AM580Selective RARα agonist CAS# 102121-60-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 102121-60-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2126 | Appearance | Powder |
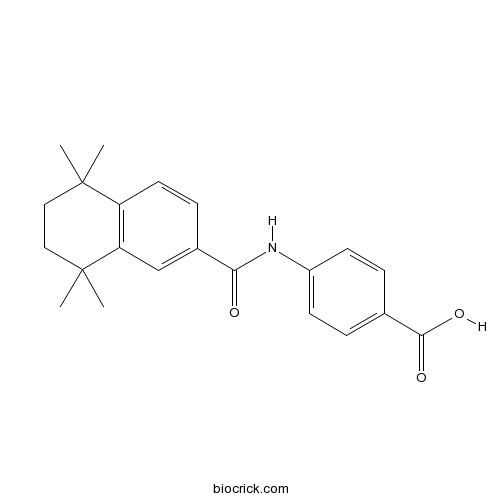
| Formula | C22H25NO3 | M.Wt | 351.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CD336; NSC608001; Ro 40-6055 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 45 mg/mL (128.04 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[(5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-6,7-dihydronaphthalene-2-carbonyl)amino]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC(C2=C1C=CC(=C2)C(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)O)(C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SZWKGOZKRMMLAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H25NO3/c1-21(2)11-12-22(3,4)18-13-15(7-10-17(18)21)19(24)23-16-8-5-14(6-9-16)20(25)26/h5-10,13H,11-12H2,1-4H3,(H,23,24)(H,25,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | An analog of retinoic acid that acts as a selective RARα agonist (EC50 values are 0.3, 8.6 and 13 nM for RARα, RARβ and RARγ respectively). Significantly induces IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 and inhibits IL-12 and IFNγ synthesis, and induces cell differentiation with over 7 times the activity of retinoic acid in vitro. |

AM580 Dilution Calculator

AM580 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8454 mL | 14.2272 mL | 28.4544 mL | 56.9087 mL | 71.1359 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5691 mL | 2.8454 mL | 5.6909 mL | 11.3817 mL | 14.2272 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2845 mL | 1.4227 mL | 2.8454 mL | 5.6909 mL | 7.1136 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0569 mL | 0.2845 mL | 0.5691 mL | 1.1382 mL | 1.4227 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0285 mL | 0.1423 mL | 0.2845 mL | 0.5691 mL | 0.7114 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AM580 is a selective agonist of retinoic acid receptor α (RARα) with IC50 and EC50 values of 8 nM and 0.36 nM, respectively [1].
RARα is ubiquitously expressed. It is important for retinoid response during growth and differentiation of epithelial cells. RARα have functions in the inhibition of cell and mammary tumour growth, increase in tumour latency, induction of cell cycle arrest, stimulation of cell death, and up-regulation of RARα and RARγ mRNA [1, 2]. In addition, RARα is involved in the production of human T cell activation and type 2 cytokine [3].
In SK-BR-3 and T47D breast cancer cell lines, treatment with AM580 at concentrations of 1 nM and 10 nM for 7 days resulted in the decrease in the number of cells [1]. AM580 at a concentration of 200 nM, enhanced the anti-proliferative effect shown by the knockdown of RAR-γ in MCF-10A breast epithelial and MCF-7 cell lines [2].
When 200 nM AM580 was applied to MMTV-Myc female mice for 96 hours, this led to impaired cell proliferation capacity. Furthermore, combination of AM580 with 100 nM CD437 and SR11253 resulted in strong growth inhibition, clearly demonstrating the ability of AM580 to reduce the tumour growth in MMTV-Myc tumour model [2].
References:
[1]. Schneider S, Offterdinger M, Huber H, et al. Activation of Retinoic Acid Receptor a Is Sufficient for Full Induction of Retinoid Responses in SK-BR-3 and T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res, 2000, 60(19):5479-87.
[2]. Bosch A, Bertran S, Lu Y, et al. Reversal by RARa agonist Am580 of c-Myc induced imbalance in RARa/RARγ expression during MMTV-Myctumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(4):R121.
[3]. Dawson H, Collins G, Pyle R, et al. The Retinoic Acid Receptor-α mediates human T-cell activation and Th2 cytokine and chemokine production. BMC Immunol, 2008, 9:16.
- rac-Rotigotine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1881
CAS No.:102120-99-0
- Cyclocytidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5555
CAS No.:10212-25-6
- Pseudoprotodioscin
Catalog No.:BCN2827
CAS No.:102115-79-7
- Pseudoproto Pb
Catalog No.:BCN2838
CAS No.:102100-46-9
- 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCN5836
CAS No.:10210-17-0
- Boc-D-Phenylglycinol
Catalog No.:BCC2711
CAS No.:102089-74-7
- Sappanone A
Catalog No.:BCN2996
CAS No.:102067-84-5
- Arctinol B
Catalog No.:BCN5835
CAS No.:102054-39-7
- 3-Deazaneplanocin,DZNep
Catalog No.:BCC1129
CAS No.:102052-95-9
- Tubeimoside I
Catalog No.:BCN1089
CAS No.:102040-03-9
- Protosappanin B
Catalog No.:BCN2281
CAS No.:102036-29-3
- Protosappanin A
Catalog No.:BCN7259
CAS No.:102036-28-2
- Atractylic acid dipotassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN5384
CAS No.:102130-43-8
- Isoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3528
CAS No.:102130-90-5
- Neoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3694
CAS No.:102130-91-6
- RJR 2429 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7000
CAS No.:1021418-53-0
- DPCPX
Catalog No.:BCC6649
CAS No.:102146-07-6
- Boc-D-Pro-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3438
CAS No.:102185-34-2
- Boc-Arg(Mts)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3054
CAS No.:102185-38-6
- Boc-D-N-Me-Phe.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3347
CAS No.:102185-45-5
- PPNDS
Catalog No.:BCC7015
CAS No.:1021868-77-8
- ARL 67156 trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7004
CAS No.:1021868-83-6
- AGN 192403 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6924
CAS No.:1021868-90-5
- ZM 39923 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2203
CAS No.:1021868-92-7
AM580, a stable benzoic derivative of retinoic acid, has powerful and selective cyto-differentiating effects on acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.[Pubmed:8608243]
Blood. 1996 Feb 15;87(4):1520-31.
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is successfully used in the cyto-differentiating treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Paradoxically, APL cells express PML-RAR, an aberrant form of the retinoic acid receptor type alpha (RAR alpha) derived from the leukemia-specific t(15;17) chromosomal translocation. We show here that AM580, a stable retinobenzoic derivative originally synthesized as a RAR alpha agonist, is a powerful inducer of granulocytic maturation in NB4, an APL-derived cell line, and in freshly isolated APL blasts. After treatment of APL cells with AM580 either alone or in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), the compound induces granulocytic maturation, as assessed by determination of the levels of leukocyte alkaline phosphatase, CD11b, CD33, and G-CSF receptor mRNA, at concentrations that are 10- to 100-fold lower than those of ATRA necessary to produce similar effects. By contrast, AM580 is not effective as ATRA in modulating the expression of these differentiation markers in the HL-60 cell line and in freshly isolated granulocytes obtained from the peripheral blood of chronic myelogenous leukemia patients during the stable phase of the disease. In NB4 cells, two other synthetic nonselective RAR ligands are capable of inducing LAP as much as AM580, whereas RAR beta- or RAR gamma-specific ligands are totally ineffective. These results show that AM580 is more powerful than ATRA in modulating the expression of differentiation antigens only in cells in which PML-RAR is present. Binding experiments, using COS-7 cells transiently transfected with PML-RAR and the normal RAR alpha, show that AM580 has a lower affinity than ATRA for both receptors. However, in the presence of PML-RAR, the synthetic retinoid is a much better transactivator of retinoic acid-responsive element-containing promoters than the natural retinoid, whereas, in the presence of RAR alpha, AM580 and ATRA have similar activity. This may explain the strong cyto-differentiating potential of AM580 in PML-RAR-containing leukemic cells.
Mechanism of inhibition of MMTV-neu and MMTV-wnt1 induced mammary oncogenesis by RARalpha agonist AM580.[Pubmed:20453882]
Oncogene. 2010 Jun 24;29(25):3665-76.
We hypothesized that specific activation of a single retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RARalpha), without direct and concurrent activation of RARbeta and gamma, will inhibit mammary tumor oncogenesis in murine models relevant to human cancer. A total of 50 uniparous mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)-neu and 50 nuliparous MMTV-wnt1 transgenic mice were treated with RARalpha agonist (retinobenzoic acid, AM580) that was added to the diet for 40 (neu) and 35 weeks (wnt1), respectively. Among the shared antitumor effects was the inhibition of epithelial hyperplasia, a significant increase (P<0.05) in tumor-free survival and a reduction in tumor incidence and in the growth of established tumors. In both models, the mechanisms responsible for these effects involved inhibition of proliferation and survival pathways, and induction of apoptosis. The treatment was more effective in the MMTV-wnt1 model in which AM580 also induced differentiation, in both in vivo and three-dimensional (3D) cultures. In these tumors AM580 inhibited the wnt pathway, measured by loss of nuclear beta-catenin, suggesting partial oncogene dependence of therapy. AM580 treatment increased RARbeta and lowered the level of RARgamma, an isotype whose expression we linked with tumor proliferation. The anticancer effect of RARalpha, together with the newly discovered pro-proliferative role of RARgamma, suggests that specific activation of RARalpha and inhibition of RARgamma might be effective in breast cancer therapy.
Reversal by RARalpha agonist Am580 of c-Myc-induced imbalance in RARalpha/RARgamma expression during MMTV-Myc tumorigenesis.[Pubmed:22920668]
Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 24;14(4):R121.
INTRODUCTION: Retinoic acid signaling plays key roles in embryonic development and in maintaining the differentiated status of adult tissues. Recently, the nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR) isotypes alpha, beta and gamma were found to play specific functions in the expansion and differentiation of the stem compartments of various tissues. For instance, RARgamma appears to be involved in stem cell compartment expansion, while RARalpha and RARbeta are implicated in the subsequent cell differentiation. We found that over-expressing c-Myc in normal mouse mammary epithelium and in a c-Myc-driven transgenic model of mammary cancer, disrupts the balance between RARgamma and RARalpha/beta in favor of RARgamma. METHODS: The effects of c-Myc on RAR isotype expression were evaluated in normal mouse mammary epithelium, mammary tumor cells obtained from the MMTV-Myc transgenic mouse model as well as human normal immortalized breast epithelial and breast cancer cell lines. The in vivo effect of the RARalpha-selective agonist 4-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-naphthyl)carboxamido]benzoic acid (AM580) was examined in the MMTV-Myc mouse model of mammary tumorigenesis. RESULTS: Modulation of the RARalpha/beta to RARgamma expression in mammary glands of normal mice, oncomice, and human mammary cell lines through the alteration of RAR-target gene expression affected cell proliferation, survival and tumor growth. Treatment of MMTV-Myc mice with the RARalpha-selective agonist AM580 led to significant inhibition of mammary tumor growth (~90%, P<0.001), lung metastasis (P<0.01) and extended tumor latency in 63% of mice. Immunocytochemical analysis showed that in these mice, RARalpha responsive genes such as Cyp26A1, E-cadherin, cellular retinol-binding protein 1 (CRBP1) and p27, were up-regulated. In contrast, the mammary gland tumors of mice that responded poorly to AM580 treatment (37%) expressed significantly higher levels of RARgamma. In vitro experiments indicated that the rise in RARgamma was functionally linked to promotion of tumor growth and inhibition of differentiation. Thus, activation of the RARalpha pathway is linked to tumor growth inhibition, differentiation and cell death. CONCLUSIONS: The functional consequence of the interplay between c-Myc oncogene expression and the RARgamma to RARalpha/beta balance suggests that prevalence of RARgamma over-RARalpha/beta expression levels in breast cancer accompanied by c-Myc amplification or over-expression in breast cancer should be predictive of response to treatment with RARalpha-isotype-specific agonists and warrant monitoring during clinical trials.
Rapid and efficient reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells by retinoic acid receptor gamma and liver receptor homolog 1.[Pubmed:21990348]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Nov 8;108(45):18283-8.
Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) by expressing four transcription factors: Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc. Here we report that enhancing RA signaling by expressing RA receptors (RARs) or by RA agonists profoundly promoted reprogramming, but inhibiting it using a RAR-alpha dominant-negative form completely blocked it. Coexpressing Rarg (RAR-gamma) and Lrh-1 (liver receptor homologue 1; Nr5a2) with the four factors greatly accelerated reprogramming so that reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells to ground-state iPSCs requires only 4 d induction of these six factors. The six-factor combination readily reprogrammed primary human neonatal and adult fibroblast cells to exogenous factor-independent iPSCs, which resembled ground-state mouse ES cells in growth properties, gene expression, and signaling dependency. Our findings demonstrate that signaling through RARs has critical roles in molecular reprogramming and that the synergistic interaction between Rarg and Lrh1 directs reprogramming toward ground-state pluripotency. The human iPSCs described here should facilitate functional analysis of the human genome.
Novel non-carboxylic acid retinoids: 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-one derivatives.[Pubmed:19058965]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jan 15;19(2):489-92.
We have successfully obtained 1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-one bioisoteres of AM580 or Tazarotene-like retinoids. In particular compound 4 displays an EC(50) of 26nM on RAR-beta.
The Retinoic Acid Receptor-alpha mediates human T-cell activation and Th2 cytokine and chemokine production.[Pubmed:18416830]
BMC Immunol. 2008 Apr 16;9:16.
BACKGROUND: We have recently demonstrated that all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and 9-cis-retinoic acid (9-cis RA) promote IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 synthesis, while decreasing IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha expression by activated human T cells and reduces the synthesis of IL-12p70 from accessory cells. Here, we have demonstrated that the observed effects using ATRA and 9-cis RA are shared with the clinically useful RAR ligand, 13-cis retinoic acid (13-cis RA), and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RAR-alpha)-selective agonist, AM580 but not with the RAR-beta/gamma ligand, 4-hydroxyphenylretinamide (4-HPR). RESULTS: The increase in type 2 cytokine production by these retinoids correlated with the expression of the T cell activation markers, CD69 and CD38. The RAR-alpha-selective agonist, AM580 recapitulated all of the T cell activation and type 2 cytokine-inducing effects of ATRA and 9-cis-RA, while the RAR-alpha-selective antagonist, RO 41-5253, inhibited these effects. CONCLUSION: These results strongly support a role for RAR-alpha engagement in the regulation of genes and proteins involved with human T cell activation and type 2 cytokine production.
Retinobenzoic acids. 1. Structure-activity relationships of aromatic amides with retinoidal activity.[Pubmed:3184125]
J Med Chem. 1988 Nov;31(11):2182-92.
Two types of aromatic amides, terephthalic monoanilides and (arylcarboxamido)benzoic acids, have been shown to possess potent retinoidal activities and can be classified as retinoids. The structure-activity relationships of these amides are discussed on the basis of differentiation-inducing activity on human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. In generic formula 4 (X = NHCO or CONH), the necessary factors to elicit the retinoidal activities are a medium-sized alkyl group (isopropyl, tert-butyl, etc.) at the meta position and a carboxyl group at the para position of the other benzene ring. The bonding of the amide structure can be reversed, this moiety apparently having the role of locating the two benzene rings at suitable positions with respect to each other. Substitution at the ring position ortho to the amide group or N-methylation of the amide group caused loss of activity, presumably owing to the resultant change of conformation. It is clear that the mutual orientation of the benzylic methyl group(s) and the carboxyl group and their distance apart are essential factors determining the retinoidal activity. Among the synthesized compounds, 4-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-naphthalenyl)carbamoyl]benz oic acid (Am80) and 4-[(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-naphthalenyl)carboxamido] benzoic acid (AM580) were several times more active than retinoic acid in the assay. They are structurally related to retinoic acid, as is clear from the biological activity of the hybrid compounds (M2 and R2).


