PPNDSPotent, selective P2X1 antagonist CAS# 1021868-77-8 |
- BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa)
Catalog No.:BCC2139
CAS No.:211914-51-1
- BIBR-1048
Catalog No.:BCC3738
CAS No.:211915-06-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1021868-77-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311367 | Appearance | Powder |
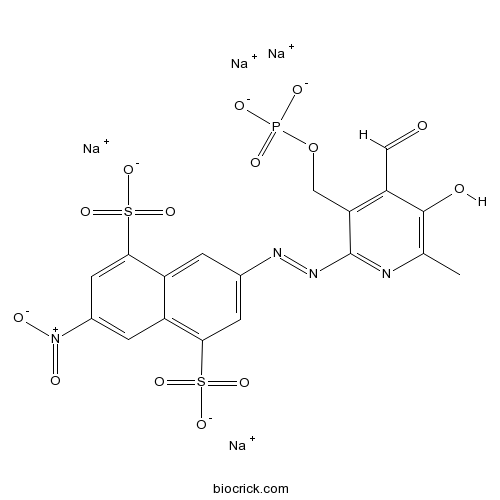
| Formula | C18H11N4Na4O14PS2 | M.Wt | 694.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | tetrasodium;3-[[4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-(phosphonatooxymethyl)pyridin-2-yl]diazenyl]-7-nitronaphthalene-1,5-disulfonate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C(C(=N1)N=NC2=CC(=C3C=C(C=C(C3=C2)S(=O)(=O)[O-])[N+](=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C=O)O.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XHWIRFKQZFSILU-UHFFFAOYSA-J | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H15N4O14PS2.4Na/c1-8-17(24)13(6-23)14(7-36-37(27,28)29)18(19-8)21-20-9-2-11-12(15(3-9)38(30,31)32)4-10(22(25)26)5-16(11)39(33,34)35;;;;/h2-6,24H,7H2,1H3,(H2,27,28,29)(H,30,31,32)(H,33,34,35);;;;/q;4*+1/p-4 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective P2X1 receptor antagonist (pKB = 7.43 in rat vas deferens). Up to 52-fold selective over P2Y1 receptors, and selective over ecto-nucleotidase, α1A-adrenoceptors, A1, A2B, H1 and M3 receptors. |

PPNDS Dilution Calculator

PPNDS Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4402 mL | 7.2009 mL | 14.4018 mL | 28.8035 mL | 36.0044 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.288 mL | 1.4402 mL | 2.8804 mL | 5.7607 mL | 7.2009 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.144 mL | 0.7201 mL | 1.4402 mL | 2.8804 mL | 3.6004 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0288 mL | 0.144 mL | 0.288 mL | 0.5761 mL | 0.7201 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0144 mL | 0.072 mL | 0.144 mL | 0.288 mL | 0.36 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-D-N-Me-Phe.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3347
CAS No.:102185-45-5
- Boc-Arg(Mts)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3054
CAS No.:102185-38-6
- Boc-D-Pro-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3438
CAS No.:102185-34-2
- DPCPX
Catalog No.:BCC6649
CAS No.:102146-07-6
- RJR 2429 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7000
CAS No.:1021418-53-0
- Neoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3694
CAS No.:102130-91-6
- Isoprocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3528
CAS No.:102130-90-5
- Atractylic acid dipotassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN5384
CAS No.:102130-43-8
- AM580
Catalog No.:BCC5373
CAS No.:102121-60-8
- rac-Rotigotine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1881
CAS No.:102120-99-0
- Cyclocytidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5555
CAS No.:10212-25-6
- Pseudoprotodioscin
Catalog No.:BCN2827
CAS No.:102115-79-7
- ARL 67156 trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7004
CAS No.:1021868-83-6
- AGN 192403 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6924
CAS No.:1021868-90-5
- ZM 39923 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2203
CAS No.:1021868-92-7
- 3-O-Methyltirotundin
Catalog No.:BCN5837
CAS No.:1021945-29-8
- Boc-4-oxo-Pro-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC3436
CAS No.:102195-80-2
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC2020
CAS No.:1021950-26-4
- ARN2966
Catalog No.:BCC8074
CAS No.:102212-26-0
- Btk inhibitor 1 R enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC5125
CAS No.:1022150-12-4
- SGX-523
Catalog No.:BCC1055
CAS No.:1022150-57-7
- Epoxyparvinolide
Catalog No.:BCN5838
CAS No.:102227-61-2
- (R)-Eriodictyol-8-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8028
CAS No.:1023271-51-3
- Cadensin D
Catalog No.:BCN7260
CAS No.:102349-35-9
PPNDS is an agonist, not an antagonist, for the ATP receptor of Paramecium.[Pubmed:12502783]
J Exp Biol. 2003 Feb;206(Pt 3):627-36.
Paramecium represents a simple, eukaryotic model system to study the cellular effects of some neuroactive drugs. They respond to the agonist beta,gamma-methylene ATP with a transient depolarizing receptor potential, Ca(2+)-based action potentials and repetitive bouts of forward and backward swimming called 'avoiding reactions' (AR). In vivo [(32)P]ATP binding assays showed saturable [(32)P]ATP binding with an apparent K(d) of approximately 23 nmol l(-1). Prolonged (15 min) exposure to 25 micro mol l(-1) beta,gamma-methylene ATP caused behavioral adaptation and losses of AR, ATP receptor potentials and [(32)P]ATP binding. While screening various ATP receptor inhibitors, we found that the P2X1 'antagonist' pyridoxal-phosphate naphthylazo-nitro-disulfate (PPNDS) is actually an agonist, producing the same responses as beta,gamma-methylene ATP. [(32)P]ATP binding assays suggest that both agonists may bind to the same site as [(32)P]ATP. Cross-adaptation is also seen between PPNDS and beta,gamma-methylene ATP in terms of losses in AR, depolarizing receptor potentials and [(32)P]ATP binding. We conclude that the inhibition caused by PPNDS in Paramecium is due to agonist-induced desensitization. Either this represents a unique new class of ATP receptors, in which PPNDS is an agonist instead of an antagonist, or PPNDS (and other drugs like it) may actually be an agonist in many other cell types in which prolonged exposure is necessary for inhibition.
The novel pyridoxal-5'-phosphate derivative PPNDS potently antagonizes activation of P2X(1) receptors.[Pubmed:10650184]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jan 17;387(3):R19-21.
Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-6-(2'-naphthylazo-6'-nitro-4',8'-disulfonat e) (PPNDS) potently antagonized P2X(1) receptor-mediated responses in rat vas deferens (pK(B)=7.43) and Xenopus laevis oocytes (pIC(50)=7. 84). It showed lower (up to 20,000-fold) inhibitory potency on ecto-nucleotidase in Xenopus oocytes and on P2Y(1) receptors in guinea-pig ileum (pA(2)=6.13). PPNDS did not interact with alpha(1A)-adrenoceptors, adenosine A(1) and A(2B), histamine H(1) and muscarinic M(3) receptors. Thus, PPNDS is a novel, specific P2 receptor antagonist and represents the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate derivative with the highest potency at P2X(1) receptors.
PPNDS inhibits murine Norovirus RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase mimicking two RNA stacking bases.[Pubmed:24657439]
FEBS Lett. 2014 May 2;588(9):1720-5.
Norovirus (NV) is a major cause of gastroenteritis worldwide. Antivirals against such important pathogens are on demand. Among the viral proteins that orchestrate viral replication, RNA-dependent-RNA-polymerase (RdRp) is a promising drug development target. From an in silico-docking search focused on the RdRp active site, we selected the compound PPNDS, which showed low micromolar IC50vs. murine NV-RdRp in vitro. We report the crystal structure of the murine NV-RdRp/PPNDS complex showing that two molecules of the inhibitor bind in antiparallel stacking interaction, properly oriented to block exit of the newly synthesized RNA. Such inhibitor-binding mode mimics two stacked nucleotide-bases of the RdRp/ssRNA complex.
Divergent effects of the purinoceptor antagonists suramin and pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-6-(2'-naphthylazo-6'-nitro-4',8'-disulfonate) (PPNDS) on alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors.[Pubmed:15448189]
Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;66(6):1738-47.
Suramin is a large naphthyl-polysulfonate compound that inhibits an array of receptors and enzymes, and it has also been reported to block currents mediated by glutamate receptors. This study shows that suramin and several structurally related compounds [8,8'-[carbonylbis(imino-3,1-phenylenecarbonylamino)]bis-(1,3,5-naphthalenetrisul fonic acid), 6Na (NF023), 8,8'-(carbonylbis(imino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino-4,1-phenylenecarbonylimino))bi s-1,3,5-naphthalenetrisulfonic acid, Na (NF279), and 4,4',4'',4'''-[carbonyl-bis[imino-5,1,3-benzenetriyl-bis-(carbonylimino)]]tetraki s-benzene-1,3-disulfonic acid, 8Na (NF449)] reduce binding of [3H]alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) and [3H]fluorowillardiine to rat brain membranes and homomeric GluR1-4 receptors, with IC50 values in the range of 5 to 180 microM. Inhibition often was less than complete at saturating drug concentrations and thus seems to be noncompetitive in nature. Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-6-(2'-naphthylazo-6'-nitro-4',8'-disulfonate) (PPNDS) is a potent antagonist of purinoceptors that shares some structural elements with suramin yet is smaller than the latter. PPNDS also had potent effects on AMPA receptors (EC50 value of 4 microM) but of a kind not seen with the other compounds in that it increased binding affinity for radioagonists severalfold. In addition, PPNDS slowed association and dissociation rates more than 10 times. In physiological experiments with GluR2 receptors, PPNDS at 50 microM reduced the peak current by 30 to 50% but had only small effects on other waveform aspects such desensitization and steady-state currents. This pattern of effects differentiates PPNDS from other compounds such as thiocyanate and up-modulators, which increase agonist binding by enhancing desensitization or slowing deactivation, respectively. Receptor model simulations indicate that most effects can be accounted for by assuming that PPNDS slows agonist binding/unbinding and stabilizes the bound-closed state of the receptor. By extension, suramin is proposed to stabilize the unbound state and thereby to reduce affinity for agonists. These drugs thus act through a novel type of noncompetitive antagonism.


