4-O-beta-Glucopyranosyl-cis-coumaric acidCAS# 117405-48-8 |
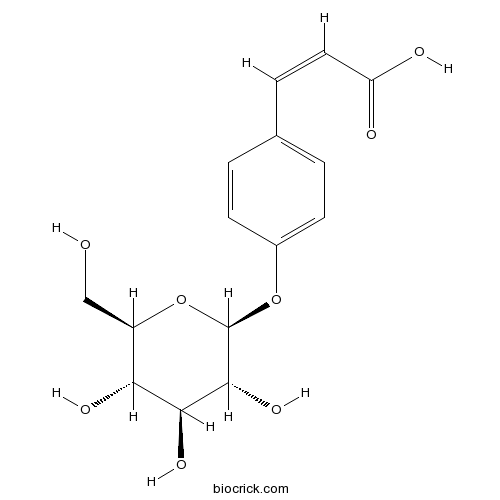
- trans-p-Coumaric acid 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1068
CAS No.:117405-49-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 117405-48-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10604651 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H18O8 | M.Wt | 326.29 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (Z)-3-[4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]prop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)O)OC2C(C(C(C(O2)CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LJFYQZQUAULRDF-LSSWKVNRSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Structure Identification | Food Chemistry, 2002, 76(2):207-212.Polymeric fractions containing phenol glucosides in flaxseed.[Reference: WebLink]
|

4-O-beta-Glucopyranosyl-cis-coumaric acid Dilution Calculator

4-O-beta-Glucopyranosyl-cis-coumaric acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0648 mL | 15.3238 mL | 30.6476 mL | 61.2952 mL | 76.619 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.613 mL | 3.0648 mL | 6.1295 mL | 12.259 mL | 15.3238 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3065 mL | 1.5324 mL | 3.0648 mL | 6.1295 mL | 7.6619 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3065 mL | 0.613 mL | 1.2259 mL | 1.5324 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1532 mL | 0.3065 mL | 0.613 mL | 0.7662 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- AZD2461
Catalog No.:BCC2214
CAS No.:1174043-16-3
- Dimethylwulignan A1
Catalog No.:BCN3624
CAS No.:117404-43-0
- Artoheterophyllin B
Catalog No.:BCN6050
CAS No.:1174017-37-8
- Endothelin 3 (human, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5713
CAS No.:117399-93-6
- AZD6482
Catalog No.:BCC2523
CAS No.:1173900-33-8
- 2-Hydroxysaclofen
Catalog No.:BCC6579
CAS No.:117354-64-0
- 9,9-Bis[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]fluorene
Catalog No.:BCC8796
CAS No.:117344-32-8
- Emeheterone
Catalog No.:BCN7285
CAS No.:117333-12-7
- Clocinnamox mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC5684
CAS No.:117332-69-1
- PKI-402
Catalog No.:BCC3843
CAS No.:1173204-81-3
- U0126-EtOH
Catalog No.:BCC1066
CAS No.:1173097-76-1
- GW 583340 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7300
CAS No.:1173023-85-2
- D-CPP-ene
Catalog No.:BCC6999
CAS No.:117414-74-1
- 2-Methyl-6-(p-tolyl)heptane-2,3-diol
Catalog No.:BCN7249
CAS No.:117421-22-4
- Xenin 8
Catalog No.:BCC5876
CAS No.:117442-28-1
- Wilforol E
Catalog No.:BCN8058
CAS No.:117456-86-7
- Triptonodiol
Catalog No.:BCN6782
CAS No.:117456-87-8
- BCECF-AM
Catalog No.:BCC5969
CAS No.:117464-70-7
- Cefditoren Pivoxil
Catalog No.:BCC4898
CAS No.:117467-28-4
- Prionitin
Catalog No.:BCN4855
CAS No.:117469-56-4
- Sesamoside
Catalog No.:BCN6051
CAS No.:117479-87-5
- ROX NHS ester, pure 6- isomer
Catalog No.:BCC3587
CAS No.:117491-83-5
- Neuromedin U (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5847
CAS No.:117505-80-3
- Ustusol A
Catalog No.:BCN7719
CAS No.:1175543-02-8
The value of grip test, lysophosphatidlycholines, glycerophosphocholine, ornithine, glucuronic acid decrement in assessment of nutritional and metabolic characteristics in hepatitis B cirrhosis.[Pubmed:28384211]
PLoS One. 2017 Apr 6;12(4):e0175165.
The liver is essential for the regulation of energy, protein and amino acids, as well as in other aspects of metabolism. To identify efficient indexes for evaluation of nutritional status and metabolic characteristics during different Child-Pugh stages of hepatitis B cirrhosis, 83 patients and 35 healthy individuals were enrolled in our study. We found that grip strength, triceps skinfold thickness (TSF), body fat and skeletal muscle of the patients were reduced compared to the control group (P<0.05). Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography data combined with mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) showed that levels of a variety of metabolites, including lysophosphatidylcholines (LysoPCs), glycerophosphocholine, ornithine and glucuronic acid were reduced in the serum of patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis (P<0.001). However, glycerophosphoserine and taurocholic acid levels were higher than in the control group (P<0.001). Moreover, grip strength was correlated with the Child-Pugh score (P<0.05). Serum albumin, total cholesterol, LDL, LysoPCs, glycerophosphocholine, ornithine, glucuronic acid, glycerophosphoserine and taurocholic acid were correlated with the Child-Pugh score (P<0.01). These findings suggested that grip strength and the above small molecular substances might be considered as sensitive and important indexes for evaluating nutritional status and metabolic characteristics of patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, which may help assess prognosis and adjust nutritional treatment.
Prevention of TGF-beta-induced early liver fibrosis by a maleic acid derivative anti-oxidant through suppression of ROS, inflammation and hepatic stellate cells activation.[Pubmed:28384213]
PLoS One. 2017 Apr 6;12(4):e0174008.
Current anti-fibrotic effect of antioxidants in vivo is disappointing due probably to the fact that once liver fibrogenesis is established it is too advanced to be reversed by anti-oxidation mechanism. We consider antioxidant may only act on the early phase of fibrogenesis. Thus, we had previously established an early liver fibrosis animal model using an inducible expression vector (pPK9a), which contains TGF-beta gene and was hydro-dynamically transferred into mice to induce a transient liver fibrosis. TGF-beta1 has been well documented to up-regulate the expression of alpha2(1) collagen (Col 1A2) gene in the liver via the reactive oxygen species (ROS); the process triggers inflammation, leading to hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation and liver fibrogenesis. Using our animal model and ROS, cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) and Col 1A2 promoter assays as screening targets, we report here that a maleic acid derivative isolated from the Antrodia camphorata mycelium strongly decreases ROS production, promoter activity of Cox-2 and Col 1A2, intracellular calcium, expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA), Smad4-p-Smad2/3 co-localization in cell nucleus and the DNA binding activity of Sp1. Our results suggest that the maleic acid derivative prevents liver fibrosis at an early phase both in vitro and in vivo through the inhibition of ROS, inflammation and the activation of HSC.
Thermo-acid-stable phytase-mediated enhancement of bioethanol production using Colocasia esculenta.[Pubmed:28384593]
Bioresour Technol. 2017 Jul;235:396-404.
Phytase production by the thermophilic mould Thermomyces lanuginosus SSBP was enhanced 8.56-fold in submerged fermentation, which was further improved in fed-batch cultivations. The protein was purified to homogeneity using ammonium sulphate precipitation, Resource Q anion exchange and Superdex gel-filtration chromatography, with an overall purification of 24.7-fold and a yield of 5.16%. The purified 49kDa protein was optimally active at 55 degrees C and pH 5.0, and was stable between 50 and 90 degrees C from pH 3.0-6.0, with a half-life of 138.6min at 70 degrees C. It was moderately stimulated by Ba(+2) and Mg(+2). The enzyme reduced phytate content in Colocasia esculenta starch (from 1.43mg/g to 0.05mg/g) that resulted in an improvement in the availability of fermentable sugars with a concomitant reduction in viscosity and 1.59-fold improvement in ethanol production. Thermo-acid-stable phytase from T. lanuginosus SSBP could be of major biotechnological interest, especially due to its robustness and wide applicability.


