NSC 87877Shp2 /shp1 PTP inhibitor CAS# 56990-57-9 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 56990-57-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5459322 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H13N3O7S2 | M.Wt | 459.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 5 mg/mL (10.88 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
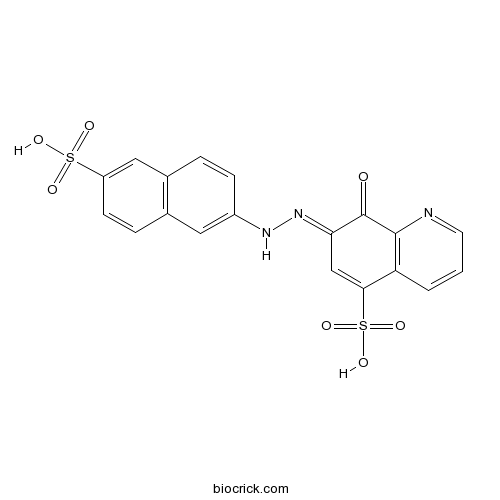
| Chemical Name | (7E)-8-oxo-7-[(6-sulfonaphthalen-2-yl)hydrazinylidene]quinoline-5-sulfonic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C(=O)C(=NNC3=CC4=C(C=C3)C=C(C=C4)S(=O)(=O)O)C=C2S(=O)(=O)O)N=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BIQBDHSYQMHHPU-CJLVFECKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H13N3O7S2/c23-19-16(10-17(31(27,28)29)15-2-1-7-20-18(15)19)22-21-13-5-3-12-9-14(30(24,25)26)6-4-11(12)8-13/h1-10,21H,(H,24,25,26)(H,27,28,29)/b22-16+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of shp2 and shp1 protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP) (IC50 values are 0.318, 0.355, 1.691, 7.745, 65.617, 84.473 and 150.930 μM for shp2, shp1, PTP1B, HePTP, DEP1, CD45 and LAR respectively). Inhibits EGF-induced Erk1/2 activation in HEK293 cells and significantly reduces MDA-MB-468 cell viability/proliferation. |

NSC 87877 Dilution Calculator

NSC 87877 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1765 mL | 10.8826 mL | 21.7652 mL | 43.5303 mL | 54.4129 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4353 mL | 2.1765 mL | 4.353 mL | 8.7061 mL | 10.8826 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2177 mL | 1.0883 mL | 2.1765 mL | 4.353 mL | 5.4413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0435 mL | 0.2177 mL | 0.4353 mL | 0.8706 mL | 1.0883 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0218 mL | 0.1088 mL | 0.2177 mL | 0.4353 mL | 0.5441 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: NSC-87877 potently inhibited Shp2 with an IC50 of 0.318 ± 0.049 μM. NSC-87877 seemed to have no selectivity between human Shp2 and Shp1 (IC50 0.355 ± 0.073μM). In addition, NSC-87877 showed approximately 5-, 24-, 206-, 266-, and 475-fold selectivity for Shp2 over PTP1B (IC50 1.691 ± 0.407μM), HePTP (IC50 7.745 ± 1.561μM), DEP1 (IC50 65.617± 4.120μM), CD45 (IC50 84.473 ± 16.185μM), and LAR (IC50 150.930 ± 9.077μM), respectively [1].
Shp2, a nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) encoded by the PTPN11 gene, is involved in the growth factorinduced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases Erk1 and Erk2. Moreover, gain-of-function Shp2 mutations have been found in Noonan syndrome and childhood leukemias. Therefore, Shp2 PTP inhibitors are required for the evaluation of Shp2 as a therapeutic target. NSC87877, a novel SHP-2 inhibitor, has been observed dose-dependent cytotoxicity in leukemic cell lines.
In vitro: Molecular modeling and site-directed mutagenesis studies suggested that NSC-87877 binds to the catalytic cleft of Shp2 PTP. It is noteworthy that NSC-87877 inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced activation of Shp2 PTP, Ras, and Erk1/2 in cell cultures but did not block EGF-induced Gab1 tyrosine phosphorylation or Gab1-Shp2 association. Furthermore, NSC-87877 inhibited Erk1/2 activation by a Gab1-Shp2 chimera but did not affect the Shp2-independent Erk1/2 activation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. These results identified NSC-87877 as the first PTP inhibitor capable of inhibiting Shp2 PTP in cell cultures without a detectable off-target effect [1].
In vivo: An mice in-vivo study aimed to investigate the effects of S NSC-87877 on inflammatory pain and its underlying mechanisms. In this study, immediately after behavioral tests, sinistral spinal dorsal horn was collected for immunoblotting analysis of the expression of NMDA receptors. Results showed that NSC-87877 alleviated CFA-induced mechanical allodynia, which had no effects on the nociceptive responses in naive mice. Moreover, NSC-87877 specifically abolished the increase in the synaptic expression of NMDA receptor NR2B subunits in inflamed mice. These findings indicated that NSC-87877 could ameliorate inflammatory pain by inhibiting the synaptic accumulation of NR2B in spinal dorsal horn [2].
Clinical trial: NSC-87877 is currently in the preclinical development and no clinical trial is ongoing.
Reference:
[1] Liwei Chen, Shen-Shu Sung, M. L. Richard Yip, Harshani R. Lawrence, Yuan Ren, Wayne C. Guida, Said M. Sebti, Nicholas J. Lawrence, and Jie Wu. Discovery of a Novel Shp2 Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol 2006,70:562–570
[2] YANG Hong-bin, YANG Xian, CAO Jing, LI Shuai, LIU Yan-ni, SUO Zhan-wei, ZHENG Cheng-rong, CUI Hong-bin, GUO Zhong, HU Xiao-dong. Inhibitory effects of SHP2 blocker NSC-87877 on inflammatory pain and its underlying mechanisms. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 2010-09
- U 46619
Catalog No.:BCC7207
CAS No.:56985-40-1
- Boc-Cys(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3379
CAS No.:56976-06-8
- Gabexate mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2096
CAS No.:56974-61-9
- 9,9'-Di-O-(E)-feruloylsecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN1415
CAS No.:56973-66-1
- Platyphyllenone
Catalog No.:BCN5766
CAS No.:56973-65-0
- Alnusdiol
Catalog No.:BCN6503
CAS No.:56973-51-4
- Withanolide B
Catalog No.:BCN8011
CAS No.:56973-41-2
- 2'-O-Galloylmyricitrin
Catalog No.:BCN8252
CAS No.:56939-52-7
- UBP 301
Catalog No.:BCC7172
CAS No.:569371-10-4
- Boc-Ser(Tos)-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3446
CAS No.:56926-94-4
- Splitomicin
Catalog No.:BCC3652
CAS No.:5690-03-9
- Rhamnocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN4619
CAS No.:569-92-6
- Flupirtine
Catalog No.:BCC4282
CAS No.:56995-20-1
- Palmitic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1206
CAS No.:57-10-3
- Stearic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN3820
CAS No.:57-11-4
- Urea
Catalog No.:BCC8034
CAS No.:57-13-6
- Vincristine
Catalog No.:BCN5411
CAS No.:57-22-7
- Strychnine
Catalog No.:BCN4978
CAS No.:57-24-9
- Phenobarbital sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6230
CAS No.:57-30-7
- Pentobarbital sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6231
CAS No.:57-33-0
- Benactyzine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8841
CAS No.:57-37-4
- Phenytoin
Catalog No.:BCC5070
CAS No.:57-41-0
- Esromiotin
Catalog No.:BCC8325
CAS No.:57-47-6
- Fructose
Catalog No.:BCN4969
CAS No.:57-48-7
NSC-87877, inhibitor of SHP-1/2 PTPs, inhibits dual-specificity phosphatase 26 (DUSP26).[Pubmed:19233143]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Apr 17;381(4):491-5.
Protein phosphorylation plays critical roles in many regulatory mechanisms controlling cell activities and thus involved in various diseases. The cellular equilibrium of phosphorylation is regulated through the actions of protein kinases and phosphatases. Therefore, these regulatory proteins have emerged as promising targets for drug development. In this study, we screened protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) by in vitro phosphatase assays to identify PTPs that are inhibited by 8-hydroxy-7-(6-sulfonaphthalen-2-yl)diazenyl-quinoline-5-sulfonic acid (NSC-87877), a potent inhibitor of SHP-1 and SHP-2 PTPs. Phosphatase activity of dual-specificity protein phosphatase 26 (DUSP26) was decreased by the inhibitor in a dose-dependent manner. Kinetic studies with NSC-87877 and DUSP26 revealed a competitive inhibition. NSC-87877 effectively inhibited DUSP26-mediated dephosphorylation of p38, a member of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. Since DUSP26 is involved in survival of anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) cells, NSC-87877 could be a therapeutic reagent for treating ATC.
NSC-87877 inhibits DUSP26 function in neuroblastoma resulting in p53-mediated apoptosis.[Pubmed:26247726]
Cell Death Dis. 2015 Aug 6;6:e1841.
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 26 (DUSP26) is overexpressed in high-risk neuroblastoma (NB) and contributes to chemoresistance by inhibiting p53 function. In vitro, DUSP26 has also been shown to effectively inhibit p38 MAP kinase. We hypothesize that inhibiting DUSP26 will result in decreased NB cell growth in a p53 and/or p38-mediated manner. NSC-87877 (8-hydroxy-7-[(6-sulfo-2-naphthyl)azo]-5-quinolinesulfonic acid), a novel DUSP26 small molecule inhibitor, shows effective growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in NB cell lines. NB cell lines treated with small hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting DUSP26 also exhibit a proliferation defect both in vitro and in vivo. Treatment of NB cell lines with NSC-87877 results in increased p53 phosphorylation (Ser37 and Ser46) and activation, increased activation of downstream p38 effector proteins (heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) and MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MAPKAPK2)) and poly ADP ribose polymerase/caspase-3 cleavage. The cytotoxicity resulting from DUSP26 inhibition is partially reversed by knocking down p53 expression with shRNA and also by inhibiting p38 activity with SB203580 (4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-methylsulfinylphenyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]pyridine). In an intrarenal mouse model of NB, NSC-87877 treatment results in decreased tumor growth and increased p53 and p38 activity. Together, these results suggest that DUSP26 inhibition with NSC-87877 is an effective strategy to induce NB cell cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo through activation of the p53 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) tumor-suppressor pathways.
hTRPC1-associated alpha-actinin, and not hTRPC1 itself, is tyrosine phosphorylated during human platelet activation.[Pubmed:17892531]
J Thromb Haemost. 2007 Dec;5(12):2476-83.
BACKGROUND: Canonical transient receptor potential channels (TRPCs), which are regulated by several processes, including tyrosine phosphorylation, are candidates for the conduction of store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE). OBJECTIVES: To assess hTRPC phosphotyrosine content upon platelet stimulation. METHODS: A new protein complex immunological separation assay (ProCISA) was developed to allow assessment of isolated hTRPC tyrosine phosphorylation by Western blotting. RESULTS: Classical immunoprecipitation suggested that thrombin (Thr) evoked an initial decrease in hTRPC1 phosphotyrosine content, which reached a minimum at 1 s, and then increased again, exceeding basal levels after 3 min. However, TRPC isolation from protein complexes using ProCISA revealed that hTRPC1, 4 and 5 were not tyrosine phosphorylated at rest or after Thr stimulation. Stimulation with Thr for 3 min increased the phosphotyrosine content of alpha-actinin, which shows similar electrophoretic properties to hTRPCs and coimmunoprecipitates with hTRPC1. Thr-evoked alpha-actinin tyrosine phosphorylation was increased by inhibiting the alpha-actinin phosphatase, SHP-1, which enhanced phosphorylation of the TRPC complex and SOCE. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation impaired the interaction between hTRPC1 and the intracellular Ca(2+) sensor STIM1. CONCLUSIONS: hTRPC1, 4 and 5 are not tyrosine phosphorylated during SOCE in human platelets although tyrosine phosphorylation is important for SOCE. The results obtained using ProCISA caution the use of classical immunoprecipitation for the determination of the tyrosine phosphorylation state of a given protein, where the presence of other proteins with similar electrophoretic mobilities may give misleading results.
Regulation of ACh receptor clustering by the tyrosine phosphatase Shp2.[Pubmed:17659592]
Dev Neurobiol. 2007 Nov;67(13):1789-801.
At the vertebrate neuromuscular junction (NMJ), postsynaptic aggregation of muscle acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) depends on the activation of MuSK, a muscle-specific tyrosine kinase that is stimulated by neural agrin and regulated by muscle-intrinsic tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. We recently reported that Shp2, a tyrosine phosphatase containing src homology two domains, suppressed MuSK-dependent AChR clustering in cultured myotubes, but how this effect of Shp2 is controlled has remained unclear. In this study, biochemical assays showed that agrin-treatment of C2 mouse myotubes enhanced the tyrosine phosphorylation of signal regulatory protein alpha1 (SIRPalpha1), a known activator of Shp2, and promoted SIRPalpha1's interaction with Shp2. Moreover, in situ experiments revealed that treatment of myotubes with the Shp2-selective inhibitor NSC-87877 increased spontaneous and agrin-induced AChR clustering, and that AChR clustering was also enhanced in myotubes ectopically expressing inactive (dominant-negative) Shp2; in contrast, AChR clustering was reduced in myotubes expressing constitutively active Shp2. Significantly, expression of truncated (nonShp2-binding) and full-length (Shp2-binding) forms of SIRPalpha1 in myotubes also increased and decreased AChR clustering, respectively, and coexpression of truncated SIRPalpha1 with active Shp2 and full-length SIRPalpha1 with inactive Shp2 reversed the actions of the exogenous Shp2 proteins on AChR clustering. These results suggest that SIRPalpha1 is a novel downstream target of MuSK that activates Shp2, which, in turn, suppresses AChR clustering. We propose that an inhibitory loop involving both tyrosine kinases and phosphatases sets the level of agrin/MuSK signaling and constrains it spatially to help generate high-density AChR clusters selectively at NMJs.
Discovery of a novel shp2 protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor.[Pubmed:16717135]
Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;70(2):562-70.
Shp2 is a nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) encoded by the PTPN11 gene. It is involved in growth factorinduced activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases Erk1 and Erk2 (Erk1/2) and has been implicated in the pathogenicity of the oncogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Moreover, gain-of-function Shp2 mutations have been found in childhood leukemias and Noonan syndrome. Thus, small molecule Shp2 PTP inhibitors are much needed reagents for evaluation of Shp2 as a therapeutic target and for chemical biology studies of Shp2 function. By screening the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Diversity Set chemical library, we identified 8-hydroxy-7-(6-sulfonaphthalen-2-yl)diazenyl-quinoline-5-sulfonic acid (NSC-87877) as a potent Shp2 PTP inhibitor. Molecular modeling and site-directed mutagenesis studies suggested that NSC-87877 binds to the catalytic cleft of Shp2 PTP. NSC-87877 cross-inhibited Shp1 in vitro, but it was selective for Shp2 over other PTPs (PTP1B, HePTP, DEP1, CD45, and LAR). It is noteworthy that NSC-87877 inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced activation of Shp2 PTP, Ras, and Erk1/2 in cell cultures but did not block EGF-induced Gab1 tyrosine phosphorylation or Gab1-Shp2 association. Furthermore, NSC-87877 inhibited Erk1/2 activation by a Gab1-Shp2 chimera but did not affect the Shp2-independent Erk1/2 activation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. These results identified NSC-87877 as the first PTP inhibitor capable of inhibiting Shp2 PTP in cell cultures without a detectable off-target effect. Our study also provides the first pharmacological evidence that Shp2 mediates EGF-induced Erk1/2 MAP kinase activation.


