Panax ginseng
Panax ginseng
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Panax ginseng
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN1064
Ginsenoside Rb211021-13-9
Instructions

-
BCN1072
Ginsenoside Rc11021-14-0
Instructions
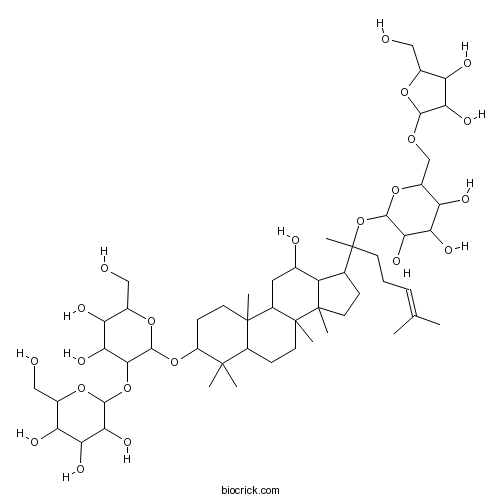
-
BCN2484
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rh2112246-15-8
Instructions

-
BCN1068
Ginsenoside Rg314197-60-5
Instructions
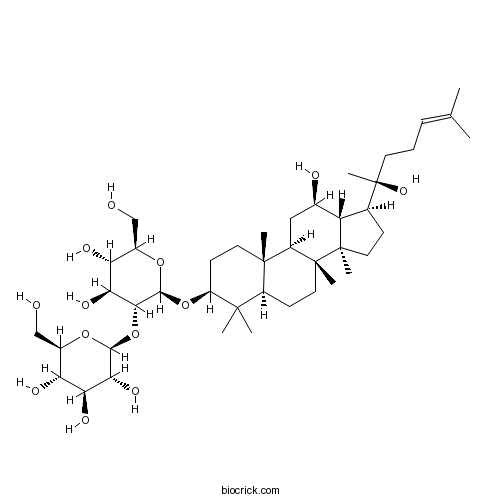
-
BCN1079
20(R)-Protopanaxatriol1453-93-6
Instructions
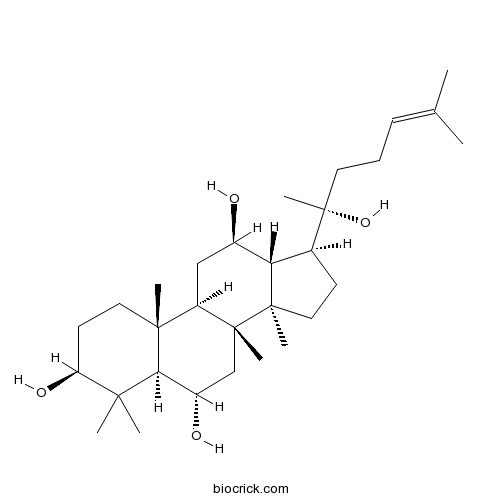
-
BCN3503
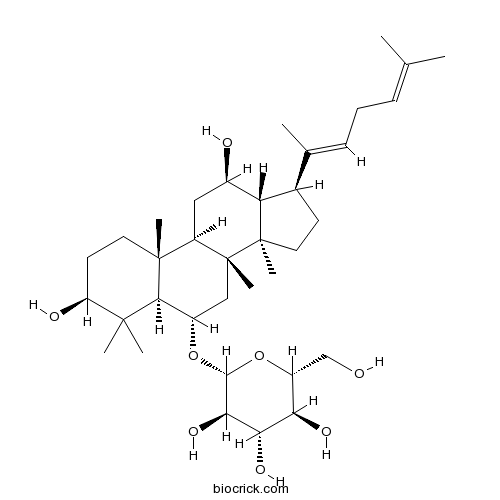
Ginsenoside Rh4174721-08-5
Instructions
-
BCN3551
Ginsenoside Rg5186763-78-0
Instructions

-
BCN1080
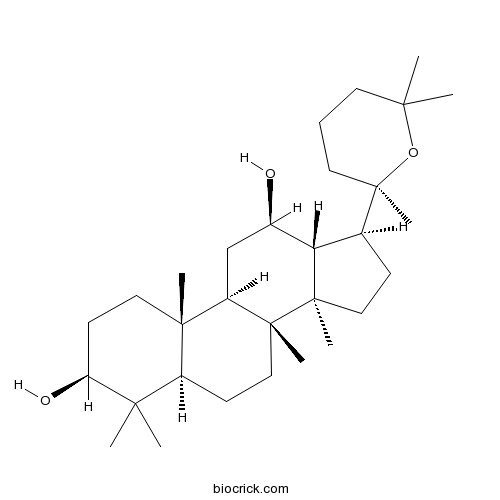
Panaxadiol19666-76-3
Instructions
-
BCN1066
Ginsenoside Rg122427-39-0
Instructions

-
BCN1254
(20S)-Protopanaxdiol30636-90-9
Instructions

-
BCN1081
Panaxatriol32791-84-7
Instructions

-
BCN2705
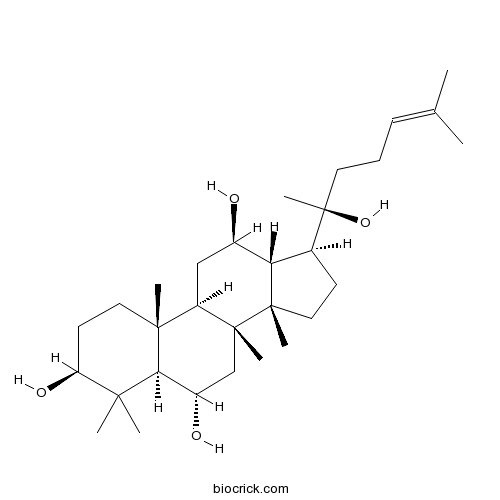
(20S)-Protopanaxatriol34080-08-5
Instructions
-
BCN3502
Ginsenoside Rk3364779-15-7
Instructions

-
BCN5018
20(R)-Ginsenoside Rg338243-03-7
Instructions

-
BCN1246
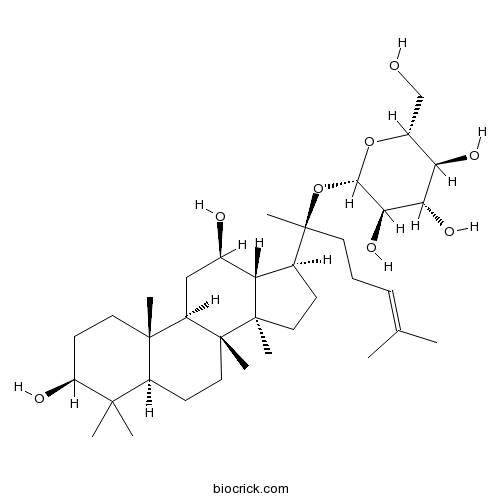
Ginsenoside Compound K39262-14-1
Instructions
-
BCN1063
Ginsenoside Rb141753-43-9
Instructions

-
BCN3552
Ginsenoside Rk1494753-69-4
Instructions

-
BCN1075
Ginsenoside Rf52286-58-5
Instructions

-
BCN1073
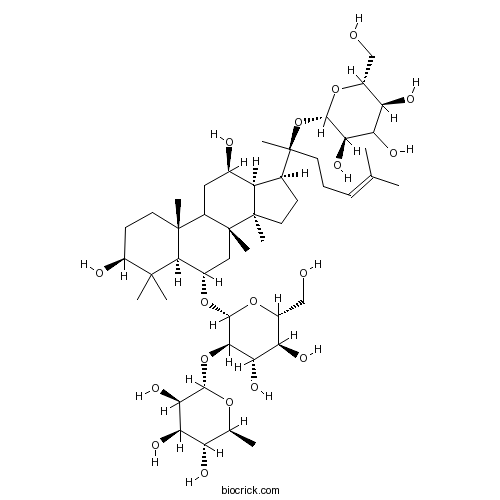
Ginsenoside Re52286-59-6
Instructions
-
BCN1067
Ginsenoside Rg252286-74-5
Instructions

-
BCN1074
Ginsenoside Rd52705-93-8
Instructions

-
BCN1244
Ginsenoside F153963-43-2
Instructions

-
BCN5807
Caffeine58-08-2
Instructions

-
BCN1077
Ginsenoside F362025-50-7
Instructions

-
BCN1069
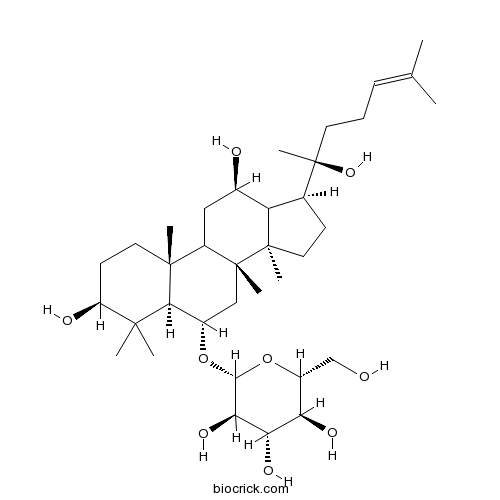
Ginsenoside Rh163223-86-9
Instructions
-
BCN1065
Ginsenoside Rb368406-26-8
Instructions

-
BCN1078
(20R)-Protopanaxdiol7755-01-3
Instructions

-
BCN1070
20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh278214-33-2
Instructions

-
BCN1097
Notoginsenoside R180418-24-2
Instructions

-
BCN3328
Notoginsenoside R280418-25-3
Instructions

-
BCN3700
(20R)-Ginsenoside Rh180952-71-2
Instructions

-
BCN2554
20R-Ginsenoside Rg280952-72-3
Instructions

-
BCN4376
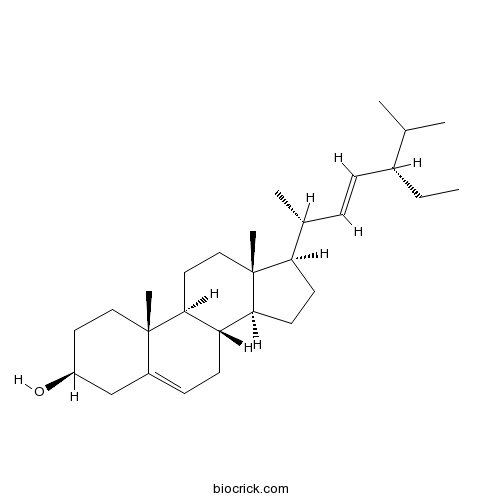
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
-
BCN3852
Notoginsenoside Fe88105-29-7
Instructions

-
BCN3864
20(R)-Notoginsenoside R2948046-15-9
Instructions

Characterization of UDP-glycosyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of ginsenosides Rh1 and Rd and identification of critical conserved amino acid residues for its function.[Pubmed: 30095259]
Ginsenosides attract great attention for their bioactivities. However, their contents are low, and many UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs) that play crucial roles in the ginsenosides biosynthesis pathways have not been identified, which hinders the biosynthesis of ginsenosides. In this study, we reported one UDP-glycosyltransferase, UGTPg71A29 from Panax ginseng could glycosylate the C20-OH of Rh1, and transfer a glucose moiety to Rd, producing ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1, respectively. Ectopic expression of UGTPg71A29 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae stably generated Rg1 and Rb1 under its corresponding substrate, respectively. Overexpression of UGTPg71A29 in transgenic cells of P. ginseng could significantly enhance the accumulation of Rg1 and Rb1 with their contents of 3.2-fold and 3.5-fold higher than those in control, respectively. Homology modeling, molecular dynamics and mutational analysis revealed the key catalytic site, Gln283, which provided insights into the catalytic mechanism of UGTPg71A29. These results not only provide an efficient enzymatic tool for the synthesis of glycosides but also help achieve large-scale industrial production of glycosides.
Identification of candidate UDP-glycosyltransferases involved in protopanaxadiol-type ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng.[Pubmed: 30082711]
Ginsenosides are dammarane-type or triterpenoidal saponins that contribute to the various pharmacological activities of the medicinal herb Panax ginseng. The putative biosynthetic pathway for ginsenoside biosynthesis is known in P. ginseng, as are some of the transcripts and enzyme-encoding genes. However, few genes related to the UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs), enzymes that mediate glycosylation processes in final saponin biosynthesis, have been identified. Here, we generated three replicated Illumina RNA-Seq datasets from the adventitious roots of P. ginseng cultivar Cheongsun (CS) after 0, 12, 24, and 48 h of treatment with methyl jasmonate (MeJA). Using the same CS cultivar, metabolomic data were also generated at 0 h and every 12-24 h thereafter until 120 h of MeJA treatment. Differential gene expression, phylogenetic analysis, and metabolic profiling were used to identify candidate UGTs. Eleven candidate UGTs likely to be involved in ginsenoside glycosylation were identified. Eight of these were considered novel UGTs, newly identified in this study, and three were matched to previously characterized UGTs in P. ginseng. Phylogenetic analysis further asserted their association with ginsenoside biosynthesis. Additionally, metabolomic analysis revealed that the newly identified UGTs might be involved in the elongation of glycosyl chains of ginsenosides, especially of protopanaxadiol (PPD)-type ginsenosides.


