Lonicera japonica
Lonicera japonica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Lonicera japonica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
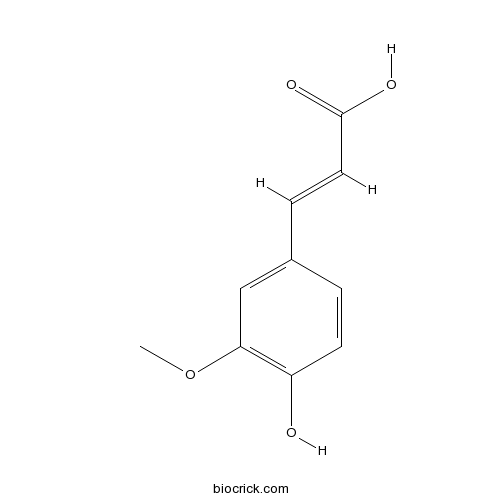
BCN5948
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
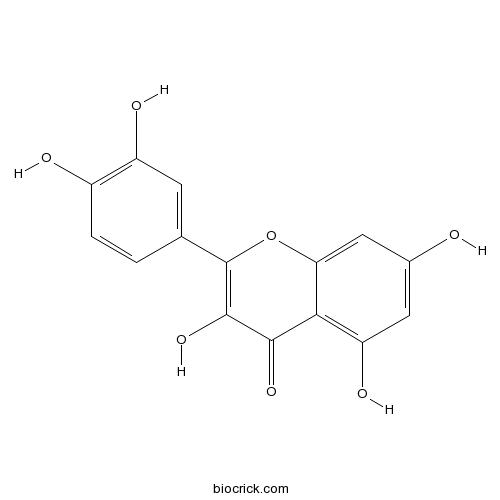
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN6059
Syringin118-34-3
Instructions

-
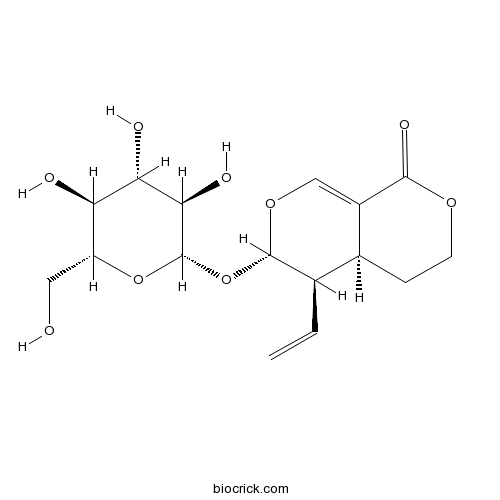
BCN6219
Sweroside14215-86-2
Instructions
-
BCN9087
Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, 3-[[(2E)-3-[4-(D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxyphenyl]-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl...1629852-63-6
Instructions

-
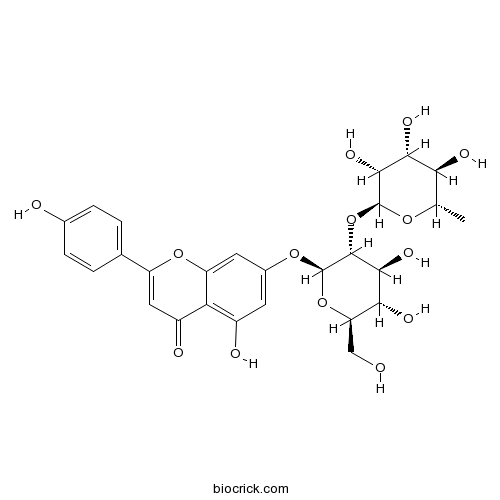
BCN1112
Rhoifolin17306-46-6
Instructions
-
BCN1153
Loganin18524-94-2
Instructions
-
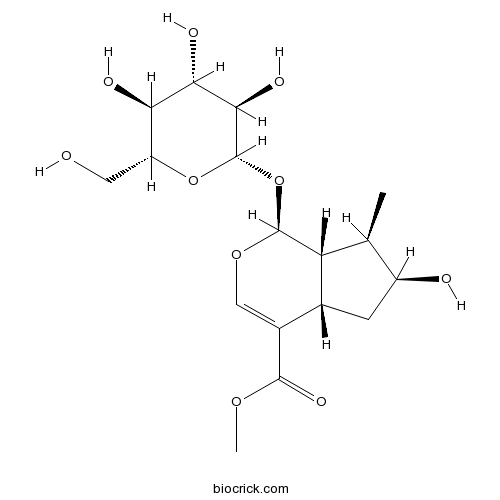
BCN5328
Diosmetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside20126-59-4
Instructions
-
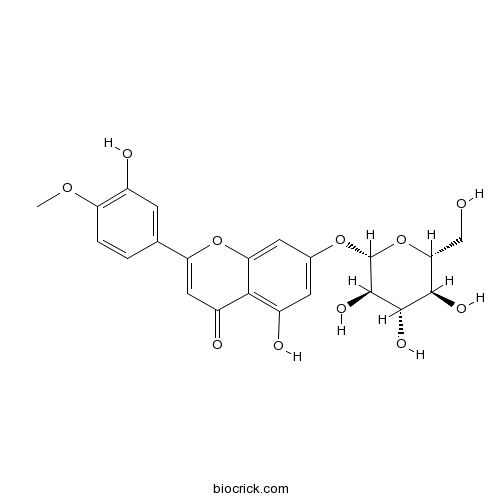
BCN5908
Isochlorogenic acid A2450-53-5
Instructions
-
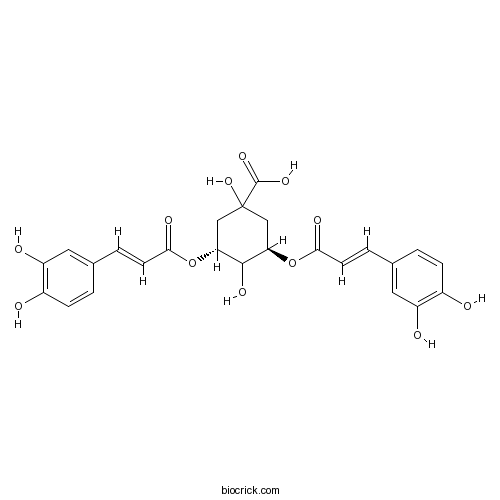
BCN5009
Morroniside25406-64-8
Instructions

-
BCN5159
alpha-Hederin27013-91-8
Instructions

-
BCN5906
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
-
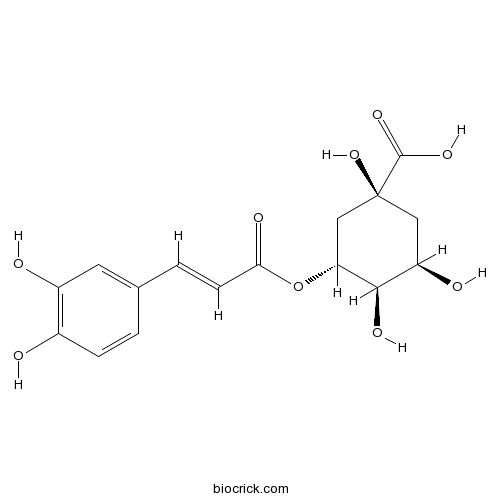
BCN5979
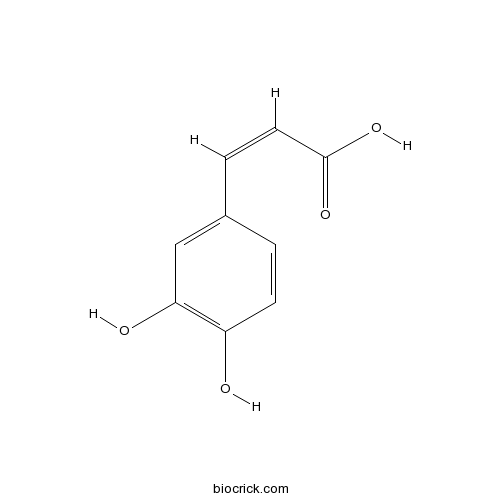
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5940
Dipsacoside B33289-85-9
Instructions

-
BCN5513
Hederagenin465-99-6
Instructions

-
BCN3181
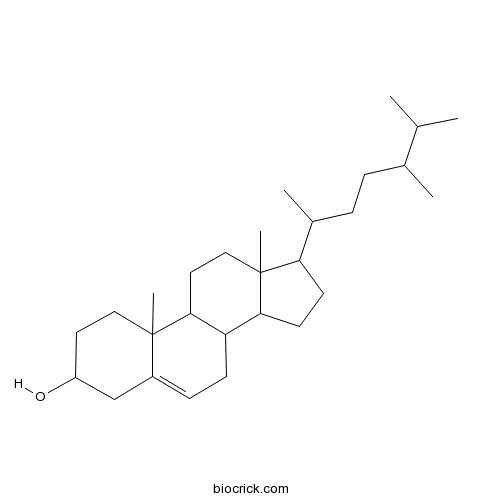
Campesterol474-62-4
Instructions
-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions

-
BCN5569
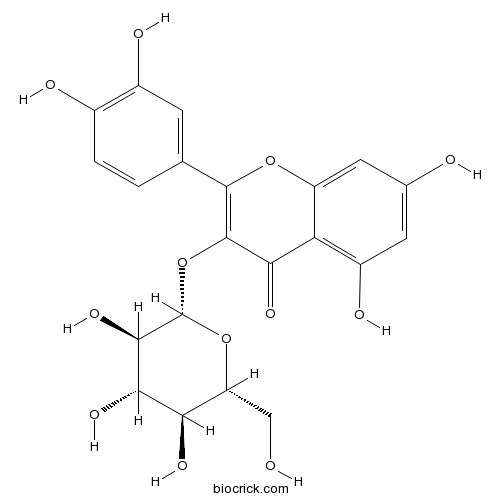
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
BCN5600
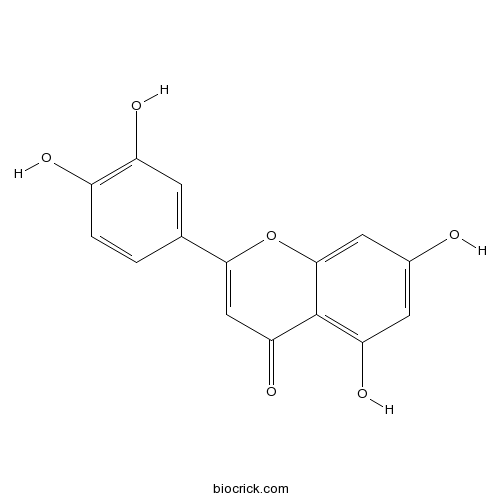
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN2633
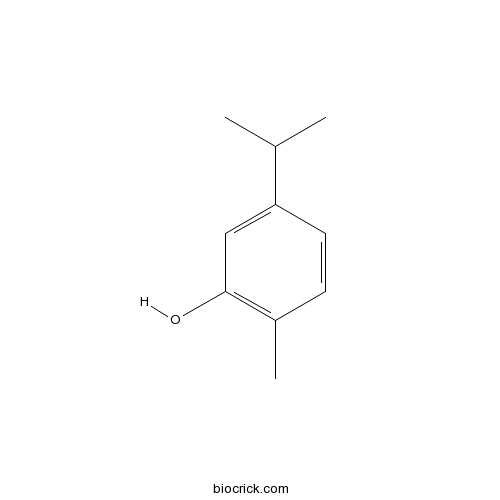
5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol499-75-2
Instructions
-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
BCN5654
Hesperidin520-26-3
Instructions

-
BCN4993
Diosimin520-27-4
Instructions
-
BCN5388
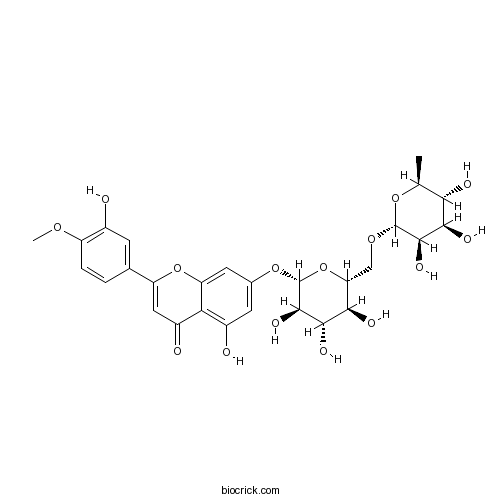
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside5373-11-5
Instructions

-
BCN5944
Liquiritin551-15-5
Instructions

-
BCN1206
Palmitic acid57-10-3
Instructions

-
BCN5800
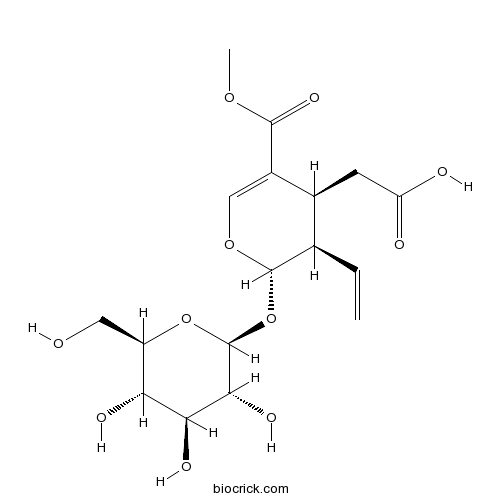
Secoxyloganin58822-47-2
Instructions
-
BCN1015
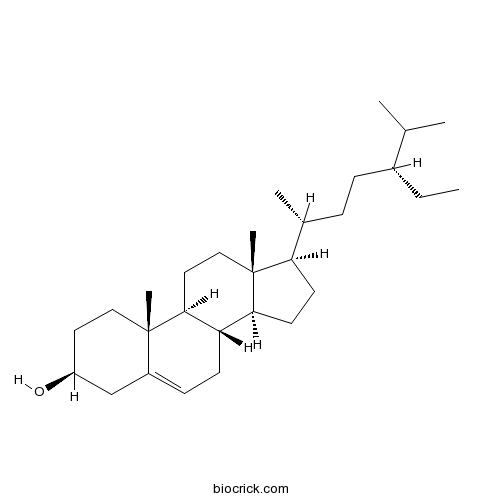
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
-
BCN5907
Cryptochlorogenic acid905-99-7
Instructions

-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid906-33-2
Instructions

-
BCN5964
Eugenol97-53-0
Instructions
[Comparative Analysis of Different Strains of Lonicera japonica on Appearance and Internal Quality].[Pubmed: 30088873]
To provide the reference for germplasm identification and breeding of Lonicera japonica.
[Chemical fingerprinting and similarity analysis of Lonicera japonica resources].[Pubmed: 29950078]
LC-MS was used to detect 41 population of Lonicera japonica from different areas. LC-MS chemical chromatographic profile has been established. There were 23 common peaks, seventeen of which were identified according to reference standard and reference; SPSS software was applied to calculate the similarity of chemical fingerprints of 41 batches and the range was from 0.99 to 0.12. On this basis, the L. japonica's metabolites consistency was classified. Combined with comprehensive analysis of genetic identity, we can provide a theoretical basis for the authenticity research of Dao-di herbs and reference information for the breeding of excellent L. japonica.
[Establishment of DNA identity card and analysis of genetic similarity among 58 varieties in Lonicera japonica].[Pubmed: 29902892]
A total of 58 varieties in Lonicera japonica from 20 producing areas were amplified by 22 pairs of SSR primers. Seven pairs of polymorphic primers were screened and their primers were used to establish DNA identity card and analyze genetic similarity.All the 58 varieties could be distinguished each other by the DNA identity card constituted by 7 pairs of core SSR primers.The genetic similarity coefficients of 58 varieties ranged from 0.366 7 to 0.916 7 by using PopGene32(vesion1.32). Furthermore, all the varieties consistency were classified into 4 groups and constructed an evaluation table according to cluster analysis by an un-weighted pair-group average method with arithmetic mean. As expected, the results of cluster and evaluation table reflected 58 varieties relatives, which provide reference information for the selection of fine germplasm of L. japonica and the theoretical basis for the study of Dao-di herbs.
Bioactive luteoloside produced by Myroides odoratimimus, solvent-tolerant bacterium form the rhizosphere of Lonicera japonica.[Pubmed: 29882431]
Luteoloside (luteolin-7-O-glucoside), the biomarker of Lonicera japonica, was efficiently bio-synthetized from its cheaper precursor luteolin. The structure of luteoloside was characterized by LC-MS and NMR analyses. Compared to the significant inhibitory effect of luteolin on human hepatocyte cell line LO2 at high doses, luteoloside did not show obvious cytotoxic effects at any test dose. Moreover, luteoloside exhibited obvious promotive effects on human hepatocyte cells, suggesting a potential application in hepatoprotective therapies.
The anti-inflammatory NHE-06 restores antitumor immunity by targeting NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.[Pubmed: 29574282]
The NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 inflammatory axis is highly activated in a variety of inflammation-related cancers and contributes to suppression of antitumor immunity. In this study, we generated a novel herbal formula NHE-06, a water-decocting extract from six natural herbals, Ficus carica, Taraxacum mongolicum, Angelica sinensis, Lonicera japonica, Pseudo-ginseng and Folium ginkgo. We investigated the anti-inflammatory properties of NHE-06 and its antitumor efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma, a typical inflammation-related cancer. We found that NHE-06 effectively suppressed NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 signaling and enhanced antitumor immunity both in vitro and in HCC-bearing mice. In a subcutaneous HCC mouse model, we found that NHE-06 possessed both preventive and therapeutic functions. Moreover, rather than the cytotoxic effects, the antitumor efficacy of NHE-06 was indispensable of intact immunity, since the therapeutic effect was only achieved in immunocompetent mice whereas failed in immunocompromised mice. Taken together, the novel formula of the anti-inflammatory NHE-06 effectively restores antitumor immunosurveillance and can be applied for prevention and/or treatment of inflammation-related cancers.


