UBP 301CAS# 569371-10-4 |
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996)
Catalog No.:BCC1014
CAS No.:96249-43-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 569371-10-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6604913 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14IN3O6 | M.Wt | 459.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 5 mM in DMSO with gentle warming | ||
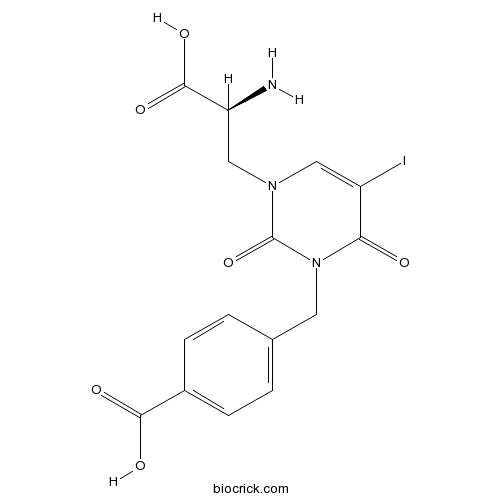
| Chemical Name | 4-[[3-[(2S)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]-5-iodo-2,6-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl]methyl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1CN2C(=O)C(=CN(C2=O)CC(C(=O)O)N)I)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JHSYCOCOIYSZGI-NSHDSACASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14IN3O6/c16-10-6-18(7-11(17)14(23)24)15(25)19(12(10)20)5-8-1-3-9(4-2-8)13(21)22/h1-4,6,11H,5,7,17H2,(H,21,22)(H,23,24)/t11-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent kainate receptor antagonist (apparent Kd = 5.94 μM). Displays ~ 30-fold selectivity over AMPA receptors. |

UBP 301 Dilution Calculator

UBP 301 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1777 mL | 10.8885 mL | 21.777 mL | 43.554 mL | 54.4425 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4355 mL | 2.1777 mL | 4.3554 mL | 8.7108 mL | 10.8885 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2178 mL | 1.0889 mL | 2.1777 mL | 4.3554 mL | 5.4443 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0436 mL | 0.2178 mL | 0.4355 mL | 0.8711 mL | 1.0889 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0218 mL | 0.1089 mL | 0.2178 mL | 0.4355 mL | 0.5444 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-Ser(Tos)-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3446
CAS No.:56926-94-4
- Splitomicin
Catalog No.:BCC3652
CAS No.:5690-03-9
- Rhamnocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN4619
CAS No.:569-92-6
- Nepetin-7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2580
CAS No.:569-90-4
- Xanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN5768
CAS No.:569-83-5
- Penduletin
Catalog No.:BCN5767
CAS No.:569-80-2
- Chlorotrianisene
Catalog No.:BCC6442
CAS No.:569-57-3
- Carcinine ditrifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC7291
CAS No.:56897-53-1
- 8-Demethyleucalyptin
Catalog No.:BCN5765
CAS No.:5689-38-3
- Hemopressin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5807
CAS No.:568588-77-2
- Z-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2777
CAS No.:5680-86-4
- H-Ser-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3029
CAS No.:5680-80-8
- 2'-O-Galloylmyricitrin
Catalog No.:BCN8252
CAS No.:56939-52-7
- Withanolide B
Catalog No.:BCN8011
CAS No.:56973-41-2
- Alnusdiol
Catalog No.:BCN6503
CAS No.:56973-51-4
- Platyphyllenone
Catalog No.:BCN5766
CAS No.:56973-65-0
- 9,9'-Di-O-(E)-feruloylsecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN1415
CAS No.:56973-66-1
- Gabexate mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2096
CAS No.:56974-61-9
- Boc-Cys(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3379
CAS No.:56976-06-8
- U 46619
Catalog No.:BCC7207
CAS No.:56985-40-1
- NSC 87877
Catalog No.:BCC2468
CAS No.:56990-57-9
- Flupirtine
Catalog No.:BCC4282
CAS No.:56995-20-1
- Palmitic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1206
CAS No.:57-10-3
- Stearic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN3820
CAS No.:57-11-4
The utility of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists in the treatment of nociception induced by epidural glutamate infusion in rats.[Pubmed:24032081]
Surg Neurol Int. 2013 Aug 21;4:106.
BACKGROUND: The authors have previously demonstrated that human herniated disc material contains high concentrations of free glutamate. In an experimental model, elevated epidural glutamate concentrations in the lumbar spine can cause a focal hyperesthetic state. METHODS: Rats underwent epidural glutamate infusion in the lumbar spine by a miniosmotic pump over a 72-hour period. Some rats underwent coinfusion with glutamate and ionotropic glutamate antagonists. Nociception was assessed by von Frey fibers and by assessment of glutamate receptor expression in the corresponding dorsal horn of the spinal cord. RESULTS: The kainic acid antagonist, UBP 301, decreased epidural glutamate-based hyperesthesia in a dose dependent manner. Concordant with these findings, there was significant decrease in kainate receptor expression in the dorsal horn. The N-Methyl-4-isoxazoleproionic acid (NMDA) antagonist Norketamine also significantly diminished hyperesthesia and decreased receptor expression in the dorsal horn. CONCLUSIONS: Both UBP 301, the kainic acid receptor antagonist and Norketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, dampened epidural glutamate-based nociception. Focal epidural injections of Kainate or NMDA receptor antagonists could be effective treatments for disc herniation-based lumbar radiculopathy.
Rapid onset of a kainate-induced mirror focus in rat hippocampus is mediated by contralateral AMPA receptors.[Pubmed:23668947]
Epilepsy Res. 2013 Sep;106(1-2):35-46.
The development of an epileptic "mirror" focus in an area of the brain contralateral to the primary epileptic focus typically evolves over days in the experimental setting after status epilepticus or electrical kindling of the primary focal region. In contrast, we observed the rapid development of an apparent mirror focus in the contralateral hippocampus following microinjection of kainic acid (KA) in the ipsilateral hippocampus in rats. Using multisite intracranial recordings, local field potentials were recorded in anesthetized adult male rats using electrodes implanted in the CA3 region of both hippocampi and in the anteromedial nucleus of the thalamus. Epileptogenesis was induced by microinjection of KA in the ipsilateral CA3 region. Development of seizures was followed under three experimental perturbations to the contralateral hippocampus: (A) no treatment, (B) pre-treatment with microinjection of the AMPA/Kainate receptor antagonist CNQX, and (C) pre-treatment with microinjection of the selective kainate receptor antagonist UBP 301. Both control and UBP 301 groups had seizures preferentially originate in the contralateral hippocampus appearing within ten minutes of KA injection. In contrast, the CNQX group had seizures preferentially originate in the ipsilateral hippocampus. By tracking the order of seizure onset, the probability that a hippocampal seizure would propagate across commissural fibers prior to any thalamic seizure activity was significantly reduced in the CNQX group compared to control and UBP groups suggesting that the AMPA receptor mediated component responsible for mirror focus development was also necessary for the spread of ictal activity via the commissural fibers. Understanding how a complex circuit in the brain develops may be critical to uncovering ways of either disrupting its development or treating its effects. The rapid appearance of a contralateral mirror focus via AMPA receptors in a limbic epilepsy model might be the mechanism by which a putative long-term mirror focus is established in vivo and may also underlie how secondary generalization progresses in some cases.
Structural requirements for novel willardiine derivatives acting as AMPA and kainate receptor antagonists.[Pubmed:12684265]
Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;138(6):1093-100.
1. The natural product willardiine is an AMPA receptor agonist. We have examined the structural changes required to convert willardiine into an antagonist at AMPA and kainate receptors. Structure-activity analysis has been carried out to discover the structural features required to increase the potency and/or selectivity of the antagonists at AMPA or kainate receptors. 2. Reduction of the fast component of the dorsal root-evoked ventral root potential (fDR-VRP) has been used to investigate AMPA receptor antagonist activity. To examine antagonist activity at kainate receptors, the ability of compounds to depress kainate-induced depolarisations of dorsal root fibres was assessed. 3. Blocking ionisation of the uracil ring by adding a methyl group to the N(3) position was not sufficient to convert willardiine into an antagonist. However, willardiine derivatives with a side-chain bearing a carboxylic acid group at the N(3)-position of the uracil ring could antagonise AMPA and kainate receptors. 4. S stereochemistry was optimal for antagonism. When compounds with differing interacidic group chain lengths were compared, a group chain length of two methylene groups was preferable for AMPA receptor antagonism in the series of compounds bearing a carboxyalkyl side chain (UBP275, UBP277 and UBP279 reduced the fDR-VRP with IC(50) values of 287+/-41, 23.8+/-3.9 and 136+/-17 micro M, respectively). For kainate receptor antagonism, two or three methylene groups were almost equally acceptable (UBP277 and UBP279 reduced dorsal root kainate responses with apparent K(D) values of 73.1+/-4.5 and 60.5+/-4.1 micro M, respectively). 5. Adding an iodo group to the 5-position of UBP277 and UBP282 enhanced activity at kainate receptors (UBP291 and UBP301 antagonised kainate responses on the dorsal root with apparent K(D) values of 9.83+/-1.62 and 5.94+/-0.63 micro M, respectively). 6. The most useful antagonist identified in this study was UBP301, which was a potent and approximately 30-fold selective kainate receptor antagonist. UBP282 may also be of use in isolating a non-GluR5-mediated kainate response.


