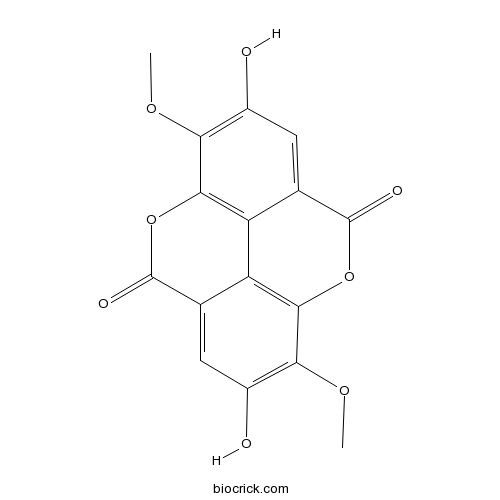
3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acidCAS# 2239-88-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2239-88-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5488919 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H10O8 | M.Wt | 330.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C3=C1OC(=O)C4=CC(=C(C(=C43)OC2=O)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KLAGYIBJNXLDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid reveals moderate antibacterial activity, it also shows strong DPPH radical scavenging activities with SC50 of 123.3 ug/mL. It has a lower capacity of stimulating murine peritoneal macrophages to release nitric oxide and tumoural-alpha necrose factor. 3,3'-Di-O-methylellagic acid may be a useful as pharmacological agent for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Targets | Antifection | NO | TNF-α |
| In vitro | Identification of ellagic acid derivatives in methanolic extracts from Qualea species.[Pubmed: 19227825]Z Naturforsch C. 2008 Nov-Dec;63(11-12):794-800.
Active compounds from Lagerstroemia speciosa, insulin-like glucose uptake-stimulatory/inhibitory and adipocyte differentiation-inhibitory activities in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed: 19053366 ]J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Dec 24;56(24):11668-74.
Chemical Constituents with DPPH Radical Scavenging, Elastase Inhnbition and Tyrosinase Inhibition Activities from Cleyera japonica Thunb[Reference: WebLink]Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2011,4, 272-272.Bioassay-guided investigation of the stem of Cleyera japonica Thunb. led to the isolation of five compounds such as 3,5,7-trihydroxylchromone 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (1), aviculin (2), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid,3), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid 4'-O-β-D-xylopyranoside (4) and betulinic acid (5). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectral studies as well as by comparison of their data with literature values. |
| Cell Research | Induction of neuronal differentiation in neurosphere stem cells by ellagic acid derivatives.[Pubmed: 19475997]Nat Prod Commun. 2009 Apr;4(4):517-20.
|
| Structure Identification | Nat Prod Res. 2008 Mar 10;22(4):353-9.Chemical constituents with antibacterial activity from Euphorbia sororia.[Pubmed: 18322851 ]
|

3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid Dilution Calculator

3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0276 mL | 15.1378 mL | 30.2755 mL | 60.551 mL | 75.6888 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6055 mL | 3.0276 mL | 6.0551 mL | 12.1102 mL | 15.1378 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3028 mL | 1.5138 mL | 3.0276 mL | 6.0551 mL | 7.5689 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0606 mL | 0.3028 mL | 0.6055 mL | 1.211 mL | 1.5138 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0303 mL | 0.1514 mL | 0.3028 mL | 0.6055 mL | 0.7569 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Serratenediol
Catalog No.:BCN5061
CAS No.:2239-24-9
- Pedalitin
Catalog No.:BCN3954
CAS No.:22384-63-0
- Bestatin trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC3909
CAS No.:223763-80-2
- NPE-caged-HPTS
Catalog No.:BCC5950
CAS No.:223759-19-1
- Sodium Monensin
Catalog No.:BCC5319
CAS No.:22373-78-0
- 4-Methoxysalicylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7783
CAS No.:2237-36-7
- Eupatilin
Catalog No.:BCN2336
CAS No.:22368-21-4
- Mirabegron (YM178)
Catalog No.:BCC3814
CAS No.:223673-61-8
- Collagen proline hydroxylase inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1494
CAS No.:223666-07-7
- Collagen proline hydroxylase inhibitor-1
Catalog No.:BCC1495
CAS No.:223663-32-9
- K-115 free base
Catalog No.:BCC5501
CAS No.:223645-67-8
- Tiadinil
Catalog No.:BCC8070
CAS No.:223580-51-6
- Aristola-1(10),8-dien-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7608
CAS No.:22391-34-0
- Cyclobuxine D
Catalog No.:BCC9221
CAS No.:2241-90-9
- 3-Epiturraeanthin
Catalog No.:BCN5063
CAS No.:22415-24-3
- Siramesine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5134
CAS No.:224177-60-0
- Incensole
Catalog No.:BCN3831
CAS No.:22419-74-5
- 2,2'-Anhydro-5-methyluridine
Catalog No.:BCC8486
CAS No.:22423-26-3
- Bayogenin methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3722
CAS No.:22425-81-6
- Ginsenoside Rg1
Catalog No.:BCN1066
CAS No.:22427-39-0
- Retapamulin
Catalog No.:BCC4837
CAS No.:224452-66-8
- Benfotiamine
Catalog No.:BCC1415
CAS No.:22457-89-2
- MLCK inhibitor peptide 18
Catalog No.:BCC5828
CAS No.:224579-74-2
- Gymnemagenin
Catalog No.:BCN7841
CAS No.:22467-07-8
Identification of ellagic acid derivatives in methanolic extracts from Qualea species.[Pubmed:19227825]
Z Naturforsch C. 2008 Nov-Dec;63(11-12):794-800.
The methanolic extract from the barks of the medicinal plant Qualea parviflora (Vochysiaceae) was fractionated by column chromatography over silica gel followed by gel permeation over Sephadex LH-20 to give 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid-4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (1), 3-O-methylellagic acid-4'-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (2), 3,3',4-tri-O-methylellagic acid-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), and 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (4), together with triterpenes and saponins. We also performed comparative analyses among this species and Q. grandiflora and Q. multiflora using high-pressure liquid chromatography. The biological assays showed that, when compared to the standard ellagic acid, compounds 1-4 are less cytotoxic but have a lower capacity of stimulating murine peritoneal macrophages to release nitric oxide and tumoural-alpha necrose factor.
Active compounds from Lagerstroemia speciosa, insulin-like glucose uptake-stimulatory/inhibitory and adipocyte differentiation-inhibitory activities in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed:19053366]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Dec 24;56(24):11668-74.
Seven ellagitannins, lagerstroemin (1), flosin B (2), stachyurin (3), casuarinin (4), casuariin (5), epipunicacortein A (6), and 2, 3-(S)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-alpha/beta-D-glucose (7), together with one ellagic acid sulfate, 3-O-methyl-ellagic acid 4'-sulfate (8), ellagic acid (9), and four methyl ellagic acid derivatives, 3-O-methylellagic acid (10), 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (11), 3,4,3'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (12), and 3,4,8,9,10-pentahydroxydibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-one (13), were identified by the bioassay-directed isolation from the leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers. The chemical structures of these components were established on the basis of one- and two-dimensional NMR and high-resolution mass spectroscopic analyses. Other known compounds, including corosolic acid, gallic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3-O-methylprotocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, kaempferol, quercetin, and isoquercitrin, were also isolated from the same plant. The obtained ellagitannins exhibited strong activities in both stimulating insulin-like glucose uptake (1-5 and 7) and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation (1 and 4) in 3T3-L1 cells. Meanwhile, ellagic acid derivatives (10-13) showed an inhibitory effect on glucose transport assay. This study is the first to report an inhibitory effect for methyl ellagic acid derivatives.
Chemical constituents with antibacterial activity from Euphorbia sororia.[Pubmed:18322851]
Nat Prod Res. 2008 Mar 10;22(4):353-9.
A group of ceramide (1) was isolated from the aerial parts of Euphorbia sororia. On the basis of spectroscopic data, chemical methods and GC-MS analysis, the structure of 1 was characterised as (2S,3S,4R,8E)-2-(eicosanoyl approximately octacosanoyl amino)-1,3,4-octadecanetriol-8-ene. In addition, four known ellagic acid derivatives 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (2), 3,3',4'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (3), 4-O-sulfooxy-3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid (4) and 4-O-sulfooxy- 3,3',4'-tri-O-methylellagic acid (5) were isolated from the plant. Biological screening of all compounds revealed moderate antibacterial activity.


