3-Deazaneplanocin,DZNepCell-permeable histone methyltransferase inhibitor CAS# 102052-95-9 |
- UNC 0224
Catalog No.:BCC2430
CAS No.:1197196-48-7
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3604
CAS No.:120964-45-6
- UNC0638
Catalog No.:BCC1135
CAS No.:1255580-76-7
- UNC 0631
Catalog No.:BCC4143
CAS No.:1320288-19-4
- Chaetocin
Catalog No.:BCC2429
CAS No.:28097-03-2
- BIX 01294
Catalog No.:BCC1131
CAS No.:935693-62-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 102052-95-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73087 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H24N4O3 | M.Wt | 272.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Water | ||
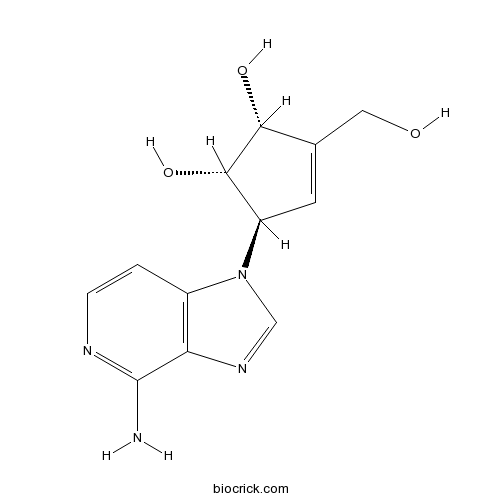
| Chemical Name | (1S,2R,5R)-5-(4-aminoimidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopent-3-ene-1,2-diol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CN=C(C2=C1N(C=N2)C3C=C(C(C3O)O)CO)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OMKHWTRUYNAGFG-IEBDPFPHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H14N4O3/c13-12-9-7(1-2-14-12)16(5-15-9)8-3-6(4-17)10(18)11(8)19/h1-3,5,8,10-11,17-19H,4H2,(H2,13,14)/t8-,10-,11+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNeP), an analog of adenosine, is a competitive inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase with Ki of 50 pM. | |||||
| Targets | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase | |||||
| IC50 | 50 pM (Ki) | |||||
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
| Cell lines | Human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 100-750 nM; 24-72h |
| Applications | DZNep induced apoptosis in cultured and primary AML cells. DZNep exhausted EZH2 levels, and inhibits trimethylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 in the AML HL-60 and OCI-AML3 cells. DZNep induced the levels of p16, p21, p27, and FBXO32 after cyclin E and HOXA9 levels run out. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
| Animal models
| Sprague-Dawley rats (120–140 g) |
| Dosage form
| 5μM DZNep for 24 h pre-treatment before experiment, orally taken with diets |
| Application | DZNep significantly reduced EZH2 expression and activity, and it increased lipid accumulation, inflammatory molecules and microRNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) mouse model. |
| Other notes
| Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Fiskus W1, Wang Y, Sreekumar A et al. Combined epigenetic therapy with the histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A and the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat against human AML cells. Blood. 2009 Sep 24;114(13):2733-43. 2. Vella S, Gnani D, Crudele A et al. EZH2 down-regulation exacerbates lipid accumulation and inflammation in vitro and in vivo NAFLD.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Dec 12;14(12):24154-68. | |

3-Deazaneplanocin,DZNep Dilution Calculator

3-Deazaneplanocin,DZNep Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6724 mL | 18.3621 mL | 36.7242 mL | 73.4484 mL | 91.8105 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7345 mL | 3.6724 mL | 7.3448 mL | 14.6897 mL | 18.3621 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3672 mL | 1.8362 mL | 3.6724 mL | 7.3448 mL | 9.1811 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0734 mL | 0.3672 mL | 0.7345 mL | 1.469 mL | 1.8362 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1836 mL | 0.3672 mL | 0.7345 mL | 0.9181 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
A novel probe derived from DzNep, an inhibitor of histone methylation, was used to identify potential cellular targets of DzNep in living mammalian cells.
Abstract
DZNep significantly induced erythroid differentiation in K562 cells and human primary erythroblasts derived from cord blood CD34-positive cells and reduced levels of ETO2 protein in K562 cells, which indicates DZNep induced erythroid differentiation may be partially attributed to its inhibition of ETO2 rather than EZH2 inhibition.
Abstract
DZNep inhibited the growth of TP53 wild-type cells by promoting p53 protein accumulation and activating p53 pathways and failed to inhibit the growth of TP53 mutant-type cells, even though DZNep induced EZH2 depletion and H3K27me3 histone mark reduction were observed in both thyroid cancer cells. However, the combination of DZNep/PRIMA-1 restored the sensitivity of TP53 mutant-type cells to DZNep by reactivating p53.
Abstract
DZNep exhibits its anticancer activity by depleting EZH2.
Abstract
DZNep depleted EZH2, inhibited histone lysine 27 trimethylation and suppressed proliferation partially through upregulation of p16INK4a and p17KIP1 in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines RBE and TFK-1 resulting in induced G1 arrest and apoptosis.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
3-Deazaneplanocin is a highly potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase with Ki value of 0.05 nM [1].
3-Deazaneplanocin was synthesized as an inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. It is an analog of adenosine and inhibits S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase through competing with the substrate, adenosine. 3-Deazaneplanocin was not so that potent in cell growth inhibition. 10 μM 3-Deazaneplanocin treatment resulted in moderate cell growth reduction in HL-60 cells. In HCC cell lines Huh1 and Huh7, 3-Deazaneplanocin inhibited growth and non-adherent sphere formation dose-dependently. It decreased the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAMhigh fraction from 49.0% to 12.5% in Huh1 cells and from 44.4% to 11.6% in Huh7 cells. Moreover, in mice implanted with Huh7 cells, administration of 3-Deazaneplanocin suppressed tumor initiation and growth via directly affecting the growth and self-renewal of tumor-initiating cells [1, 2].
References:
[1] Glazer R I, Hartman K D, Knode M C, et al. 3-Deazaneplanocin: a new and potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and its effects on human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 1986, 135(2): 688-694.
[2] Chiba T, Suzuki E, Negishi M, et al. 3-Deazaneplanocin A is a promising therapeutic agent for the eradication of tumor-initiating hepatocellular carcinoma cells. International Journal of Cancer, 2012, 130(11): 2557-2567.
- Tubeimoside I
Catalog No.:BCN1089
CAS No.:102040-03-9
- Protosappanin B
Catalog No.:BCN2281
CAS No.:102036-29-3
- Protosappanin A
Catalog No.:BCN7259
CAS No.:102036-28-2
- PF-04457845
Catalog No.:BCC1851
CAS No.:1020315-31-4
- (R)-4-Benzyl-2-oxazolidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8395
CAS No.:102029-44-7
- DCC-2036 (Rebastinib)
Catalog No.:BCC4390
CAS No.:1020172-07-9
- SGI-1027
Catalog No.:BCC4588
CAS No.:1020149-73-8
- 20,24-Epoxy-24-methoxy-23(24-25)abeo-dammaran-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1639
CAS No.:1020074-97-8
- Sulfaclozine
Catalog No.:BCC9155
CAS No.:102-65-8
- Phenyethyl 3-methylcaffeate
Catalog No.:BCN8457
CAS No.:71835-85-3
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8281
CAS No.:102-32-9
- Acetoacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8803
CAS No.:102-01-2
- Arctinol B
Catalog No.:BCN5835
CAS No.:102054-39-7
- Sappanone A
Catalog No.:BCN2996
CAS No.:102067-84-5
- Boc-D-Phenylglycinol
Catalog No.:BCC2711
CAS No.:102089-74-7
- 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCN5836
CAS No.:10210-17-0
- Pseudoproto Pb
Catalog No.:BCN2838
CAS No.:102100-46-9
- Pseudoprotodioscin
Catalog No.:BCN2827
CAS No.:102115-79-7
- Cyclocytidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5555
CAS No.:10212-25-6
- rac-Rotigotine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1881
CAS No.:102120-99-0
- AM580
Catalog No.:BCC5373
CAS No.:102121-60-8
- Atractylic acid dipotassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN5384
CAS No.:102130-43-8
- Isoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3528
CAS No.:102130-90-5
- Neoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3694
CAS No.:102130-91-6
TP53 genomic status regulates sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to the histone methylation inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep).[Pubmed:22675170]
Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 1;18(15):4201-12.
PURPOSE: DZNep (3-deazaneplanocin A) depletes EZH2, a critical component of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which is frequently deregulated in cancer. Despite exhibiting promising anticancer activity, the specific genetic determinants underlying DZNep responsiveness in cancer cells remain largely unknown. We sought to determine molecular factors influencing DZNep response in gastric cancer. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Phenotypic effects of DZNep were evaluated in a panel of gastric cancer cell lines. Sensitive lines were molecularly interrogated to identify potential predictors of DZNep responsiveness. The functional importance of candidate predictors was evaluated using short hairpin RNA (shRNA) and siRNA technologies. RESULTS: DZNep depleted PRC2 pathway components in almost all gastric cancer lines, however, only a subset of lines exhibited growth inhibition upon treatment. TP53 genomic status was significantly associated with DZNep cellular responsiveness, with TP53 wild-type (WT) lines being more sensitive (P < 0.001). In TP53-WT lines, DZNep stabilized p53 by reducing ubiquitin conjugation through USP10 upregulation, resulting in activation of canonical p53 target genes. TP53 knockdown in TP53-WT lines attenuated DZNep sensitivity and p53 target activation, showing the functional importance of an intact p53 pathway in regulating DZNep cellular sensitivity. In primary human gastric cancers, EZH2 expression was negatively correlated with p53 pathway activation, suggesting that higher levels of EZH2 may repress p53 activity. CONCLUSION: Our results highlight an important role for TP53 genomic status in influencing DZNep response in gastric cancer. Clinical trials evaluating EZH2-targeting agents such as DZNep should consider stratifying patients with gastric cancer by their TP53 genomic status.
3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, induces apoptosis and reduces cell migration in chondrosarcoma cells.[Pubmed:24852755]
PLoS One. 2014 May 22;9(5):e98176.
OBJECTIVE: Growing evidences indicate that the histone methyltransferase EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) may be an appropriate therapeutic target in some tumors. Indeed, a high expression of EZH2 is correlated with poor prognosis and metastasis in many cancers. In addition, 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), an S-adenosyl-L homocysteine hydrolase inhibitor which induces EZH2 protein depletion, leads to cell death in several cancers and tumors. The aim of this study was to determine whether an epigenetic therapy targeting EZH2 with DZNep may be also efficient to treat chondrosarcomas. METHODS: EZH2 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry and western-blot. Chondrosarcoma cell line CH2879 was cultured in the presence of DZNep, and its growth and survival were evaluated by counting adherent cells periodically. Apoptosis was assayed by cell cycle analysis, Apo2.7 expression using flow cytometry, and by PARP cleavage using western-blot. Cell migration was assessed by wound healing assay. RESULTS: Chondrosarcomas (at least with high grade) highly express EZH2, at contrary to enchondromas or chondrocytes. In vitro, DZNep inhibits EZH2 protein expression, and subsequently reduces the trimethylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me3). Interestingly, DZNep induces cell death of chondrosarcoma cell lines by apoptosis, while it slightly reduces growth of normal chondrocytes. In addition, DZNep reduces cell migration. CONCLUSION: These results indicate that an epigenetic therapy that pharmacologically targets EZH2 via DZNep may constitute a novel approach to treat chondrosarcomas.
3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), an inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, promotes erythroid differentiation.[Pubmed:24492606]
J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 21;289(12):8121-34.
EZH2, a core component of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), plays a role in transcriptional repression through histone H3 Lys-27 trimethylation and is involved in various biological processes, including hematopoiesis. It is well known that 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), an inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase that targets the degradation of EZH2, preferentially induces apoptosis in various hematological malignancies, suggesting that EZH2 may be a new target for epigenetic treatment. Because PRC2 participates in epigenetic silencing of a subset of GATA-1 target genes during erythroid differentiation, inhibition of EZH2 may influence erythropoiesis. To explore this possibility, we evaluated the impact of DZNep on erythropoiesis. DZNep treatment significantly induced erythroid differentiation of K562 cells, as assessed by benzidine staining and quantitative RT-PCR analysis for representative erythroid-related genes, including globins. When we evaluated the effects of DZNep in human primary erythroblasts derived from cord blood CD34-positive cells, the treatment significantly induced erythroid-related genes, as observed in K562 cells, suggesting that DZNep induces erythroid differentiation. Unexpectedly, siRNA-mediated EZH2 knockdown had no significant effect on the expression of erythroid-related genes. Transcriptional profiling of DZNep-treated K562 cells revealed marked up-regulation of SLC4A1 and EPB42, previously reported as representative targets of the transcriptional corepressor ETO2. In addition, DZNep treatment reduced the protein level of ETO2. These data suggest that erythroid differentiation by DZNep may not be directly related to EZH2 inhibition but may be partly associated with reduced protein level of hematopoietic corepressor ETO2. These data provide a better understanding of the mechanism of action of DZNep, which may be exploited for therapeutic applications for hematological diseases, including anemia.
Cell-based proteome profiling using an affinity-based probe (AfBP) derived from 3-deazaneplanocin A (DzNep).[Pubmed:23749335]
Chem Asian J. 2013 Aug;8(8):1818-28.
3-Deazaneplanocin A (DzNep), a global histone methylation inhibitor, has attracted significant interest in epigenetic research in recent years. The molecular mechanism of action and the cellular off-targets of DzNep, however, are still not well-understood. Our aim was to develop novel DzNep-derived small-molecule probes suitable to be used in live mammalian cells for identification of potential cellular targets of DzNep under physiologically relevant settings. In the current study, we have successfully designed, synthesized, and tested one such probe, called DZ-1. DZ-1 is a 'clickable' affinity-based probe (AfBP) derived from DzNep with minimal structural modifications. The probe was found to be highly cell-permeable, and possessed similar anti-apoptotic activities as DzNep in MCF-7 mammalian cells. Two additional control probes were made as negative labeling/pull-down probes in order to minimize false identification of background proteins due to unavoidable, intrinsic nonspecific photo-crosslinking reactions. All three probes were subsequently used for in-situ proteome profiling in live mammalian cells, followed by large-scale pull-down/LC-MS/MS analysis for identification of potential cellular protein targets that might interact with DzNep in native cellular environments. Our LC-MS/MS results revealed some highly enriched proteins that had not been reported as potential DzNep targets. These proteins might constitute unknown cellular off-targets of DzNep. Though further validation experiments are needed in order to unequivocally confirm these off-targets, our findings shed new light on the future use of DzNep as a validated chemical probe for epigenetic research and as a potential drug candidate for cancer therapy.


