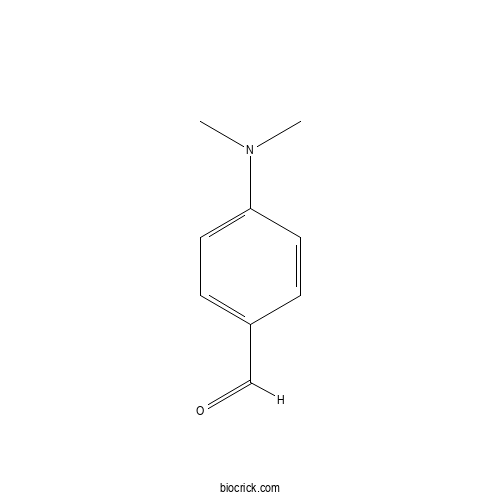
4-DimethylaminobenzaldehydeCAS# 100-10-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 100-10-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 7479.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H11NO | M.Wt | 149.19 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BGNGWHSBYQYVRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H11NO/c1-10(2)9-5-3-8(7-11)4-6-9/h3-7H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde Dilution Calculator

4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.7029 mL | 33.5143 mL | 67.0286 mL | 134.0572 mL | 167.5716 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3406 mL | 6.7029 mL | 13.4057 mL | 26.8114 mL | 33.5143 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6703 mL | 3.3514 mL | 6.7029 mL | 13.4057 mL | 16.7572 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1341 mL | 0.6703 mL | 1.3406 mL | 2.6811 mL | 3.3514 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.067 mL | 0.3351 mL | 0.6703 mL | 1.3406 mL | 1.6757 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cinnamylacetate
Catalog No.:BCX0918
CAS No.:103-54-8
- 8-Methoxyquinoline-2-carbaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0917
CAS No.:103854-64-4
- PALATINOSE
Catalog No.:BCX0916
CAS No.:13718-94-0
- Chlorine6
Catalog No.:BCX0915
CAS No.:19660-77-6
- Climbazole
Catalog No.:BCX0914
CAS No.:38083-17-9
- Oxysophoridine
Catalog No.:BCX0913
CAS No.:54809-74-4
- Graniline
Catalog No.:BCX0912
CAS No.:40737-97-1
- Dehydrocostuslactone
Catalog No.:BCX0911
CAS No.:74299-48-2
- Sodiumnewhouttuyfonate
Catalog No.:BCX0910
CAS No.:83766-73-8
- Isomaltotriose
Catalog No.:BCX0909
CAS No.:3371-50-4
- Fructo-oligosaccharideDP8/GF7
Catalog No.:BCX0908
CAS No.:62512-21-4
- 1-Kestoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX0907
CAS No.:62512-20-3
- SalicylaldehydeAzine
Catalog No.:BCX0920
CAS No.:959-36-4
- VanillylButylEther
Catalog No.:BCX0921
CAS No.:82654-98-6
- D-Pyroglutamicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0922
CAS No.:4042-36-8
- BoeravinoneA
Catalog No.:BCX0923
CAS No.:114567-33-8
- Pseudojervine
Catalog No.:BCX0924
CAS No.:36069-05-3
- MogrosideIIA
Catalog No.:BCX0925
CAS No.:1613527-65-3
- 14-Deoxy-11-oxoandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCX0926
CAS No.:42895-57-8
- Hydroxyisogermafurenolide
Catalog No.:BCX0927
CAS No.:20267-91-8
- (+)-Pinoresinolmonomethylether4-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0928
CAS No.:74957-57-6
- 3-(3-hydroxylphenyl)propanol
Catalog No.:BCX0929
CAS No.:621-54-5
- PhysalinF
Catalog No.:BCX0930
CAS No.:57517-46-1
- Cepharanoline
Catalog No.:BCX0931
CAS No.:27686-34-6
In-Source Decay MALDI and High-Energy Collision-Induced Dissociation Mass Spectrometry of Alkali Metal-Adducted Underivatized Oligosaccharides.[Pubmed:37812625]
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2023 Nov 1;34(11):2594-2606.
In-source decay (ISD) and high-energy collision-induced dissociation (HE-CID) were explored to provide structural information on alkali metal-adducted linear and stacked oligosaccharides (oligosaccharides with increased flexibility due to linkage type). These oligosaccharides include isomeric tetrasaccharides, maltoheptaose, and several human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs). Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) ion production efficiency, as well as the product ion intensities, and the number of product ions formed in ISD and HE-CID of these oligosaccharides were influenced by the matrix, the ionic radius of the metal ion used for adduction, and the affinity of metal ions for specific functional groups in the oligosaccharides. 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone (THAP) was the best matrix for HE-CID of oligosaccharides, 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMABA) worked best for ISD of tetrasaccharides and pentasaccharides, while 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) was the best matrix for ISD and HE-CID of long chain oligosaccharides. In general, the number of product ions formed followed the trend Li(+) > Na(+) > K(+) > Rb(+) > Cs(+), except for HMOs where Na(+) >/= Li(+) > K(+) > Rb(+) > Cs(+) occurred. The type of product ions formed and their intensities varied based on the position of the glycosidic bond linkage and the content of the monosaccharide. ISD and HE-CID produced diagnostic ions that could structurally differentiate isomers. Overall, HE-CID of alkali-metal adducted oligosaccharides produces intense glycosidic bond cleavages and low intensity cross-ring and internal cleavages. In contrast, ISD generates mainly cross-ring cleavages and internal cleavages at intensities higher than in HE-CID. In addition, ISD produced unique product ions that complement results from HE-CID.
Paper-based analytical device for sensitive colorimetric determination of sulfonamides in pharmaceutical samples.[Pubmed:37683435]
Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2024 Jan 5;304:123336.
Sulfa drugs are frequently used to treat infections, particularly in antibiotic resistant people. There are several techniques available to determine sulfa drugs, however, they are laborious operation, reagent consumption, expensive, and need specialized types of equipment. Here, a new, very simple and inexpensive paper-based analytical device described for the determination of five sulfa drugs: sulfacetamide, sulfadiazine, sulfamerazine, sulfamethoxazole, and sulfathiazole in pharmaceutical preparations. The method is a one-step reaction, based on the colorimetric reaction between acid-hydrolyzed sulfa drugs and 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde. Using a smartphone, the RGB value of color intensity was used as an analytical signal. The paper-based device displayed linear ranges of 0.10-5.00 microg mL(-1), linear correlations ranging from 0.9903 to 0.9972, limits of detection 0.0030 to 0.0082 microg mL(-1), and RSD of
Development of a Sensitive and Selective Method for the Determination of some Selected Aldehydes Based on Fluorescence Quenching.[Pubmed:37010648]
J Fluoresc. 2023 Nov;33(6):2253-2256.
Phenanthrene fluorescence quenching in anionic micellar system of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) was explored for the development of a sensitive and selective method for a group of selected aldehydes (2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde, 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde, 4-aminobenzaldehyde, 4-nitrobenzaldehyde, 2-chlorobenzaldehyde, benzaldehyde and 2-methoxybenzaldehyde). Experiments were performed in 0.02 mol L(- 1) SDS. All the studied aldehydes quenched the fluorescence intensity of the probe (phenanthrene). Stern-Volmer equation was useful in explaining the phenanthrene quenching by the studied aldehydes. Stern-Volmer constants ([Formula: see text]) were obtained as a result of using the Stern-Volmer equation that gives the information in respect of sensitivity of the method for the studied aldehydes. Greater the [Formula: see text] higher will be the sensitivity and vice versa. [Formula: see text], detection limit (DL) and quantification limit (QL) were observed in the order 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde > 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde > 4-aminobenzaldehyde > 4-nitrobenzaldehyde > 2-chlorobenzaldehyde > benzaldehyde > 2-methoxybenzaldehyde. Phenanthrene fluorescence quenching by the studied aldehydes is useful for their determination in environmental samples.
Interaction of Copper(II) Complexes of Bidentate Benzaldehyde Nicotinic Acid Hydrazones with BSA: Spectrofluorimetric and Molecular Docking Approach.[Pubmed:37005622]
Acta Chim Slov. 2023 Mar 20;70(1):74-85.
Two copper(II) complexes of 4-chloro- and 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde nicotinic acid hydrazones were prepared and characterized by elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, infrared and electron spectroscopy and conductometry. These rare examples of bis(hydrazonato)copper(II) complexes are neutral complex species with copper(II) center coordinated with two monoanionic bidentate O,N-donor hydrazone ligands coordinated in enol-imine form. The interaction of hydrazone ligands and corresponding copper(II) complexes with CT DNA and BSA was investigated. Copper(II) complexes are slightly effective in binding the DNA than pristine hydrazones. The results indicate groove binding or moderate intercalation which are not significantly affected by the nature of substituent at hydrazone ligands. On contrary, affinities of two copper(II) complexes toward BSA significantly differs and depends on the nature of the substituent, however in absence of thermodynamic data difference in nature of binding forces cannot be excluded. The complex bearing electron-withdrawing 4-chloro substituent has larger affinity toward BSA compared to 4-dimethyamino analogue. These findings were theoretically supported by molecular docking study.
Nanorod-like Structure of ZnO Nanoparticles and Zn(8)O(8) Clusters Using 4-Dimethylamino Benzaldehyde Liquid to Study the Physicochemical and Antimicrobial Properties of Pathogenic Bacteria.[Pubmed:36616076]
Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;13(1):166.
To study their physicochemical and antimicrobial properties, zinc oxide nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple chemical route and 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (4DB) as an organic additive. ZnO nanoparticles were characterized with XRD analysis, which confirmed the presence of a hexagonal wurtzite structure with different crystalline sizes. The SEM morphology of the synthesized nanoparticles confirmed the presence of nanorods in both modifications of ZnO nanoparticles. EDS analysis proved the chemical composition of the synthesized samples via different chemical approaches. In addition, the optical absorption results indicated that the use of 4DB increased the band gap energy of the synthesized nanoparticles. The synthesized Zn(8)O(8) and Zn(8)O(8):4DB clusters were subjected to HOMO-LUMO analysis, and their ionization energy (I), electron affinity (A), global hardness (eta), chemical potential (sigma), global electrophilicity index (omega), dipole moment (mu), polarizability (alpha(tot)), first-order hyperpolarizability (beta(tot)), and other thermodynamic properties were determined. Furthermore, the antimicrobial properties of the ZnO nanoparticles were studied against G+ (S. aureus and B. subtilis) and G- (K. pneumoniae and E. coli) bacteria in a nutrient agar according to guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
Synthesis of new flavonoid derivatives based on 3-hydroxy-4'-dimethylamino flavone and study the activity of some of them as antifungal.[Pubmed:36561670]
Heliyon. 2022 Dec 5;8(12):e12062.
Chalcone was prepared in a new route by reacting o-hydroxyacetophenone with 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde using piperidine as a catalyst. 3-Hydroxy-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl] benzopyran-4-one were prepared by Algar-Flynn-Oyamada method by cyclization of chalcone using Hydrogen peroxide. A series of alkyl and ester derivatives of the flavonoid 3-hydroxy-2-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl] benzopyran-4-one were prepared by reacting the above mentioned compound with different chemical reagents (Methyl iodide, Allyl bromide, Benzyl chloride, Bromoacetylcoumarin, Chloroacetamide, Chloroacetyl chloride, Phthalic anhydride, Maleic anhydride, Phthalimide, Cinnamoyl chloride) with potassium carbonate and acetone or DMF as a solvent. The physical and spectroscopic properties of the new compounds were studied by (FT-IR, (13)C-NMR and (1)H-NMR) spectral methods. The purity of the synthesized compounds were confirmed using TLC thin layer chromatography. The biological activity of some synthetic flavonoids (A(2), A(5), A(7), A(8), A(9), A(12)) at two different concentrations (0.5 mg/ml, 0.25 mg/ml) were studied on three types of fungi: Aspergillus flavus, Acremonium strictum, Penicillium expansum. Some of this compounds showed high activity against the tested fungi.
Genetically engineered bacterium-modified magnetic particles assisted chiral recognition and colorimetric determination of D/L-tryptophan in millets.[Pubmed:36495743]
Food Chem. 2023 May 1;407:135125.
Chiral recognition of enantiomers has always been a thorny issue since they exhibit the same properties under an achiral environment. Herein, polydopamine-functionalized magnetic particles (MP@PDA) were synthesized to immobilize the genetically engineered bacterium Escherichia coli DH5alpha (MP@PDA-E. coli). L-tryptophan (Trp) instead of D-Trp can be stereo-specifically degraded by tryptophanase in E. coli. The degradation product indole reacts with 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde to generate a rose-red adduct. Thus, MP@PDA-E. coli was employed to fabricate a chiral colorimetric method for chiral recognition and determination of L-Trp. The method averts the purification of tryptophanase. More importantly, tryptophanase demonstrates excellent enantioselective ability for L-Trp. The method can not only quantitatively detect L-Trp but also realize the measurement of the enantiomer percentage in the enantiomeric mixture. The feasibility was verified by detecting L-Trp in millet samples from different origins. Furthermore, a portable device was fabricated to make the method more convenient.
Synthesis, Structures, and Antibacterial Activities of Hydrazone Compounds Derived from 4-Dimethylaminobenzohydrazide.[Pubmed:34897529]
Acta Chim Slov. 2021 Sep;68(3):567-574.
A series of three new hydrazone compounds derived from the condensation reactions of 4-dimethylaminobenzohydrazide with 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzaldehyde and 3-methoxybenzaldehyde, respectively, were prepared. The compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, infrared and UV-vis spectra, HRMS, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra, and single crystal X-ray diffraction. Crystals of the compounds are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The compounds were assayed for antibacterial (Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence and Staphylococcus aureus) and antifungal (Aspergillus niger and Candida albicans) activities by MTT method. The results indicated that compound 2 is an effective antibacterial material.
Synthesis, In Silico Prediction and In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity, DFT Calculation and Theoretical Investigation of Novel Xanthines and Uracil Containing Imidazolone Derivatives.[Pubmed:34681643]
Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 12;22(20):10979.
Novel xanthine and imidazolone derivatives were synthesized based on oxazolone derivatives 2a-c as a key intermediate. The corresponding xanthine 3-5 and imidazolone derivatives 6-13 were obtained via reaction of oxazolone derivative 2a-c with 5,6-diaminouracils 1a-e under various conditions. Xanthine compounds 3-5 were obtained by cyclocondensation of 5,6-diaminouracils 1a-c with different oxazolones in glacial acetic acid. Moreover, 5,6-diaminouracils 1a-e were reacted with oxazolones 2a-c in presence of drops of acetic acid under fused condition yielding the imidazolone derivatives 6-13. Furthermore, Schiff base of compounds 14-16 were obtained by condensing 5,6-diaminouracils 1a,b,e with 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde in acetic acid. The structural identity of the resulting compounds was resolved by IR, (1)H-, (13)C-NMR and Mass spectral analyses. The novel synthesized compounds were screened for their antifungal and antibacterial activities. Compounds 3, 6, 13 and 16 displayed the highest activity against Escherichia coli as revealed from the IC(50) values (1.8-1.9 microg/mL). The compound 16 displayed a significant antifungal activity against Candia albicans (0.82 microg/mL), Aspergillus flavus (1.2 microg/mL) comparing to authentic antibiotics. From the TEM microgram, the compounds 3, 12, 13 and 16 exhibited a strong deformation to the cellular entities, by interfering with the cell membrane components, causing cytosol leakage, cellular shrinkage and irregularity to the cell shape. In addition, docking study for the most promising antimicrobial tested compounds depicted high binding affinity against acyl carrier protein domain from a fungal type I polyketide synthase (ACP), and Baumannii penicillin- binding protein (PBP). Moreover, compound 12 showed high drug- likeness, and excellent pharmacokinetics, which needs to be in focus for further antimicrobial drug development. The most promising antimicrobial compounds underwent theoretical investigation using DFT calculation.
Effect of Ultraviolet Irradiation on Polystyrene Containing Cephalexin Schiff Bases.[Pubmed:34503022]
Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 2;13(17):2982.
The scale of production of polystyrene has escalated in the recent past in order to meet growing demand. As a result, a large quantity of polystyrene waste continues to be generated along with associated health and environmental problems. One way to tackle such problems is to lengthen the lifetime of polystyrene, especially for outdoor applications. Our approach is the synthesis and application of new ultraviolet photostabilizers for polystyrene and this research is focused on four cephalexin Schiff bases. The reaction of cephalexin and 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde, 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, 4-methoxybenzaldehyde, and 4-bromobanzaldehyde under acidic condition afforded the corresponding Schiff bases in high yields. The Schiff bases were characterized and their surfaces were examined. The Schiff bases were mixed with polystyrene to form homogenous blends and their effectiveness as photostabilizers was explored using different methods. The methods included monitoring the changes in the infrared spectra, weight loss, depression in molecular weight, and surface morphology on irradiation. In the presence of the Schiff bases, the formation of carbonyl group fragments, weight loss, and decrease in molecular weight of polystyrene were lower when compared with pure polystyrene. In addition, undesirable changes in the surface such as the appearance of dark spots, cracks, and roughness were minimal for irradiated polystyrene containing cephalexin Schiff bases. Mechanisms by which cephalexin Schiff bases stabilize polystyrene against photodegradation have also been suggested.
New suitable deprotonating matrices for the analysis of carboxylic acids and some acidic compounds by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry in negative ion mode.[Pubmed:32979299]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan 15;35(1):e8954.
RATIONALE: Direct non-derivatization analysis of organic acids and acidic compounds by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry (MS) in positive ion mode is not always possible due to the low ionization efficiency of analytes. Some new efficient deprotonating matrices were suggested that allowed the production of negative ions from acidic compounds during MALDI-MS experiments. METHODS: Various tested carboxyl-containing compounds as well as compounds with acidic properties were mixed with the suggested deprotonating matrices [4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMABA), N,N-dimethylamino-p-phenylenediamine or 3-aminoquinoline] and applied on a standard MALDI target followed by recording MALDI mass spectra in negative ion mode. RESULTS: All the tested acidic compounds mixed with the suggested deprotonating matrices produced abundant [M - H](-) ions under MALDI conditions. DMABA produced the strongest signals reflecting greater sensitivity of analysis. CONCLUSIONS: The suggested deprotonating matrices are commercially available compounds and are good alternatives to well-known matrices of this kind and, in particular, the often used 9-aminoacridine. DMABA is the best of the tested potential matrices and is suitable for the detection of low molecular weight carboxyl-containing compounds, substituted phenols, and mixtures of naphthenic acids by (-)MALDI-MS.
Synthesis and Biological Activities of Some New Benzotriazinone Derivatives Based on Molecular Docking; Promising HepG2 Liver Carcinoma Inhibitors.[Pubmed:32258913]
ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 19;5(12):6781-6791.
In one-pot strategy, diazotization of methyl anthranilate 5 followed by addition of amino acid ester hydrochloride, we have prepared methyl-2-(4-oxobenzotriazin-3(4H)-yl)alkanoates 6a-c. Starting with hydrazides 7a,b, N-alkyl-2-(4-oxobenzotriazin-3(4H)-yl)alkanamides 9-10(a-h) and methyl-2-(2-(4-oxobenzotriazin-3(4H)-yl)alkanamido)alkanoates 11-12(a-e) were prepared via azide coupling. Hydrazones 13-15 were prepared via condensation of hydrazides 7a,b with 4-methoxybenzaldehyde, 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, and/or arabinose. Molecular docking was done for synthesized compounds using MOE 2008-10 software. The compounds 9a, 12a, 12c, 13a, 13b, and 14b have the most pronounced strong binding affinities toward the target E. coli Fab-H receptor, whereas compounds 3, 11e, 12e, and 13a have the most pronounced strong binding affinities toward the target vitamin D receptor. The in vitro antibacterial activities of the highest binding affinity docked compounds were tested against E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella spp. Majority of the tested compounds showed effective positive results against E. coli, while they were almost inactive against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella spp . The in vitro cytotoxic activities of the highest binding affinity-docked compounds were tested against the human liver carcinoma cell line (HepG2). Some compounds showed potent cytotoxic activity with low IC(50) values, especially for 3 (6.525 muM) and 13a (10.97 muM) than that for standard drug doxorubicin (2.06 muM).
A long lasting sunscreen controversy of 4-aminobenzoic acid and 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde derivatives resolved by ultrafast spectroscopy combined with density functional theoretical study.[Pubmed:32239002]
Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2020 Apr 15;22(15):8006-8020.
4-Aminobenzoic acid (PABA) is one of the earliest patented and most commonly used sunscreen components. There is however a long-lasting controversy on its photo-protective efficacy owing to the lack of information on its protolytic equilibrium and photo-dynamics after absorption of ultraviolet radiation in physiologically relevant aqueous solution. The excitation dynamics in water also remains largely unknown for analogs of PABA such as 4-dimethylaminoacetophenone (DMAAP) and 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMABA) which are recognized as prototypes for photo-induced twisted intramolecular charge transfer (TICT). Herein we report a combined application of femtosecond broadband time-resolved fluorescence and transient absorption coupled with density functional theoretical study for PABA, DMAAP, and DMABA under several solvent conditions with representative properties in terms of the pH, polarity and hydrogen bonding capacity. The results we gained demonstrate that, in a neutral aqueous solution, PABA taking the deprotonated anion form in the ground state undergoes rapid protonation after excitation, producing excited state species in the neutral form that may shift effectively by intersystem crossing (ISC) to the long-lasting triplet state capable of damaging nucleic acids. This provides evidence at the molecular level for the detrimental effect of PABA if used as a sunscreen ingredient. In contrast, our investigation on DMAAP and DMABA unveils an unusual solvent controlled deactivation dynamics rendered by the participation of the carbonyl oxygen associated nOpi* state featuring energy and structure strongly responsive to solvent properties. In particular, these molecules in water exhibit solute-solvent hydrogen bonding at the sites of the carbonyl oxygen and the amino nitrogen which is, respectively, weakened and strengthened after the excitation, leading to state reversal and formation of a nOpi* state with a peculiar non-planar structure. This quenches strongly the excitation, eliminates the TICT, suppresses the ISC and opens up the otherwise inaccessible internal conversion (IC) to account for approximately 80% of the entire deactivation. The IC, observed to proceed at a rate of approximately 2.5 ps, allows the effective recovery of the ground state, providing substantial protection against ultraviolet irradiation. Moreover, the revelation of highly solvent sensitive fluorescence emission from DMABA and DMAAP implies the potential application of these molecules as the functional element in the design of sensory materials for probing the polarity and hydrogen bonding character of the surrounding environment.
Preparation, physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial activities of novel two phenolic chitosan Schiff base derivatives.[Pubmed:30061725]
Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 30;8(1):11416.
This study intends to develop novel two antimicrobial phenolic chitosan Schiff bases (I) and (II) via coupling of chitosan with Indole-3-carboxaldehyde and 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, respectively, for boosting the antimicrobial activity of native chitosan. The alterations in the chemical structure and morphology of the Schiff bases were verified using FT-IR, electronic spectrum analysis, and SEM, whereas the thermal properties were investigated by TGA and DSC instruments. The results obtained from the potentiometric analysis referred that the degrees of substitution were 1.15 and 12.05% for Schiff bases (I) and (II), respectively. The antimicrobial activities of Schiff base (I) were significantly augmented more than Schiff base (II) and chitosan. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Schiff base (I) was perceived at 50 microg/ml against tested microorganisms except for B. cereus and C. albicans. The highest concentration of Schiff base (I) could inhibit the growth of Gram-positive up to 99%. However, Schiff base (II) recorded the maximum inhibition rate versus Gram-positive approximately 82%. The cytotoxicity of the developed materials was estimated by MTT assay that substantiated their safety to fibroblast cells. The findings emphasized that the developed Schiff bases might be implemented as antimicrobial contenders to pure chitosan for treatments of wound infections.
Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, Thermal and Optical Studies of Novel Complexes: 4-(Dimethylamino)benzylidene-4-acetamideaniline and 4-(Dimethylamino)benzylidene-4-nitroaniline.[Pubmed:28849303]
J Fluoresc. 2017 Nov;27(6):2263-2277.
The phase diagram representing solid-liquid equilibrium of entire range of composition and thermodynamic studies of two binary organic systems of 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (DMAB) with two NLO active compounds, p-aminoacetanilide (PAA) and p-nitroaniline (PNA), have been studied by solid state synthetic route. Both systems are independently forming a new entity called intermolecular complex (IMC) and two eutectics on either side of intermolecular complexes. The various thermodynamic parameters such as heat of mixing, entropy of fusion, roughness parameter, interfacial energy and excess thermodynamic functions of IMCs and eutectics were calculated using the heat of fusion values. The TGA and DTA studies were performed to understand the physico-chemical, thermal behavior and unique identity of newly synthesized organic complexes, 4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene-4-acetamideaniline (DMABPAA) and 4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene-4-nitroaniline (DMABPNA), and their respective enthalpy of fusion values were found to be 30.01 and 37.26 kJ mol(- 1). The higher melting point of both the novel complexes than their parent's compounds reveal the strong molecular interaction between parent components to yield the complex. The FTIR spectral analysis predicts the disappearance of aldehyde peaks of DMAB and NH(2) peaks of PAA and PNA while the appearance of entirely new peaks than that of parent's compounds are the supportive for the formation of new molecular entities. These findings are further supported by FTNMR spectrum studies by observation of disappearance of proton peak of aldehyde of DMAB and amine peaks of PAA and PNA rather formation of new imine proton peak or peaks were observed. The appearance of new peaks in Powder XRD of complexes than those of parent components is further indicative for the formation of complexes. The absorption spectrum of DMABPAA and DMABPNA showed intra-molecular charge-transfer (ICT) excited state absorption at 258 and 241 nm, respectively. Both the IMCs, DMABPAA and DMABPNA, show strong fluorescence with quantum yield 0.66 and 0.93, respectively, in methanol solution.


