EupatilinCAS# 22368-21-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 22368-21-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5273755 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
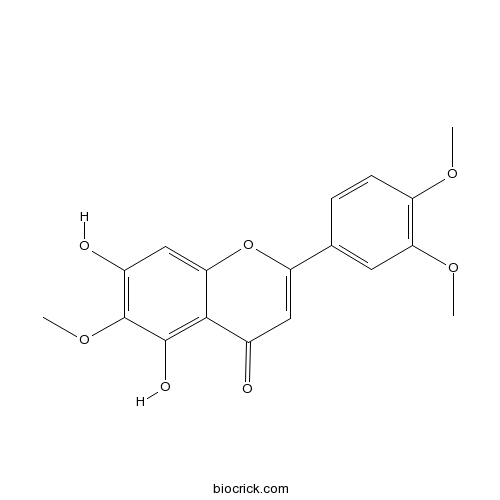
| Formula | C18H16O7 | M.Wt | 344.31 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 5,7-Dihydroxy 3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (145.21 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DRRWBCNQOKKKOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-22-12-5-4-9(6-14(12)23-2)13-7-10(19)16-15(25-13)8-11(20)18(24-3)17(16)21/h4-8,20-21H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Eupatilin has anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor properties, it inhibits the MKN-1 gastric cancer cell proliferation via activation of caspase-3 and the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells via down-regulation of NF-κB activity followed by reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated MMPs expressions. Eupatilin inhibits the signalling of MAPK, IKK, NF-κB and eotaxin-1 in bronchial epithelial cells, leading to inhibition of eosinophil migration. Eupatilin is also a promising therapeutic agent against acute ischemia-induced renal damage, it significantly increases the levels of heat shock protein 70 and B-cell lymphoma protein, and it attenuates inducible nitric oxide synthase, Bcl-2-associated X protein, and caspase-3 levels. |
| Targets | TNF-α | p65 | NF-kB | IL Receptor | STAT | MAPK | NOS | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | Akt | ERK | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | Wnt/β-catenin | GSK-3 |
| In vitro | The effects of eupatilin (stillen®) on motility of human lower gastrointestinal tracts.[Pubmed: 25352757]Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;18(5):383-90.Gastrointestinal motility consists of phasic slow-wave contractions and the migrating motor complex (MMC). Eupatilin (Stillen®) has been widely used to treat gastritis and peptic ulcers, and various cytokines and neuropeptides are thought to be involved, which can affect gastrointestinal motility. Inhibitory effects of eupatilin on tumor invasion of human gastric cancer MKN-1 cells.[Pubmed: 23292941]Tumour Biol. 2013 Apr;34(2):875-85.Extracts of the whole herb of Artemisia asiatica Nakai (Asteraceae) are used in traditional oriental medicine to treat inflammation. Eupatilin (5,7-dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone) is one of the pharmacologically active components found in A. asiatica, and has been shown to possess anti-tumoral effects in some malignancies, including gastric cancer. However, its anti-metastatic effect in gastric cancer is hardly known. |
| In vivo | Eupatilin ameliorates collagen induced arthritis.[Pubmed: 25729243]J Korean Med Sci. 2015 Mar;30(3):233-9.Eupatilin is the main active component of DA-9601, an extract from Artemisia. Recently, Eupatilin was reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. We investigated the anti-arthritic effect of Eupatilin in a murine arthritis model and human rheumatoid synoviocytes. |
| Kinase Assay | The flavone eupatilin inhibits eotaxin expression in an NF-κB-dependent and STAT6-independent manner.[Pubmed: 25565108]Scand J Immunol. 2015 Mar;81(3):166-76.The CC chemokine eotaxin contributes to epithelium-induced inflammation in airway diseases such as asthma. Eupatilin (5,7-dihydroxy-3',4',6'-trimethoxyflavone), a bioactive component of Artemisia asiatica Nakai (Asteraceae), is reported to inhibit the adhesion of eosinophils to bronchial epithelial cells. However, little is known about the molecular mechanism of Eupatilin-induced attenuation of bronchial epithelium-induced inflammation. |
| Animal Research | Protective effect of eupatilin against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.[Pubmed: 25891726]Transplant Proc. 2015 Apr;47(3):757-62. Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia species, is known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major complication after renal transplantation, with inflammatory responses to IRI exacerbating the resultant renal injury. In the present study, we investigated whether Eupatilin exhibits renoprotective activities against ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice. |

Eupatilin Dilution Calculator

Eupatilin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9044 mL | 14.5218 mL | 29.0436 mL | 58.0872 mL | 72.609 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8087 mL | 11.6174 mL | 14.5218 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4522 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8087 mL | 7.2609 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0581 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 1.1617 mL | 1.4522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1452 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 0.7261 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Eupatilin, a lipophilic flavonoid isolated from Artemisia species, is a PPARα agonist, and possesses anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities.
In Vitro:Eupatilin is a PPARα agonist. Eupatilin (10, 30, 100 μM) suppresses IL-4 expression and degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells[1]. Eupatilin (50-100 μM) slightly reduces cell viability of HaCaT cells. Eupatilin (10, 30, 50, 100 μM) increases PPARα transactivation and expression in HaCaT cells. Eupatilin (10, 30, 50 μM) also suppresses TNFα-induced MMP-2/-9 expression in HaCaT cells. Furthermore, Eupatilin inhibits TNFα-induced p65 translocation, IκBα Phosphorylation, AP-1 and MAPK signaling via PPARα[2]. Eupatilin (10-50 μM) shows no cytotoxic effects on ARPE19 cells. Eupatilin (10, 25, 50 μM) elevates cell viability from oxidative stress, and inhibits H2O2-induced ROS production in ARPE19 cells. Moreover, Eupatilin (50 μM) inbibits H2O2-induced cells apoptosis and promotes the activation of PI3K/Akt pathway in RPE cells[3].
In Vivo:Eupatilin (1.5% or 3.0%) restores PPARα mRNA expression, and improves atopic dermatitis (AD)-like symptoms in oxazolone-induced Balb/c mice. Eupatilin causes significant decrease in serum IgE, IL-4 levels, oxazolone-induced TNFα, IFNγ, IL-1β, TSLP, IL-33 and IL-25 mRNA expression in oxazolone-induced mice. Eupatilin also increases filaggrin and loricrin mRNA expression in oxazolone-induced mice[1].
References:
[1]. Jung Y, et al. Eupatilin, an activator of PPARα, inhibits the development of oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis symptoms in Balb/c mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Feb 5;496(2):508-514.
[2]. Jung Y, et al. Eupatilin with PPARα agonistic effects inhibits TNFα-induced MMP signaling in HaCaT cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Nov 4;493(1):220-226.
[3]. Du L, et al. Eupatilin prevents H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jan;85:136-140.
- Mirabegron (YM178)
Catalog No.:BCC3814
CAS No.:223673-61-8
- Collagen proline hydroxylase inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1494
CAS No.:223666-07-7
- Collagen proline hydroxylase inhibitor-1
Catalog No.:BCC1495
CAS No.:223663-32-9
- K-115 free base
Catalog No.:BCC5501
CAS No.:223645-67-8
- Tiadinil
Catalog No.:BCC8070
CAS No.:223580-51-6
- CPA inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1500
CAS No.:223532-02-3
- YM 58483
Catalog No.:BCC7817
CAS No.:223499-30-7
- ONO 4817
Catalog No.:BCC2375
CAS No.:223472-31-9
- GLP-2 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5891
CAS No.:223460-79-5
- FG2216
Catalog No.:BCC6402
CAS No.:223387-75-5
- Polygalacic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5898
CAS No.:22338-71-2
- Grandifloric acid
Catalog No.:BCN4669
CAS No.:22338-69-8
- 4-Methoxysalicylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7783
CAS No.:2237-36-7
- Sodium Monensin
Catalog No.:BCC5319
CAS No.:22373-78-0
- NPE-caged-HPTS
Catalog No.:BCC5950
CAS No.:223759-19-1
- Bestatin trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC3909
CAS No.:223763-80-2
- Pedalitin
Catalog No.:BCN3954
CAS No.:22384-63-0
- Serratenediol
Catalog No.:BCN5061
CAS No.:2239-24-9
- 3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5062
CAS No.:2239-88-5
- Aristola-1(10),8-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7608
CAS No.:22391-34-0
- Cyclobuxine D
Catalog No.:BCC9221
CAS No.:2241-90-9
- 3-Epiturraeanthin
Catalog No.:BCN5063
CAS No.:22415-24-3
- Siramesine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5134
CAS No.:224177-60-0
- Incensole
Catalog No.:BCN3831
CAS No.:22419-74-5
The flavone eupatilin inhibits eotaxin expression in an NF-kappaB-dependent and STAT6-independent manner.[Pubmed:25565108]
Scand J Immunol. 2015 Mar;81(3):166-76.
The CC chemokine eotaxin contributes to epithelium-induced inflammation in airway diseases such as asthma. Eupatilin (5,7-dihydroxy-3',4',6'-trimethoxyflavone), a bioactive component of Artemisia asiatica Nakai (Asteraceae), is reported to inhibit the adhesion of eosinophils to bronchial epithelial cells. However, little is known about the molecular mechanism of Eupatilin-induced attenuation of bronchial epithelium-induced inflammation. In this study, we investigated the effect of Eupatilin on expression of eotaxin-1 (CCL11), a potent chemoattractant for eosinophils. Eupatilin significantly inhibited eotaxin expression in bronchial epithelial cells stimulated with TNF-alpha, while NF-kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase (IKK) activities declined concurrently. Eupatilin also inhibited mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity; however, all of these anti-inflammatory activities were reversed by MAPK overexpression. In contrast, Eupatilin did not affect the signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) signalling in bronchial epithelial cells stimulated with IL-4. Furthermore, Eupatilin significantly attenuated TNF-alpha-induced eosinophil migration. These results suggest that the Eupatilin inhibits the signalling of MAPK, IKK, NF-kappaB and eotaxin-1 in bronchial epithelial cells, leading to inhibition of eosinophil migration.
Inhibitory effects of eupatilin on tumor invasion of human gastric cancer MKN-1 cells.[Pubmed:23292941]
Tumour Biol. 2013 Apr;34(2):875-85.
Extracts of the whole herb of Artemisia asiatica Nakai (Asteraceae) are used in traditional oriental medicine to treat inflammation. Eupatilin (5,7-dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone) is one of the pharmacologically active components found in A. asiatica, and has been shown to possess anti-tumoral effects in some malignancies, including gastric cancer. However, its anti-metastatic effect in gastric cancer is hardly known. In this study, anti-metastatic effect of Eupatilin was investigated in the human gastric cancer cell line, MKN-1. Eupatilin inhibited MKN-1 growth in a dose- and a time-dependent manner, and induced apoptosis with a concomitant increase of caspase-3 activity. ELISA demonstrated that release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8) was significantly reduced by Eupatilin. And p-AKT and p-ERK (p44/42) was reduced. Expression level of beta-catenin and integrin was reduced and p-GSKbeta was increased. In transcription reporter system, the activity of the transcriptional factor, NF-kappaB, was reduced by Eupatilin and the expression of p65 was down-regulated when MKN-1 cells were treated with Eupatilin. Moreover, a zymography study revealed that this reduction in invasive potential resulted from a reduction in type IV collagenolytic (gelatinolytic) activity. The expressions of metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) were also reduced in MKN-1 cells treated with Eupatilin. In vitro invasion assay, Eupatilin inhibited MKN-1 penetrating reconstituted basement membrane barriers. These results suggest that Eupatilin inhibits the MKN-1 gastric cancer cell proliferation via activation of caspase-3 and the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells via down-regulation of NF-kappaB activity followed by reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated MMPs expressions.
Eupatilin ameliorates collagen induced arthritis.[Pubmed:25729243]
J Korean Med Sci. 2015 Mar;30(3):233-9.
Eupatilin is the main active component of DA-9601, an extract from Artemisia. Recently, Eupatilin was reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. We investigated the anti-arthritic effect of Eupatilin in a murine arthritis model and human rheumatoid synoviocytes. DA-9601 was injected into collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice. Arthritis score was regularly evaluated. Mouse monocytes were differentiated into osteoclasts when Eupatilin was added simultaneously. Osteoclasts were stained with tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and then manually counted. Rheumatoid synoviocytes were stimulated with TNF-alpha and then treated with Eupatilin, and the levels of IL-6 and IL-1beta mRNA expression in synoviocytes were measured by RT-PCR. Intraperitoneal injection of DA-9601 reduced arthritis scores in CIA mice. TNF-alpha treatment of synoviocytes increased the expression of IL-6 and IL-1beta mRNAs, which was inhibited by Eupatilin. Eupatilin decreased the number of osteoclasts in a concentration dependent manner. These findings, showing that Eupatilin and DA-9601 inhibited the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the differentiation of osteoclasts, suggest that Eupatilin and DA-9601 is a candidate anti-inflammatory agent.
Protective effect of eupatilin against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.[Pubmed:25891726]
Transplant Proc. 2015 Apr;47(3):757-62.
BACKGROUND: Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia species, is known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major complication after renal transplantation, with inflammatory responses to IRI exacerbating the resultant renal injury. In the present study, we investigated whether Eupatilin exhibits renoprotective activities against ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Renal IRI was induced in male C57BL/6 mice by bilateral renal pedicle occlusion for 30 minutes followed by reperfusion for 48 hours. Eupatilin (10 mg/kg body weight p.o.) was administered 4 days before IRI. RESULTS: Treatment with Eupatilin significantly decreased neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury molecule-1 levels in urine, blood urea nitrogen level, and serum creatinine levels, as well as kidney tubular injury. Western blotting indicated that Eupatilin significantly increased the levels of heat shock protein 70 and B-cell lymphoma protein, and it attenuated inducible nitric oxide synthase, Bcl-2-associated X protein, and caspase-3 levels 48 hours after IRI. CONCLUSION: Our findings suggest that Eupatilin is a promising therapeutic agent against acute ischemia-induced renal damage.
The effects of eupatilin (stillen(R)) on motility of human lower gastrointestinal tracts.[Pubmed:25352757]
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;18(5):383-90.
Gastrointestinal motility consists of phasic slow-wave contractions and the migrating motor complex (MMC). Eupatilin (Stillen(R)) has been widely used to treat gastritis and peptic ulcers, and various cytokines and neuropeptides are thought to be involved, which can affect gastrointestinal motility. We performed a study to identify the effects of Eupatilin on lower gastrointestinal motility with electromechanical recordings of smooth muscles in the human ileum and colon. Ileum and colon samples were obtained from patients undergoing bowel resection. The tissues were immediately stored in oxygenated Krebs-Ringer's bicarbonate solution, and conventional microelectrode recordings from muscle cells and tension recordings from muscle strips and ileal or colonic segments were performed. Eupatilin was perfused into the tissue chamber, and changes in membrane potentials and contractions were measured. Hyperpolarization of resting membrane potential (RMP) was observed after administration of Eupatilin. The amplitude, AUC, and frequency of tension recordings from circular and longitudinal smooth muscle strips and bowel segments of the ileum and colon were significantly decreased after admission of Eupatilin. Eupatilin elicited dose-dependent decreases during segmental tension recordings. In conclusion, Eupatilin (Stillen(R)) showed inhibitory effects on the human ileum and colon. We propose that this drug may be useful for treating diseases that increase bowel motility, but further studies are necessary.


