D-arabinitolCAS# 488-82-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 488-82-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 827 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C5H12O5 | M.Wt | 152.1 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
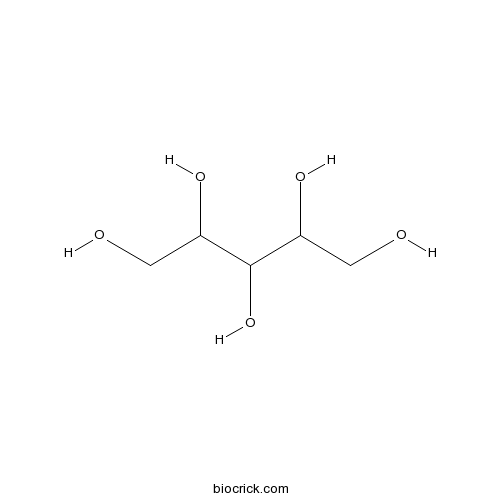
| Chemical Name | pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(C(CO)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H12O5/c6-1-3(8)5(10)4(9)2-7/h3-10H,1-2H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | D-arabinitol is a marker for the diagnosis of disseminated candidiasis and for monitoring response to antifungal therapy. |
| In vivo | Serum D-arabinitol measured by automated quantitative enzymatic assay for detection and therapeutic monitoring of experimental disseminated candidiasis: correlation with tissue concentrations of Candida albicans.[Pubmed: 7965491]J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(3):205-15.In order to further understand serum D-arabinitol (DA) as a marker for the diagnosis of disseminated candidiasis and for monitoring response to antifungal therapy, we studied the serum levels of this Candida carbohydrate metabolite by rapid automated enzymatic assay in rabbits with experimental disseminated candidiasis. As a correction for renal impairment, data were expressed as serum D-arabinitol/creatinine ratio (D-arabinitol/Cr). Serum creatinine concentrations were determined from the same sample with the same instrument, thereby allowing rapid determination of the D-arabinitol/Cr within one laboratory.
|
| Structure Identification | J Bacteriol. 2012 Apr;194(8):1868-74.Biochemical characterization of the CDP-D-arabinitol biosynthetic pathway in Streptococcus pneumoniae 17F.[Pubmed: 22328666 ]The biosynthetic pathway of D-arabinitol, which is present in the CPSs of several S. pneumoniae serotypes, has never been identified. |

D-arabinitol Dilution Calculator

D-arabinitol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5746 mL | 32.8731 mL | 65.7462 mL | 131.4924 mL | 164.3655 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3149 mL | 6.5746 mL | 13.1492 mL | 26.2985 mL | 32.8731 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6575 mL | 3.2873 mL | 6.5746 mL | 13.1492 mL | 16.4366 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1315 mL | 0.6575 mL | 1.3149 mL | 2.6298 mL | 3.2873 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3287 mL | 0.6575 mL | 1.3149 mL | 1.6437 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- D-Ribitol-5-phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4838
CAS No.:35320-17-3
- vibo-Quercitol
Catalog No.:BCN5594
CAS No.:488-76-6
- Allitol
Catalog No.:BCN5593
CAS No.:488-44-8
- 3-Methylcatechol
Catalog No.:BCN3925
CAS No.:488-17-5
- Thesinine
Catalog No.:BCN1990
CAS No.:488-02-8
- Heleurine
Catalog No.:BCN1953
CAS No.:488-00-6
- Curcumol
Catalog No.:BCN5976
CAS No.:4871-97-0
- SNAP 94847 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7658
CAS No.:487051-12-7
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
- HI TOPK 032
Catalog No.:BCC6225
CAS No.:487020-03-1
- Lindelofine
Catalog No.:BCN2043
CAS No.:487-99-0
- Kainic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6572
CAS No.:487-79-6
- Furan-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6397
CAS No.:488-93-7
- N-Acetylstepharine
Catalog No.:BCN7566
CAS No.:4880-87-9
- Elesclomol (STA-4783)
Catalog No.:BCC2337
CAS No.:488832-69-5
- Icariin
Catalog No.:BCN6311
CAS No.:489-32-7
- Limocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN3346
CAS No.:489-33-8
- Gossypetin
Catalog No.:BCN8075
CAS No.:489-35-0
- Globulol
Catalog No.:BCN6901
CAS No.:489-41-8
- Guaiazulen
Catalog No.:BCC8180
CAS No.:489-84-9
- Guaiol
Catalog No.:BCN6619
CAS No.:489-86-1
- ML 213
Catalog No.:BCC6213
CAS No.:489402-47-3
- SBC-115076
Catalog No.:BCC6440
CAS No.:489415-96-5
- a-Truxilline
Catalog No.:BCN1947
CAS No.:490-17-5
Serum D-arabinitol measured by automated quantitative enzymatic assay for detection and therapeutic monitoring of experimental disseminated candidiasis: correlation with tissue concentrations of Candida albicans.[Pubmed:7965491]
J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(3):205-15.
In order to further understand serum D-arabinitol (DA) as a marker for the diagnosis of disseminated candidiasis and for monitoring response to antifungal therapy, we studied the serum levels of this Candida carbohydrate metabolite by rapid automated enzymatic assay in rabbits with experimental disseminated candidiasis. The enzymatic reaction steps were performed on a standard automated clinical chemistry analyser. As a correction for renal impairment, data were expressed as serum D-arabinitol/creatinine ratio (DA/Cr). Serum creatinine concentrations were determined from the same sample with the same instrument, thereby allowing rapid determination of the DA/Cr within one laboratory. The DA/Cr was determined in 321 samples from 132 rabbits. The mean serum DA/Cr in 31 normal non-infected rabbits was 1.51 +/- 0.2 microM mg-1 dl-1. Among 84 rabbits with disseminated candidiasis and pre-terminal samples, there was a direct correlation between DA/Cr and tissue concentration of Candida albicans (r = 0.80; P < 0.001). A threshold of elevated DA/Cr (> or = 3.0 microM mg-1 dl-1) was evident in rabbits with a tissue concentration of C. albicans > or = 3 x 10(4) colony forming units (CFU) g-1. Elevated DA/Cr was detected in 48 (89%) of 54 rabbits at a C. albicans tissue concentration of > or = 3 x 10(4) CFU g-1 vs. one (3%) of 30 rabbits with < 3 x 10(4) CFU g-1 (P < 0.0001). Among all 101 rabbits with disseminated candidiasis, an elevated DA/Cr was detected at any point during infection in 60 (92%) of 65 rabbits having a C. albicans tissue concentration > or = 3 x 10(4) CFU g-1 vs. 13 (36%) of 36 rabbits with < 3 x 10(4) CFU g-1 (P < 0.0001). The relationship between the tissue response to antifungal therapy and change in DA/Cr was then further analysed. Ten (91%) of 11 rabbits with a tissue-proven response to antifungal therapy (defined as > or = 10(2)-fold reduction of CFU g-1 in comparison to untreated controls) had a > 50% reduction in elevated DA/Cr levels. By comparison, 10 (83%) of 12 treated rabbits with no response to therapy had persistently elevated DA/Cr levels (P < 0.001). These findings provide an experimental basis for understanding the patterns of expression of serum DA in disseminated candidiasis and further indicate that serial DA/Cr measurements may be useful for diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of disseminated candidiasis.
Biochemical characterization of the CDP-D-arabinitol biosynthetic pathway in Streptococcus pneumoniae 17F.[Pubmed:22328666]
J Bacteriol. 2012 Apr;194(8):1868-74.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major human pathogen associated with many diseases worldwide. Capsular polysaccharides (CPSs) are the major virulence factor. The biosynthetic pathway of D-arabinitol, which is present in the CPSs of several S. pneumoniae serotypes, has never been identified. In this study, the genes abpA (previously known as abp1) and abpB (previously known as abp2), which have previously been reported to be responsible for nucleoside diphosphate (NDP)-D-arabinitol (the nucleotide-activated form of D-arabinitol) synthesis, were cloned. The enzyme products were overexpressed, purified, and analyzed for their respective activities. Novel products produced by AbpA- and AbpB-catalyzing reactions were detected by capillary electrophoresis, and the structures of the products were elucidated using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. As a result, abpA was identified to be a D-xylulose-5-phosphate cytidylyltransferase-encoding gene, responsible for the transfer of CTP to D-xylulose-5-phosphate (D-Xlu-5-P) to form CDP-D-xylulose, and abpB was characterized to be a CDP-D-xylulose reductase-encoding gene, responsible for the conversion of CDP-D-xylulose to CDP-D-arabinitol as the final product. The kinetic parameters of AbpA for the substrates D-Xlu-5-P and CTP and those of AbpB for the substrate CDP-D-xylulose and the cofactors NADH or NADPH were measured, and the effects of temperature, pH, and cations on the two enzymes were analyzed. This study confirmed the involvement of the genes abpA and abpB and their products in the biosynthetic pathway of CDP-D-arabinitol.


