Phyllanthus urinaria
Phyllanthus urinaria
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Phyllanthus urinaria
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
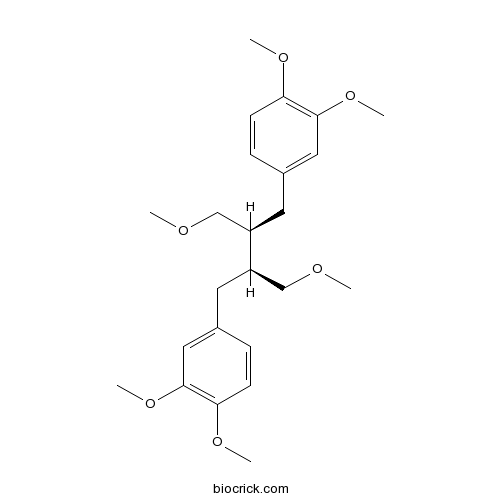
BCN5848
Phyllanthin10351-88-9
Instructions
-
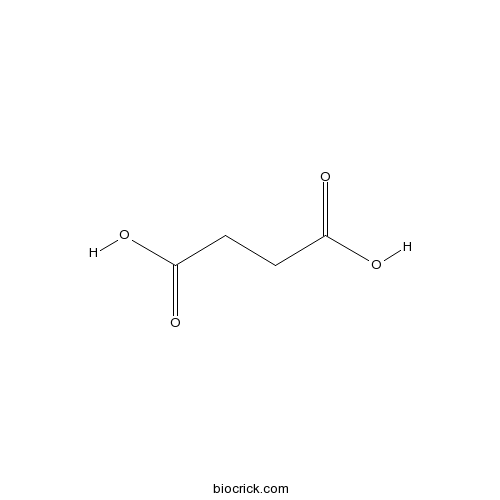
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
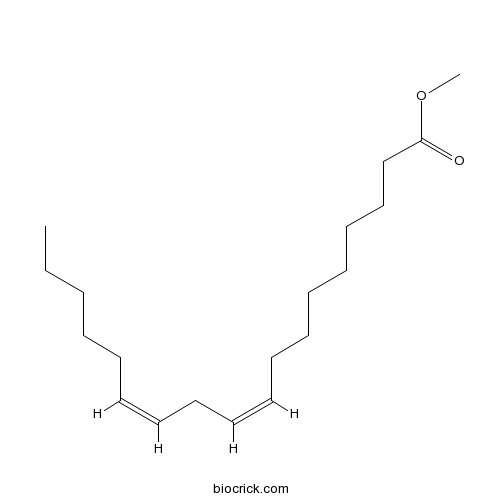
BCN8137
Methyl linoleate112-63-0
Instructions
-
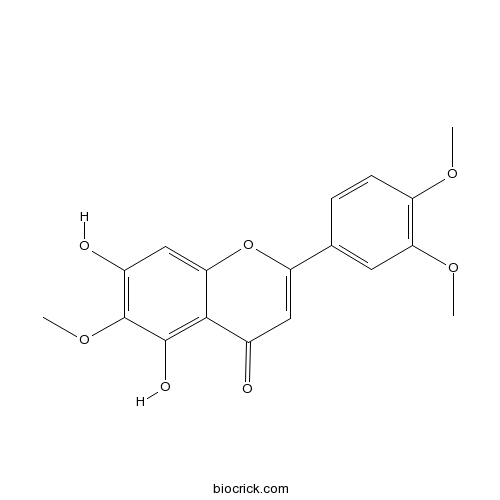
BCN2336
Eupatilin22368-21-4
Instructions
-
BCN2322
Corilagin23094-69-1
Instructions
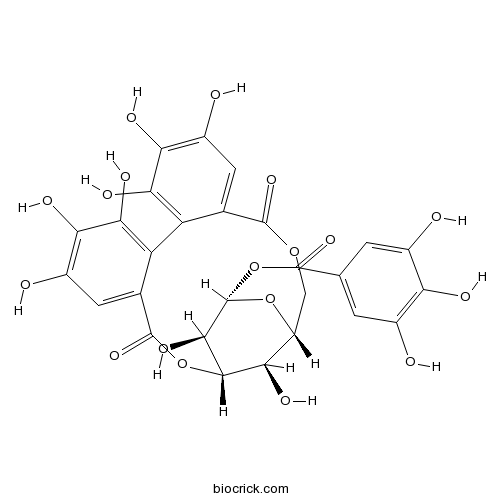
-
BCN5259
Hypophyllanthin33676-00-5
Instructions
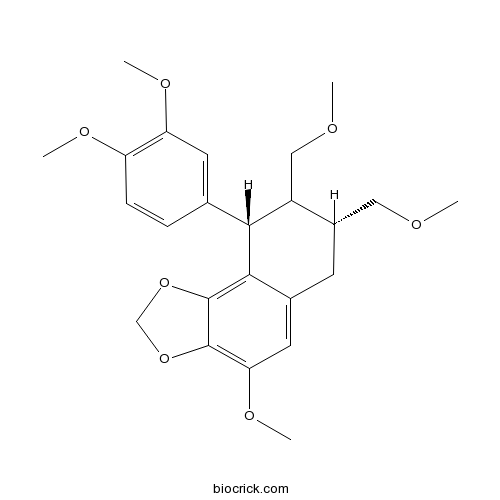
-
BCN5533
Ellagic acid476-66-4
Instructions
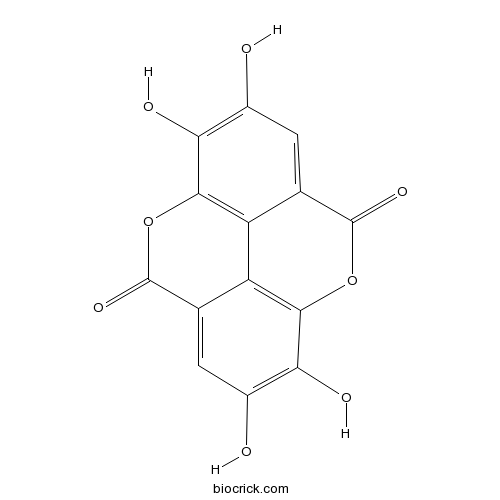
-
BCN2402
Geraniin60976-49-0
Instructions

-
BCN4376
Stigmasterol83-48-7
Instructions
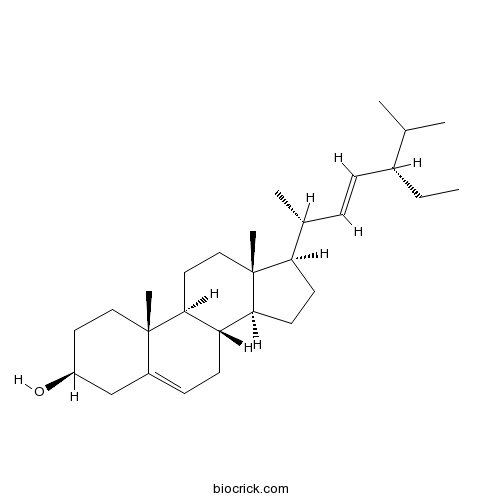
-
BCN4373
Ethyl gallate831-61-8
Instructions

-
BCN3823
Methyl gallate99-24-1
Instructions
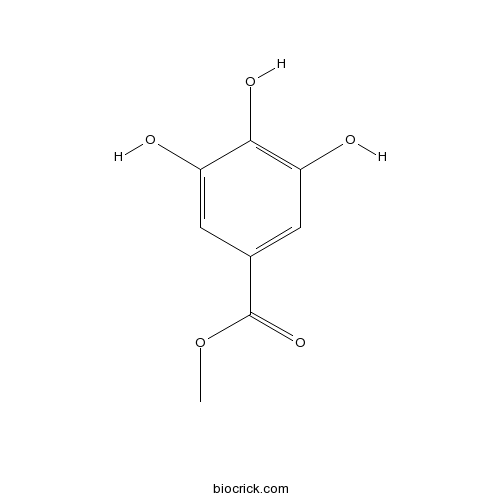
-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
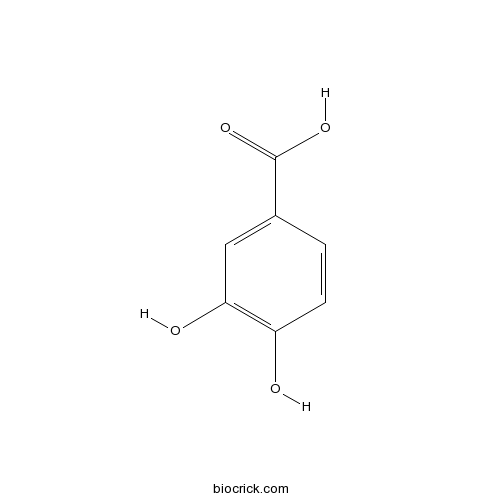
Corilagin inhibits breast cancer growth via reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis and autophagy.[Pubmed: 29923307]
Corilagin is a component of Phyllanthus urinaria extract and has been found of possessing anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-tumour properties in clinic treatments. However, the underlying mechanisms in anti-cancer particularly of its induction of cell death in human breast cancer remain undefined. Our research found that corilagin-induced apoptotic and autophagic cell death depending on reactive oxygen species (ROS) in human breast cancer cell, and it occurred in human breast cancer cell (MCF-7) only comparing with normal cells. The expression of procaspase-8, procaspase-3, PARP, Bcl-2 and procaspase-9 was down-regulated while caspase-8, cleaved PARP, caspase-9 and Bax were up-regulated after corilagin treatment, indicating apoptosis mediated by extrinsic and mitochondrial pathways occurred in MCF-7 cell. Meanwhile, autophagy mediated by suppressing Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway was detected with an increase in autophagic vacuoles and LC3-II conversion. More significantly, inhibition of autophagy by chloroquine diphosphate salt (CQ) remarkably enhanced apoptosis, while the caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk failed in affecting autophagy, suggesting that corilagin-induced autophagy functioned as a survival mechanism in MCF-7 cells. In addition, corilagin induced intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, when reduced by ROS scavenger NAC, apoptosis and autophagy were both down-regulated. Nevertheless, in SK-BR3 cell which expressed RIP3, necroptosis inhibitor Nec-1 could not alleviate cell death induced by corilagin, indicating necroptosis was not triggered. Subcutaneous tumour growth in nude mice was attenuated by corilagin, consisting with the results in vitro. These results imply that corilagin inhibits cancer cell proliferation through inducing apoptosis and autophagy which regulated by ROS release.
Suppression of ERK1/2 and hypoxia pathways by four Phyllanthus species inhibits metastasis of human breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 28911625]
Chemotherapies remain far from ideal due to drug resistance; therefore, novel chemotherapeutic agents with higher effectiveness are crucial. The extracts of four Phyllanthus species, namely Phyllanthus niruri, Phyllanthus urinaria, Phyllanthus watsonii, and Phyllanthus amarus, were shown to induce apoptosis and inhibit metastasis of breast carcinoma cells (MCF-7). The main objective of this study was to determine the pathways utilized by these four Phyllanthus species to exert anti-metastatic activities. A cancer 10-pathway reporter was used to investigate the pathways affected by the four Phyllanthus species. Results indicated that these Phyllanthus species suppressed breast carcinoma metastasis and proliferation by suppressing matrix metalloprotein 2 and 9 expression via inhibition of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. Additionally, inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α in the hypoxia pathway caused reduced vascular endothelial growth factor and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression, resulting in anti-angiogenic effects and eventually anti-metastasis. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis identified numerous proteins suppressed by these Phyllanthus species, including invasion proteins, anti-apoptotic protein, protein-synthesis proteins, angiogenic and mobility proteins, and various glycolytic enzymes. Our results indicated that ERK and hypoxia pathways are the most likely targets of the four Phyllanthus species for the inhibition of MCF-7 metastasis.
Phyllanthus urinaria's Inhibition of Human Osteosarcoma Xenografts Growth in Mice is Associated with Modulation of Mitochondrial Fission/Fusion Machinery.[Pubmed: 27776427]
Osteosarcoma is an aggressive bone cancer arising from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin to form malignant osteoid. Phyllanthus urinaria [Formula: see text]P. urinaria[Formula: see text] is a widely used folk medicine in cancer treatment, however the mechanism of P. urinaria inhibited human osteosarcoma is unclear. The present study was aimed at investigating the antitumoral effects of an aqueous P. urinaria on human osteosarcoma in vivo and the related underlying mechanisms, mainly focusing on mitochondrial dynamic dysfunction. Our results showed that oral administration of P. urinaria to mice led to significant inhibition of tumor development without substantial changes to body weight or major organs. Histological examinations with H&E, Giemsa, and Masson trichrome stains confirmed inhibition of tumor growth by the P. urinaria treatment. Immunohistochemical staining of proliferation markers antigen KI-67 (Ki67) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), as well as a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay demonstrated a decrease of tumor proliferation and an increase of apoptosis, which was associated with the modulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family activating the caspase cascade in the P. urinaria-treated mice. The neovascularization marker cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) was inhibited in P. urinaria-treated xenografts, implicating the potential anti-angiogenic effect of P. urinaria. P. urinaria treatment resulted in a significant decrease in the mitochondrial fusion proteins, including mitofusin 1/2 (Mfn1/2) and optic atrophy type 1 (Opa1), as well as an increase in the fission protein dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1). The results of this study suggest mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with dynamic change that is involved in the apoptosis and anti-angiogenesis elicited by P. urinaria.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Corilagin Following Hemorrhagic Shock are Through Akt-Dependent Pathway.[Pubmed: 27559697]
Corilagin, a component of Phyllanthus urinaria extract, possesses antioxidant, thrombolytic, antiatherogenic, and hepatoprotective properties, but the mechanism underlying these effects remains unclear. Previous studies showed that the Akt (protein kinase B) signaling pathway exerts anti-inflammatory and organ protective effects. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of action of corilagin and determine whether these effects are mediated through the Akt-dependent pathway in a trauma-hemorrhagic shock-induced liver injury rodent model. Hemorrhagic shock was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats; mean blood pressure was maintained at 35 mm Hg to 40 mm Hg for 90 min, followed by fluid resuscitation. During resuscitation, three doses of corilagin alone (1 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, or 10 mg/kg, intravenously) were administered. Furthermore, a single dose of corilagin (5 mg/kg) with and without Wortmannin (1 mg/kg, PI3K inhibitor), Wortmannin alone, or vehicle was administered. Twenty-four hours after resuscitation, plasma alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase concentration and hepatic parameters were measured. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. Hepatic myeloperoxidase activity and the concentrations of plasma alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1) and CINC-3 increased following hemorrhagic shock. These parameters were significantly attenuated in corilagin-treated rats following hemorrhagic shock. Hepatic phospho-Akt expression was also higher in corilagin-treated rats than in vehicle-treated rats. The elevation of phospho-Akt was abolished by combined treatment with Wortmannin and corilagin. Our results suggest that corilagin exerts its protective effects on hemorrhagic shock-induced liver injury, at least, via the Akt-dependent pathway.


