Polygonum orientale
Polygonum orientale
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Polygonum orientale
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
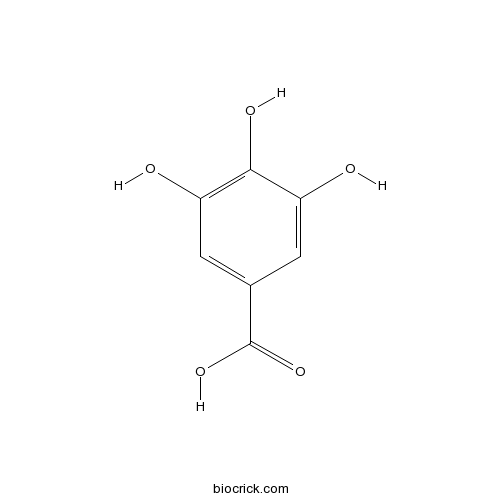
BCN1668
Gallic acid149-91-7
Instructions
-
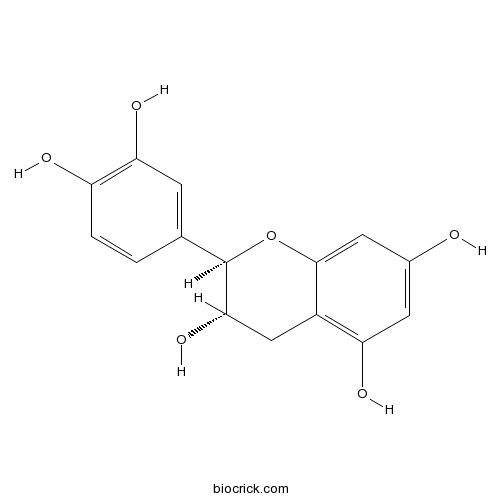
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
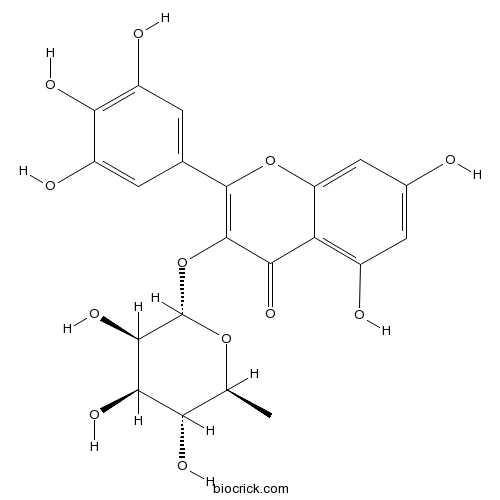
BCN1136
Myricitrin17912-87-7
Instructions
-
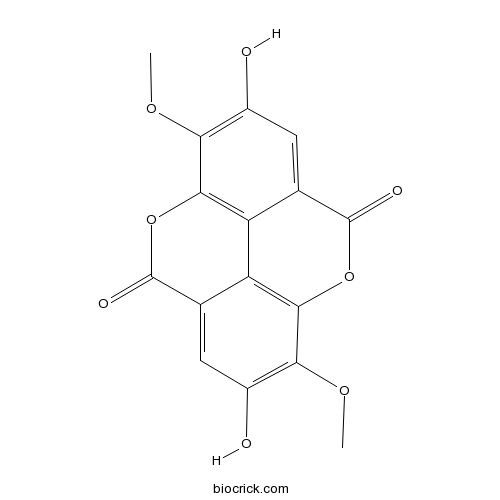
BCN5062
3,8-Di-O-methylellagic acid2239-88-5
Instructions
-
BCN3149
Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide22688-79-5
Instructions
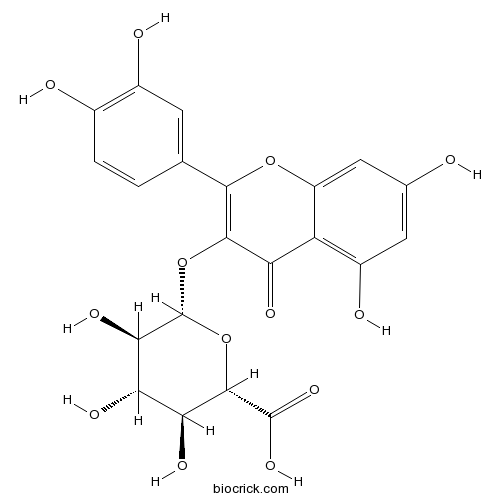
-
BCN5320
N-p-trans-Coumaroyltyramine36417-86-4
Instructions
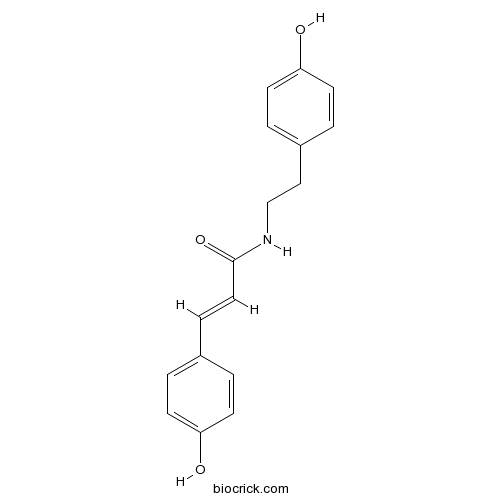
-
BCN5550
Taxifolin480-18-2
Instructions

-
BCN5600
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
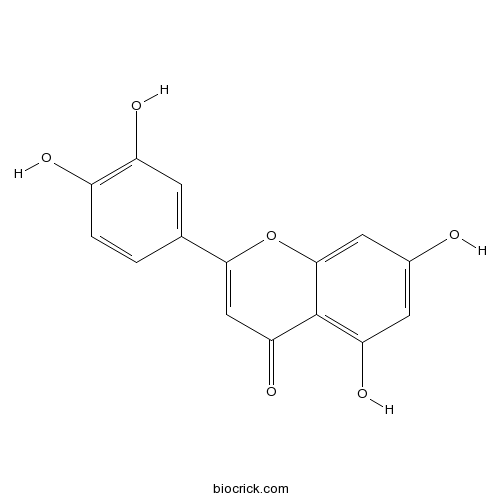
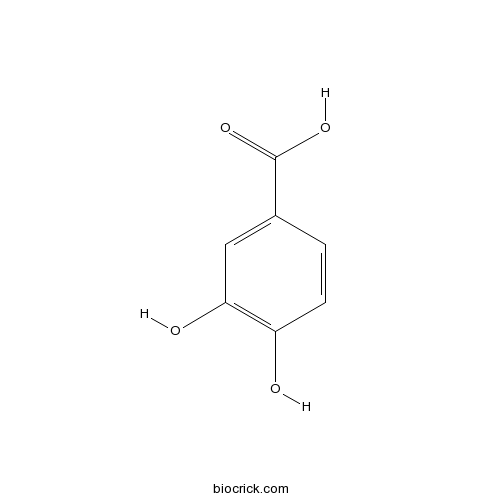
-
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
[Protective effect of Polygonum orientale flower extract on H₂O₂-induced oxidative damage of HUVEC cells].[Pubmed: 29676101]
To investigate the protective effects and mechanism of Polygonum orientale flower extract on H₂O₂-induced oxidative damage of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), H₂O₂ was used to induce the oxidativestress damage on HUVEC cells and efforts were made to screen the low, medium and high drug concentrations of P.orientale flower extract. Cell viability was detected by the MTS assay. The content of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and malondialdehyde (MDA), and the activities of superoxidedimutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were detected by biochemical kits. The mRNA and protein levels of Bax, Bcl-2 were detected respectively by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot. The protein level of cleaved caspase-3 was detected by Western blot. According to the results, the viability of HUVEC cells was reduced to around 55% after being treated with 120 μmol·L⁻¹ H₂O₂ for 0.5 h. Treatment of H₂O₂ also could increase LDH leakage rate and MDA content and attenuate the activities of SOD and CAT, up-regulate the expression level of Bax and cleaved caspase-3, and down-regulate the expression level of Bcl-2. As compared with H₂O₂ model group, P.orientale flower extract of 50-200 mg·L⁻¹ could increase the viability of HUVEC cells, reduce LDH release and MDA content, enhance the activities of SOD and CAT, down-regulate pro-apoptotic protein cleaved caspase-3 and Bax, and up-regulate apoptosis inhibitory protein Bcl-2. In summary, P.orientale flower extract showed a protective effect on H₂O₂-induced HUVEC cells injury, which may result from enhancing the cell capability of clearing the oxygen free radial, decreasing the production of lipid peroxidation and inhibiting apoptosis.
Hepatoprotective effect of the ethanol extract of Polygonum orientale on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice.[Pubmed: 29389576]
None
Identification of Polygonum orientale constituents using high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 29297257]
None
Preparation of Activated Carbon From Polygonum orientale Linn. to Remove the Phenol in Aqueous Solutions.[Pubmed: 27741305]
Phenol components are major industry contaminants of aquatic environment. Among all practical methods for removing phenol substances from polluted water, activated carbon absorption is the most effective way. Here, we have produced low-cost activated carbon using Polygonum orientale Linn, a wide spreading species with large biomass. The phenol adsorption ability of this activated carbon was evaluated at different physico-chemical conditions. Average equilibrium time for adsorption was 120 min. The phenol adsorption ability of the P. orientale activated carbon was increased as the pH increases and reached to the max at pH 9.00. By contrast, the ionic strength had little effect on the phenol absorption. The optimum dose for phenol adsorption by the P. orientale activated carbon was 20.00 g/L. The dominant adsorption mechanism of the P. orientale activated carbon was chemisorption as its phenol adsorption kinetics matched with the pseudo-second-order kinetics. In addition, the equilibrium data were fit to the Langmuir model, with the negative standard free energy and the positive enthalpy, suggesting that adsorption was spontaneous and endothermic.
Orientin protects myocardial cells against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury through induction of autophagy.[Pubmed: 26875637]
Orientin, a flavonoid exists in Chinese traditional herbal Polygonum orientale L., has been previously demonstrated to protect against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury (MIRI) through inhibition of apoptosis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated and we therefore in this study investigated the effects of orientin on autophagy during MIRI in rats. The results indicate that orientin, at the concentrations of 10 and 30 μM in the cultures of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, promoted the induction of autophagy, increasing the formation of autophagosomes and enhancing the expression of LC3 puncta, LC3-II/LC3-I ratio and Beclin 1 after hypoxia/reoxygenation. The induction of autophagy by orientin correlated with enhanced cell viability and decreased apoptosis, which was significantly attenuated by autophagy inhibitor wortmannin, a phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor. Moreover, application of orientin increased the activation of AMPK and Akt, downregulated the phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and the expression of Raptor, and enhanced the interaction between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2 in endoplasmic reticulum due to increased phosphorylation of Beclin 1 and decreased phosphorylation of Bcl-2. Our investigation suggests that the cardioprotective effects of orientin during MIRI may be mediated through the balance of autophagy through regulating AMPK, Akt, mTOR, and Bcl-2 associated signaling pathways.
[Protective Effect of Polygonum orientale Flower Extract with Different Preparation Methods on Acute Myocardial Ischemia in Mongrel Dogs].[Pubmed: 26214879]
To observe the effect of Polygonum orientale flower extract with different preparation methods on acute myocardial ischemia in mongrel dogs.
[Absorption of extractive Polygonum orientale in rat everted gut sacs].[Pubmed: 25272855]
Using in vitro everted gut to investigate the intestinal absorption of the extracts from Polygonum orientale at different concentration. UPLC-MS/MS was used to detect the content of protocatechuic acid, isoorientin, orientin, vitexin, cynaroside, quercitrin, kaempferol-rhamnoside in different intestinal segments, then compared the results with the absorption of chemical components of extractive P. orientale in each intestinal segments, and calculated the absorption parameter. We took the statistic analysis with SPSS statistic software. The influence significance of each factors were analyzed to describe the character of absorption. The absorption of each component is linearity in different intestinal segments and different dose, and the square of coeficient correlation exceed 0.95, which consistent with zero order rate process. The K(a) increase along with the raised dosage of the extractive P. orientale (R2 > 0.95), indicated it is the passive absorption; different intestinal segments have different absorption. And the absorption trend in intestinal is duodenum, jejunum, ileum are greater than the colon. As ingredients are selectively absorbed in intestinal sac, the everted intestinal sac method is selected to assess the intestinal absorption charcteristics of ingredients of extractive P. orientale.
Phytoremediation of phenol using Polygonum orientale, including optimized conditions.[Pubmed: 25208519]
Removing phenol from wastewater has become a major challenge of international concern. Phytoremediation is a novel and eco-friendly method and is attracting an increasing amount of attention for treating phenol in wastewater. We studied the ability of Polygonum orientale, which is frequently present around water bodies and in wetlands in China, to phytoremediate phenol. We determined the inhibition concentration for phenol on P. orientale using emergency toxicology experiments and morphological observations. Isothermal and kinetic models were created to assess the adsorption process involved in phenol removal. Comparison tests in sterile conditions demonstrated that metabolic removal was the main way in which the phenol concentrations were decreased, and removal by adsorption played a smaller role. An orthogonal test was performed to determine the optimum conditions under which P. orientale will remove phenol, and these were found to be an initial phenol concentration of 5 mg L(-1), 100 % natural light, and a 13-day treatment time. These results provide a theoretical basis for increasing our understanding of the mechanisms involved in the removal of phenol by P. orientale and will help in developing its application in the greening of urban areas to provide both phytoremediation and esthetic landscaping.


