Enoxacin (Penetrex)CAS# 74011-58-8 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- CCT137690
Catalog No.:BCC2188
CAS No.:1095382-05-0
- CYC116
Catalog No.:BCC2181
CAS No.:693228-63-6
- MLN8054
Catalog No.:BCC2170
CAS No.:869363-13-3
- TAK-901
Catalog No.:BCC2180
CAS No.:934541-31-8
- PF-03814735
Catalog No.:BCC2184
CAS No.:942487-16-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 74011-58-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3229 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H17FN4O3 | M.Wt | 320.32 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AT 2266; CI 919 | ||
| Solubility | >18.4mg/mL in DMSO | ||
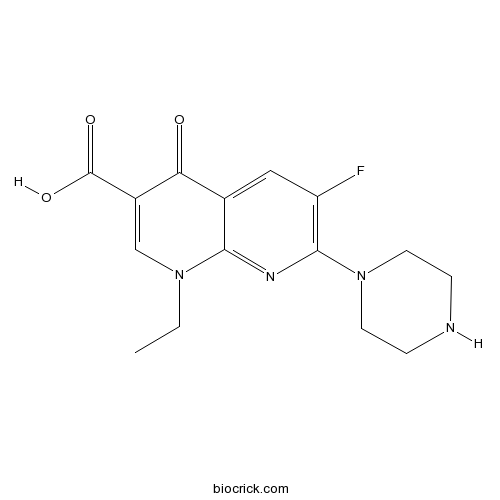
| Chemical Name | 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCN1C=C(C(=O)C2=CC(=C(N=C21)N3CCNCC3)F)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IDYZIJYBMGIQMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H17FN4O3/c1-2-19-8-10(15(22)23)12(21)9-7-11(16)14(18-13(9)19)20-5-3-17-4-6-20/h7-8,17H,2-6H2,1H3,(H,22,23) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Enoxacin is a broad-spectrum 6-fluoronaphthyridinone antibacterial agent.
Target: antibacterial
Enoxacin is a new quinolone carboxylic acid compound. Its activity against 740 bacterial isolates was determined. It inhibited 90% Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., Aeromonas sp., Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Proteus mirabilis, and Morganella morganii at less than or equal to 0.8 micrograms/ml [1]. Daily plasma theophylline concentrations were measured in 14 patients. The mean +/- s.d. theophylline concentrations increased from 8.5 +/- 2.8 micrograms ml-1 prior to enoxacin to a maximum of 21.7 +/- 7.8 micrograms ml-1 during coadministration [2]. References: | |||||

Enoxacin (Penetrex) Dilution Calculator

Enoxacin (Penetrex) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1219 mL | 15.6094 mL | 31.2188 mL | 62.4376 mL | 78.047 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6244 mL | 3.1219 mL | 6.2438 mL | 12.4875 mL | 15.6094 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3122 mL | 1.5609 mL | 3.1219 mL | 6.2438 mL | 7.8047 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6244 mL | 1.2488 mL | 1.5609 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6244 mL | 0.7805 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Enoxacin is a quinolone antibacteral agent. Acts on DNA gyrase.
- p-Hydroxy-cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5027
CAS No.:7400-08-0
- Mosloflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6796
CAS No.:740-33-0
- L-Arginine
Catalog No.:BCN2691
CAS No.:74-79-3
- Ethambutol
Catalog No.:BCC5195
CAS No.:74-55-5
- Kamebakaurin
Catalog No.:BCN8040
CAS No.:73981-34-7
- Cilostazol
Catalog No.:BCC2291
CAS No.:73963-72-1
- 7,8-Dimethoxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-3-benzazepin-2-one
Catalog No.:BCC8774
CAS No.:73942-87-7
- Isolimonexic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7141
CAS No.:73904-93-5
- Hispidone
Catalog No.:BCN4293
CAS No.:73891-72-2
- H-His-OMe.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2956
CAS No.:7389-87-9
- Foresaconitine
Catalog No.:BCC8173
CAS No.:73870-35-6
- 3-Amino-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole
Catalog No.:BCC8617
CAS No.:73834-77-2
- Lancifolin C
Catalog No.:BCN2019
CAS No.:74048-71-8
- Ketanserin
Catalog No.:BCC5050
CAS No.:74050-98-9
- Macamide B
Catalog No.:BCN1366
CAS No.:74058-71-2
- Cudratricusxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCN7649
CAS No.:740810-42-8
- ACV 1
Catalog No.:BCC5989
CAS No.:740980-24-9
- Ketorolac
Catalog No.:BCC5190
CAS No.:74103-06-3
- Ketorolac tromethamine salt
Catalog No.:BCC4431
CAS No.:74103-07-4
- SKF 83822 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7252
CAS No.:74115-10-9
- Norjuziphine
Catalog No.:BCN3367
CAS No.:74119-87-2
- DSC
Catalog No.:BCC2800
CAS No.:74124-79-1
- Bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN7351
CAS No.:74149-38-5
- Pimobendan
Catalog No.:BCC2294
CAS No.:74150-27-9
A small molecule drug promoting miRNA processing induces alternative splicing of MdmX transcript and rescues p53 activity in human cancer cells overexpressing MdmX protein.[Pubmed:28973015]
PLoS One. 2017 Oct 3;12(10):e0185801.
MdmX overexpression contributes to the development of cancer by inhibiting tumor suppressor p53. A switch in the alternative splicing of MdmX transcript, leading to the inclusion of exon 6, has been identified as the primary mechanism responsible for increased MdmX protein levels in human cancers, including melanoma. However, there are no approved drugs, which could translate these new findings into clinical applications. We analyzed the anti-melanoma activity of enoxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic inhibiting the growth of some human cancers in vitro and in vivo by promoting miRNA maturation. We found that enoxacin inhibited the growth and viability of human melanoma cell lines much stronger than a structurally related fluoroquinolone ofloxacin, which only weakly modulates miRNA processing. A microarray analysis identified a set of miRNAs significantly dysregulated in enoxacin-treated A375 melanoma cells. They had the potential to target multiple signaling pathways required for cancer cell growth, among them the RNA splicing. Recent studies showed that interfering with cellular splicing machinery can result in MdmX downregulation in cancer cells. We, therefore, hypothesized that enoxacin could, by modulating miRNAs targeting splicing machinery, activate p53 in melanoma cells overexpressing MdmX. We found that enoxacin and ciprofloxacin, a related fluoroquinolone capable of promoting microRNA processing, but not ofloxacin, strongly activated wild type p53-dependent transcription in A375 melanoma without causing significant DNA damage. On the molecular level, the drugs promoted MdmX exon 6 skipping, leading to a dose-dependent downregulation of MdmX. Not only in melanoma, but also in MCF7 breast carcinoma and A2780 ovarian carcinoma cells overexpressing MdmX. Together, our results suggest that some clinically approved fluoroquinolones could potentially be repurposed as activators of p53 tumor suppressor in cancers overexpressing MdmX oncoprotein and that p53 activation might contribute to the previously reported activity of enoxacin towards human cancer cells.
Cultivation in Space Flight Produces Minimal Alterations in the Susceptibility of Bacillus subtilis Cells to 72 Different Antibiotics and Growth-Inhibiting Compounds.[Pubmed:28821547]
Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Oct 17;83(21). pii: AEM.01584-17.
Past results have suggested that bacterial antibiotic susceptibility is altered during space flight. To test this notion, Bacillus subtilis cells were cultivated in matched hardware, medium, and environmental conditions either in space flight microgravity on the International Space Station, termed flight (FL) samples, or at Earth-normal gravity, termed ground control (GC) samples. The susceptibility of FL and GC samples was compared to 72 antibiotics and growth-inhibitory compounds using the Omnilog phenotype microarray (PM) system. Only 9 compounds were identified by PM screening as exhibiting significant differences (P < 0.05, Student's t test) in FL versus GC samples: 6-mercaptopurine, cesium chloride, enoxacin, lomefloxacin, manganese(II) chloride, nalidixic acid, penimepicycline, rolitetracycline, and trifluoperazine. Testing of the same compounds by standard broth dilution assay did not reveal statistically significant differences in the 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) between FL and GC samples. The results indicate that the susceptibility of B. subtilis cells to a wide range of antibiotics and growth inhibitors is not dramatically altered by space flight.IMPORTANCE This study addresses a major concern of mission planners for human space flight, that bacteria accompanying astronauts on long-duration missions might develop a higher level of resistance to antibiotics due to exposure to the space flight environment. The results of this study do not support that notion.
Determination of fluoroquinolones in fish tissues, biological fluids, and environmental waters by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:28852783]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017 Nov;409(27):6359-6370.
This work describes the optimization, validation, and application in real samples of accurate and precise analytical methods to determine ten fluoroquinolones (FQs) (norfloxacin, enoxacin, pefloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, danofloxacin, lomefloxacin, enrofloxacin, and sparfloxacin) in different environmental matrices, such as water (estuarine, seawater, and wastewater treatment plant effluent), fish tissues (muscle and liver), and fish biofluids (plasma and bile). The analysis step performed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was fully optimized to improve the separation and detection steps. The extraction of analytes from fish tissues was accomplished using focused ultrasound solid-liquid extraction using methanol/acetic acid (95:5 v/v) as extractant. The preconcentration and clean-up steps were optimized in terms of extraction efficiency and cleanliness and the best strategy for each matrix was selected: (i) Oasis HLB for seawater and muscle, (ii) liquid-liquid extraction combined with Oasis HLB for the lipid-rich liver, (iii) the combination of Evolute-WAX and Oasis HLB for estuarine water and wastewater treatment plant effluent, and (iv) molecular imprinted polymers for biofluids. The methods afforded satisfactory apparent recoveries (80-126%) and repeatability (RSD < 15%), except for sparfloxacin, which showed a lack of correction with the available isotopically labeled surrogates ([(2)H8]-ciprofloxacin and [(2)H5]-enrofloxacin). Ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin were detected in both water and fish liver samples from the Biscay Coast at concentrations up to 278 ng/L and 4 ng/g, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this work is one of the few analyzing up to ten FQs and in so many fish tissues and biofluids. Graphical abstract Determination of fluoroquinolones in different environmental matrices, such as water (estuarine, seawater, and wastewater treatment plant effluent), fish tissues (muscle and liver), and fish biofluids (plasma and bile).
The Beneficial Effects of Bisphosphonate-enoxacin on Cortical Bone Mass and Strength in Ovariectomized Rats.[Pubmed:28638344]
Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 7;8:355.
Osteoporosis is a major age-related bone disease characterized by low bone mineral density and a high risk of fractures. Bisphosphonates are considered as effective agents treating osteoporosis. However, long-term use of bisphosphonates is associated with some serious side effects, which limits the widespread clinical use of bisphosphonates. Here, we demonstrate a novel type of bone-targeting anti-resorptive agent, bisphosphonate-enoxacin (BE). In this study, ovariectomized rat model was established and treated with PBS, zoledronate (50 mug/kg) and different dose of BE (5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg), respectively. The rats subjected to sham-operation and PBS treatment were considered as control group. Then, micro-computed tomography scanning, biomechanical tests, nano-indentation test and Raman analysis were used to compare the effects of zoledronate and BE on cortical bone mass, strength, and composition in ovariectomized rats. We found that both zoledronate and BE were beneficial to cortical bone strength. Three-point bending and nano-indentation tests showed that zoledronate- and BE-treated groups had superior general and local biomechanical properties compared to the ovariectomized groups. Interestingly, it seemed that BE-treated group got a better biomechanical property than the zoledronate-treated group. Also, BE-treated group showed significantly increased proteoglycan content compared with the zoledronate-treated group. We hypothesized that the increased bone strength and biomechanical properties was due to altered bone composition after treatment with BE. BE, a new bone-targeting agent, may be considered a more suitable anti-resorptive agent to treat osteoporosis and other bone diseases associated with decreased bone mass.
High-performance liquid chromatography with time-programmed fluorescence detection for the quantification of Levofloxacin in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in adults with tuberculous meningitis.[Pubmed:28756357]
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Sep 1;1061-1062:256-262.
An accurate and reliable high-performance liquid chromatography with time-programmed fluorescence detection was developed and validated to measure levofloxacin in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). After solid phase extraction process using Evolute((R)) ABN 96 fixed well plate; levofloxacin and internal standard-enoxacin were separated using a mobile phase consisting of phosphate buffer 10mM with 0.025% triethylamine pH 3.0 - acetonitrile (88:12, v/v) on a Purosphere RP-8e column (5mum, 125x4.0mm) at a flow rate of 1.2mL/min at 35 degrees C. The excitation/emission wavelengths were set to 269/400nm and 294/500nm, for enoxacin and levofloxacin, respectively. The method was linear over the concentration range of 0.02 to 20.0mug/mL with a limit of detection of 0.01mug/mL. The relative standard deviation of intra-assay and inter-assay precision for levofloxacin at four quality controls concentrations (0.02, 0.06, 3.0 and 15.0mug/mL) were less than 7% and the accuracies ranged from 96.75% to 101.9% in plasma, and from 93.00% to 98.67% in CSF. The validated method was successfully applied to quantify levofloxacin in a considerable quantity of plasma (826) and CSF (477) samples collected from 232 tuberculous meningitis patients, and the preliminary intensive pharmacokinetics analysis from 14 tuberculous meningitis patients in Vietnam is described in this paper.


