp expressions at the protein and mRNA levels in the chronic epilepsy brain. By compared to the epilepsy model group, the P-gp expression was not markedly attenuated by the inhibition of NF-kappaB activity with PDTC treatment, nevertheless with a decrease of NF-kappaB expression in this intervention group. Higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines(IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha) were found both in the brain tissue and the serum in the epilepsy rats of each group. There was a declined trend of the pro-inflammatory cytokines expression of the PDTC treatment group but with no statistical significance. This study demonstrates for the first time that P-gp up-regulation is due to increase PXR expression in the chronic phase of epilepsy, differently from that NF-kappaB signaling may induce the P-gp expression in the acute seizure phase. Our results offer insights into the mechanism underlying the development of DRE using or not using CBZ treatment.
Melatonin Mediates Protective Effects against Kainic Acid-Induced Neuronal Death through Safeguarding ER Stress and Mitochondrial Disturbance.[Pubmed:28293167]
Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Feb 28;10:49.
Kainic acid (KA)-induced neuronal death is linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Melatonin is known to protect hippocampal neurons from KA-induced apoptosis, but the exact mechanisms underlying melatonin protective effects against neuronal mitochondria disorder and ER stress remain uncertain. In this study, we investigated the sheltering roles of melatonin during KA-induced apoptosis by focusing on mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress mediated signal pathways. KA causes mitochondrial dynamic disorder and dysfunction through calpain activation, leading to neuronal apoptosis. Ca(2+) chelator BAPTA-AM and calpain inhibitor calpeptin can significantly restore mitochondrial morphology and function. ER stress can also be induced by KA treatment. ER stress inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid (PBA) attenuates ER stress-mediated apoptosis and mitochondrial disorder. It is worth noting that calpain activation was also inhibited under PBA administration. Thus, we concluded that melatonin effectively inhibits KA-induced calpain upregulation/activation and mitochondrial deterioration by alleviating Ca(2+) overload and ER stress.
Neurons of the rat cervical spinal cord express vimentin and neurofilament after intraparenchymal injection of kainic acid.[Pubmed:28229936]
Neurosci Lett. 2017 Mar 16;643:103-110.
Intermediate filaments (IF) can be altered under disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases. Kainic acid (KA) induce behavioral changes and histopathological alterations of the spinal cord of injected rats. Our goal was to evaluate the IF expression in neurons during this injury model. Animals were injected with KA at the C5 segment of the cervical spinal cord and euthanized at 1, 3 and 7 post injection (pi) days. Neuronal cell counting showed a significant loss of neurons at the injection site when compared with those of sham and non-operated animals. Immunohistochemistry for vimentin and neurofilament showed positive labeling of perikarya in sham and KA-injected animals since day 1 pi that lasted for the remaining experimental days. Colocalization analysis between enolase and vimentin or neurofilament confirmed a high index of colocalization in both experimental groups at day 1 pi. This index decreased in sham animals by day 3 pi whereas that of KA-injected animals remained high throughout the experiment. These results may suggest that perikarya initiate an unconventional IF expression, which may respond to the neuronal damage induced by the mechanical injury and the excitotoxic effect of KA. It seems that vimentin and neurofilament expression may be a necessary change to promote recovery of the damaged tissue.


