p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acidCAS# 7400-08-0 |
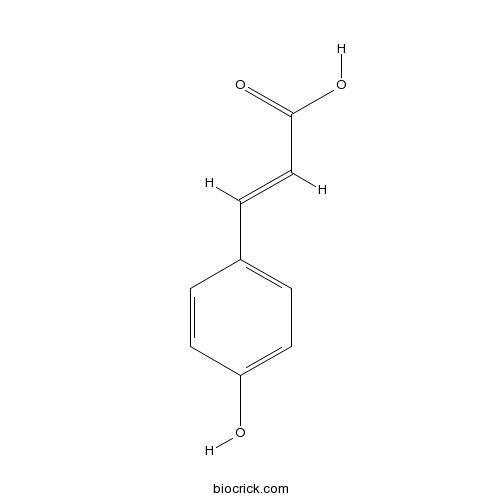
- trans-p-Coumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN0310
CAS No.:501-98-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7400-08-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 637542 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H8O3 | M.Wt | 164.16 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | p-Coumaric acid;4-Hydroxycinnamic Acid;501-98-4;4501-31-9 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (609.16 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGSWKAQJJWESNS-ZZXKWVIFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H8O3/c10-8-4-1-7(2-5-8)3-6-9(11)12/h1-6,10H,(H,11,12)/b6-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid may have in vitro antimalarial activity. p-Hydroxycinnamic acid and β-cryptoxanthin have anti-osteoporotic properties in vivo, they can antagonize NF-κB activation in MC3T3 preosteoblastic cells. Trans-4-hydroxycinnamic acid has antimicrobial, and anti-oxidant activities. |
| Targets | NF-kB | Antifection |
| In vitro | Antimalarial drug interactions of compounds isolated from Kigelia africana (Bignoniaceae) and their synergism with artemether, against the multidrug-resistant W2mef Plasmodium falciparum strain.[Pubmed: 21814840]Parasitol Res. 2012 Feb;110(2):539-44.For decades, drug resistance has been the major obstacle in the fight against malaria, and the search for new drugs together with the combination therapy constitutes the major approach in responding to this situation. Thymofolinoates A and B, new cinnamic acid derivatives from Euphorbia thymifolia.[Pubmed: 23157007]Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Oct;7(10):1351-2.Two new cinnamic acid derivatives, thymofolinoates A (1) and B (2) have been isolated from the chloroform soluble fraction of Euphorbia thymifolia and their structures assigned from 1H and 13C NMR spectra, DEPT and by 2 D COSY, HMQCand H MBC experiments. In addition, p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid(3), 5-hydroxy-6,7,8,4'-tetramethoxy flavone (4), and 5-hydroxy-3',4',6,7,8-pentamethoxy flavone (5) have also been isolated for the first time from this species. Antimicrobial activity of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid isolated and identified from rice hull.[Pubmed: 9972252]Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998 Nov;62(11):2273-6.
In vitro evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Rotula aquatica and Ancistrocladus heyneanus: Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of medicinal plants.[Reference: WebLink]J. Pharm. Res., 2013, 6(2):313-7.In the present study, the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the medicinal plants Rotula aquatica and Ancistrocladus heyneanus were evaluated. |
| In vivo | The bone anabolic carotenoids p-hydroxycinnamic acid and β-cryptoxanthin antagonize NF-κB activation in MC3T3 preosteoblasts.[Pubmed: 21475879]Mol Med Rep. 2009 Jul-Aug;2(4):641-4.The carotene p-hydroxycinnamic acid and the xanthophyll β-cryptoxanthin are members of the carotenoid family of plant-derived pigments, which are endowed with anti-osteoporotic properties in vivo. p-Hydroxycinnamic acid and β-cryptoxanthin have been demonstrated to stimulate osteoblastic bone formation while simultaneously repressing osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. However, their mechanisms of action remain poorly elucidated. It is well established that the NF-;kgr;B signal transduction pathway plays a critical role in osteoclast differentiation. Moreover, we recently demonstrated that NF-κB activity potently antagonizes osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in vitro. |
| Structure Identification | Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Aug;49(8):1150-4.Chemical constituents of lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx.[Pubmed: 25322557]In order to find the cardiotonic constituents of lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., the investigation was carried out. |

p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid Dilution Calculator

p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0916 mL | 30.4581 mL | 60.9162 mL | 121.8324 mL | 152.2904 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2183 mL | 6.0916 mL | 12.1832 mL | 24.3665 mL | 30.4581 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6092 mL | 3.0458 mL | 6.0916 mL | 12.1832 mL | 15.229 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1218 mL | 0.6092 mL | 1.2183 mL | 2.4366 mL | 3.0458 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3046 mL | 0.6092 mL | 1.2183 mL | 1.5229 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Mosloflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6796
CAS No.:740-33-0
- L-Arginine
Catalog No.:BCN2691
CAS No.:74-79-3
- Ethambutol
Catalog No.:BCC5195
CAS No.:74-55-5
- Kamebakaurin
Catalog No.:BCN8040
CAS No.:73981-34-7
- Cilostazol
Catalog No.:BCC2291
CAS No.:73963-72-1
- 7,8-Dimethoxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-3-benzazepin-2-one
Catalog No.:BCC8774
CAS No.:73942-87-7
- Isolimonexic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7141
CAS No.:73904-93-5
- Hispidone
Catalog No.:BCN4293
CAS No.:73891-72-2
- H-His-OMe.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2956
CAS No.:7389-87-9
- Foresaconitine
Catalog No.:BCC8173
CAS No.:73870-35-6
- 3-Amino-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole
Catalog No.:BCC8617
CAS No.:73834-77-2
- Boc-Glu(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3390
CAS No.:73821-97-3
- Enoxacin (Penetrex)
Catalog No.:BCC3775
CAS No.:74011-58-8
- Lancifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN2019
CAS No.:74048-71-8
- Ketanserin
Catalog No.:BCC5050
CAS No.:74050-98-9
- Macamide B
Catalog No.:BCN1366
CAS No.:74058-71-2
- Cudratricusxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7649
CAS No.:740810-42-8
- ACV 1
Catalog No.:BCC5989
CAS No.:740980-24-9
- Ketorolac
Catalog No.:BCC5190
CAS No.:74103-06-3
- Ketorolac tromethamine salt
Catalog No.:BCC4431
CAS No.:74103-07-4
- SKF 83822 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7252
CAS No.:74115-10-9
- Norjuziphine
Catalog No.:BCN3367
CAS No.:74119-87-2
- DSC
Catalog No.:BCC2800
CAS No.:74124-79-1
- Bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN7351
CAS No.:74149-38-5
Antimicrobial activity of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid isolated and identified from rice hull.[Pubmed:9972252]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998 Nov;62(11):2273-6.
Two antimicrobial substances in rice hull were isolated and identified as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid by LC-MS, and 1H- and 13C-NMR. An evaluation of 50% inhibition of growth (IC50) revealed that the two substances had different inhibition profiles against various microorganisms. Most of the gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria were sensitive to trans 4-hydroxycinnamic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid at IC50 concentrations of 100-170 and 160 micrograms/ml, respectively.
Thymofolinoates A and B, new cinnamic acid derivatives from Euphorbia thymifolia.[Pubmed:23157007]
Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Oct;7(10):1351-2.
Two new cinnamic acid derivatives, thymofolinoates A (1) and B (2) have been isolated from the chloroform soluble fraction of Euphorbia thymifolia and their structures assigned from 1H and 13C NMR spectra, DEPT and by 2 D COSY, HMQCand H MBC experiments. In addition, p-hydroxy cinnamic acid(3), 5-hydroxy-6,7,8,4'-tetramethoxy flavone (4), and 5-hydroxy-3',4',6,7,8-pentamethoxy flavone (5) have also been isolated for the first time from this species.
Antimalarial drug interactions of compounds isolated from Kigelia africana (Bignoniaceae) and their synergism with artemether, against the multidrug-resistant W2mef Plasmodium falciparum strain.[Pubmed:21814840]
Parasitol Res. 2012 Feb;110(2):539-44.
For decades, drug resistance has been the major obstacle in the fight against malaria, and the search for new drugs together with the combination therapy constitutes the major approach in responding to this situation. The present study aims at assessing the in vitro antimalarial activity of four compounds isolated from Kigelia africana stem bark (atranorin - KAE1, specicoside - KAE7, 2beta,3beta,19alpha-trihydroxy-urs-12-20-en-28-oic acid - KAE3, and p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid - KAE10) and their drug interactions among themselves and their combination effects with quinine and artemether. The antiplasmodial activity and drug interactions were evaluated against the multidrug-resistant W2mef strain of Plasmodium falciparum using the parasite lactate dehydrogenase assay. Three of the four compounds tested were significantly active against W2mef: specicoside (IC(50) = 1.02 +/- 0.17 muM), 2beta,3beta,19alpha-trihydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid (IC(50) = 1.86 +/- 0.15 muM) and atranorin (IC(50) = 1.78 +/- 0.18 muM), whereas p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid showed a weak activity (IC(50) = 12.89 +/- 0.87 muM). A slight synergistic effect was observed between atranorin and 2beta,3beta,19alpha-trihydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid (Combination index, CI = 0.82) whereas the interaction between specicoside and p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid were instead antagonistic (CI = 2.67). All the three compounds showed synergistic effects with artemether, unlike the slight antagonistic interactions of atranorin and 2beta,3beta,19alpha-trihydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid in combination with quinine. K. africana compounds are therefore likely to serve as leads in the development of new partner drugs in artemether-based combination therapy.
The bone anabolic carotenoids p-hydroxycinnamic acid and beta-cryptoxanthin antagonize NF-kappaB activation in MC3T3 preosteoblasts.[Pubmed:21475879]
Mol Med Rep. 2009 Jul-Aug;2(4):641-4.
The carotene p-hydroxycinnamic acid and the xanthophyll beta-cryptoxanthin are members of the carotenoid family of plant-derived pigments, which are endowed with anti-osteoporotic properties in vivo. p-Hydroxycinnamic acid and beta-cryptoxanthin have been demonstrated to stimulate osteoblastic bone formation while simultaneously repressing osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. However, their mechanisms of action remain poorly elucidated. It is well established that the NF-;kgr;B signal transduction pathway plays a critical role in osteoclast differentiation. Moreover, we recently demonstrated that NF-kappaB activity potently antagonizes osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in vitro. In this study, we used transient transfection assays of a NF-kappaB luciferase reporter to demonstrate that p-hydroxycinnamic acid and beta-cryptoxanthin antagonize NF-kappaB activation in MC3T3 preosteoblastic cells. The data obtained suggest that NF-kappaB may be a common molecular target by which several bone active agents, including carotenoids, promote osteoblastic bone formation.
[Chemical constituents of lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx].[Pubmed:25322557]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Aug;49(8):1150-4.
In order to find the cardiotonic constituents of lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx., the investigation was carried out. Silica gel column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20, medium-pressure MCI and reverse phase ODS column chromatography were used to separate the 90% EtOH extract of the lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. The structures of the isolated compounds have been identified by chemical properties and spectroscopic analyses. Ten compounds were isolated and their structures were elucidated as benzoic acid-5-hydroxy-2-benzoyl-amino methyl ester (1), honokiol (2), pinoresinol (3), salicylic acid (4), p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid (5), songorine (6), karakoline (7), mesaconitine (8), hypaconitine (9) and 14-benzoylhypaconitine (10), separetely. Compound 1 is a new compound and its structure has been established by NMR, HR-ESI-MS, UV, IR and X-Ray. Compound 2-5 are isolated from the lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. for the first time.


