CitroptenCAS# 487-06-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 487-06-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2775 | Appearance | Yellowish powder |
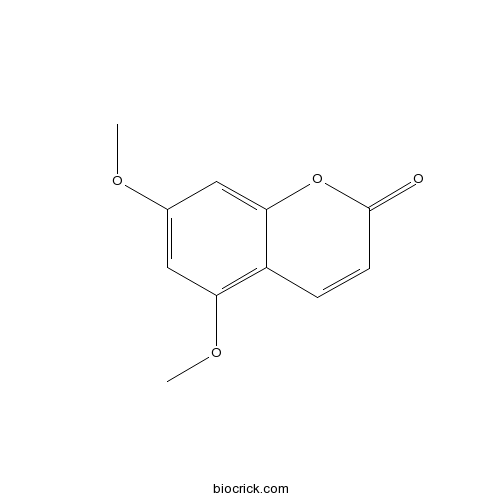
| Formula | C11H10O4 | M.Wt | 206.2 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 5,7-Dimethoxycoumarin; Limettin | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dimethoxychromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=C2C=CC(=O)OC2=C1)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NXJCRELRQHZBQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H10O4/c1-13-7-5-9(14-2)8-3-4-11(12)15-10(8)6-7/h3-6H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Citropten and valproic acid show antiproliferative effects against A2058 human melanoma cells. |
| In vitro | Antiproliferative effect of valproic acid and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin against A2058 human melanoma cells.[Pubmed: 25745779]Acta Pol Pharm. 2014 Nov-Dec;71(6):1056-9.Melanoma is one of the most malignant tumors of a dangerous high incidence and high metastatic potential. It grows quickly and in an advanced stage is resistant to radio-, chemo- and immunotherapy, which makes it difficult to cure. Therefore, research efforts are focused on the development of new therapeutics or chemopreventive strategies. Inactivation of plant-pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum acutatum with natural plant-produced photosensitizers under solar radiation.[Pubmed: 27434699 ]J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016 Sep;162:402-11.The increasing tolerance to currently used fungicides and the need for environmentally friendly antimicrobial approaches have stimulated the development of novel strategies to control plant-pathogenic fungi such as antimicrobial phototreatment (APT). |
| Cell Research | EPR studies of free radicals in A-2058 human melanoma cells treated by valproic acid and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin.[Pubmed: 25745781]Acta Pol Pharm. 2014 Nov-Dec;71(6):1066-72.Free radicals in A-2058 human melanoma cells were studied by the use of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. The aim of this work was to determine the changes in relative free radical concentrations in tumor A-2058 cells after treatment by valproic acid (VPA) and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin ((Citropten, DMC). |

Citropten Dilution Calculator

Citropten Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.8497 mL | 24.2483 mL | 48.4966 mL | 96.9932 mL | 121.2415 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9699 mL | 4.8497 mL | 9.6993 mL | 19.3986 mL | 24.2483 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.485 mL | 2.4248 mL | 4.8497 mL | 9.6993 mL | 12.1242 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.097 mL | 0.485 mL | 0.9699 mL | 1.9399 mL | 2.4248 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2425 mL | 0.485 mL | 0.9699 mL | 1.2124 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cyclocalopin A
Catalog No.:BCN5587
CAS No.:486430-94-8
- O-Acetylcyclocalopin A
Catalog No.:BCN5586
CAS No.:486430-93-7
- CIQ
Catalog No.:BCC7862
CAS No.:486427-17-2
- AZD2858
Catalog No.:BCC4509
CAS No.:486424-20-8
- Thermopsine
Catalog No.:BCN2603
CAS No.:486-90-8
- Anagyrine
Catalog No.:BCN3049
CAS No.:486-89-5
- alpha-Isolupanine
Catalog No.:BCN7989
CAS No.:486-87-3
- N-Methylcytisine
Catalog No.:BCN1266
CAS No.:486-86-2
- Harman
Catalog No.:BCN3998
CAS No.:486-84-0
- Daidzein
Catalog No.:BCN5590
CAS No.:486-66-8
- Vasicinone
Catalog No.:BCN5589
CAS No.:486-64-6
- Isoformononetin
Catalog No.:BCN8206
CAS No.:486-63-5
- Elemicin
Catalog No.:BCN2818
CAS No.:487-11-6
- Scopoline
Catalog No.:BCN1942
CAS No.:487-27-4
- Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3042
CAS No.:487-35-4
- Pinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5591
CAS No.:487-36-5
- Phillygenin
Catalog No.:BCN2653
CAS No.:487-39-8
- Phillyrin
Catalog No.:BCN1096
CAS No.:487-41-2
- Ononetin
Catalog No.:BCC6367
CAS No.:487-49-0
- Butein
Catalog No.:BCN5592
CAS No.:487-52-5
- Hypaphorine
Catalog No.:BCN2775
CAS No.:487-58-1
- Kainic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6572
CAS No.:487-79-6
- Lindelofine
Catalog No.:BCN2043
CAS No.:487-99-0
- HI TOPK 032
Catalog No.:BCC6225
CAS No.:487020-03-1
Inactivation of plant-pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum acutatum with natural plant-produced photosensitizers under solar radiation.[Pubmed:27434699]
J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016 Sep;162:402-411.
The increasing tolerance to currently used fungicides and the need for environmentally friendly antimicrobial approaches have stimulated the development of novel strategies to control plant-pathogenic fungi such as antimicrobial phototreatment (APT). We investigated the in vitro APT of the plant-pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum acutatum with furocoumarins and coumarins and solar radiation. The compounds used were: furocoumarins 8-methoxypsoralen (8-MOP) and 5,8-dimethoxypsoralen (isopimpinellin), coumarins 2H-chromen-2-one (coumarin), 7-hydroxycoumarin, 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin (Citropten) and a mixture (3:1) of 7-methoxycoumarin and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin. APT of conidia with crude extracts from 'Tahiti' acid lime, red and white grapefruit were also performed. Pure compounds were tested at 50muM concentration and mixtures and extracts at 12.5mgL(-1). The C. acutatum conidia suspension with or without the compounds was exposed to solar radiation for 1h. In addition, the effects of APT on the leaves of the plant host Citrus sinensis were determined. APT with 8-MOP was the most effective treatment, killing 100% of the conidia followed by the mixture of two coumarins and isopimpinellin that killed 99% and 64% of the conidia, respectively. APT with the extracts killed from 20% to 70% of the conidia, and the extract from 'Tahiti' lime was the most effective. No damage to sweet orange leaves was observed after APT with any of the compounds or extracts.
Antiproliferative effect of valproic acid and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin against A2058 human melanoma cells.[Pubmed:25745779]
Acta Pol Pharm. 2014 Nov-Dec;71(6):1056-9.
Melanoma is one of the most malignant tumors of a dangerous high incidence and high metastatic potential. It grows quickly and in an advanced stage is resistant to radio-, chemo- and immunotherapy, which makes it difficult to cure. Therefore, research efforts are focused on the development of new therapeutics or chemopreventive strategies. The aim of the study was to investigate whether the valproic acid and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin have an antiproliferative activity against A2058 human melanoma cell line. Investigated compounds inhibited the proliferation of cells, however, no synergistic effect of their co-administration was observed.
EPR studies of free radicals in A-2058 human melanoma cells treated by valproic acid and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin.[Pubmed:25745781]
Acta Pol Pharm. 2014 Nov-Dec;71(6):1066-72.
Free radicals in A-2058 human melanoma cells were studied by the use of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. The aim of this work was to determine the changes in relative free radical concentrations in tumor A-2058 cells after treatment by valproic acid (VPA) and 5,7-dimethoxycoumarin (DMC). The influences of VPA and DMC on free radicals in A-2058 cells were compared with those for human melanoma malignum A-375 and G-361 cells, which were tested by us earlier. Human malignant melanoma A-2058 cells were exposed to interactions with VPA, DMC, and both VPA and DMC. The tumor cells A-2058 were purchased from LGC Standards (Lomianki, Poland), and they were grown in the standard conditions: at 37 degrees C and in an atmosphere containing 95% air and 5% CO2, in the Minimum Essential Medium Eagle (MEM, Sigma-Aldrich). The A-2058 cells were incubated with VPA (1 mM) and DMC (10 muM) for 4 days. The first-derivative EPR spectra of the control A-2058 cells, and the cells treated with VPA, DMC, and both VPA and DMC, were measured by the electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometer of Radiopan (Poznan, Poland) with microwaves from an X-band (9.3 GHz). The parameters of the EPR lines: amplitudes (A), integral intensities (I), line widths (DeltaBpp), and g-factors, were analyzed. The changes of amplitudes and line widths with microwave power increasing from 2.2 to 70 mW were drawn evaluated, o-Semiquinone free radicals of melanin biopolymer are mainly responsible for the EPR lines of A-2058 melanoma malignum cells. The amounts of free radicals in A-2058 cells treated with VPA, and both VPA and DMC, were lower than in the untreated control cells. Application of the tested substances (VPA, and both VPA and DMC) as the antitumor compounds was discussed. DMC without VPA did not decrease free radicals concentration in A-2058 cells. The studies con-firmed that EPR spectroscopy may be used to examine interactions of free radicals with antitumor compounds.


