Aflatoxin G1CAS# 1165-39-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1165-39-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 14421 | Appearance | Powder |
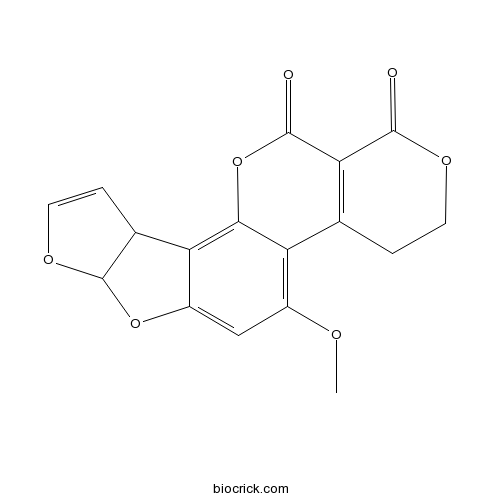
| Formula | C17H12O7 | M.Wt | 328.3 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C2C3=C(C(=O)OCC3)C(=O)OC2=C4C5C=COC5OC4=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XWIYFDMXXLINPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H12O7/c1-20-9-6-10-12(8-3-5-22-17(8)23-10)14-11(9)7-2-4-21-15(18)13(7)16(19)24-14/h3,5-6,8,17H,2,4H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Aflatoxin G1 (AFG1 ), a member of the AF family with cytotoxic and carcinogenic properties, could cause DNA damage in alveolar type II (AT-II) cells and induce lung adenocarcinoma. AFG1 induces TNF-α-dependent lung inflammation, which upregulates CYP2A13 to promote the metabolic activation of AFG1 and enhance oxidative DNA damage in AT-II cells. Dillapiol as a specific inhibitor of aflatoxin G1 production, it inhibited aflatoxin G1 production by Aspergillus parasiticus with an IC50 value of 0.15 microM. |
| Targets | TNF-α | NF-κB | CYP2A13 |
| In vitro | Aflatoxin G1 uptake by cells of Flavobacterium aurantiacum.[Reference: WebLink]Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1967, 13(6):629.
Dillapiol and Apiol as specific inhibitors of the biosynthesis of aflatoxin G1 in Aspergillus parasiticus.[Pubmed: 17827697 ]Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007 Sep;71(9):2329-32.
|
| In vivo | Aflatoxin G1 induced TNF-α-dependent lung inflammation to enhance DNA damage in alveolar epithelial cells.[Pubmed: 30478833]J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9194-9206.Aflatoxin G1 (AFG1 ), a member of the AF family with cytotoxic and carcinogenic properties, could cause DNA damage in alveolar type II (AT-II) cells and induce lung adenocarcinoma. Recently, we found AFG1 could induce chronic lung inflammation associated with oxidative stress in the protumor stage. Chronic inflammation plays a critical role in cigarette smoke or benzo[a]pyrene-induced lung tissues damage. However, it is unclear whether and how AFG1 -induced lung inflammation affects DNA damage in AT-II cells.
|
| Structure Identification | Food Chem. 2019 Aug 29;305:125429.Multi-mycotoxins analysis in liquid milk by UHPLC-Q-Exactive HRMS after magnetic solid-phase extraction based on PEGylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes.[Pubmed: 31505415]
|

Aflatoxin G1 Dilution Calculator

Aflatoxin G1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.046 mL | 15.23 mL | 30.4599 mL | 60.9199 mL | 76.1499 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6092 mL | 3.046 mL | 6.092 mL | 12.184 mL | 15.23 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3046 mL | 1.523 mL | 3.046 mL | 6.092 mL | 7.615 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3046 mL | 0.6092 mL | 1.2184 mL | 1.523 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0305 mL | 0.1523 mL | 0.3046 mL | 0.6092 mL | 0.7615 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 9alpha,13alpha-Epidioxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1611
CAS No.:116499-73-1
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6043
CAS No.:116498-58-9
- ML 145
Catalog No.:BCC7876
CAS No.:1164500-72-4
- Sal 003
Catalog No.:BCC2465
CAS No.:1164470-53-4
- Curcumadione
Catalog No.:BCN3525
CAS No.:116425-36-6
- Aerugidiol
Catalog No.:BCN3529
CAS No.:116425-35-5
- Fargesone B
Catalog No.:BCN6415
CAS No.:116424-70-5
- Fargesone A
Catalog No.:BCN6417
CAS No.:116424-69-2
- 9S-10alpha-Hydroxyepigambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3080
CAS No.:1164201-85-7
- SR 3576
Catalog No.:BCC7999
CAS No.:1164153-22-3
- Androstanolone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8826
CAS No.:1164-91-6
- Z-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2747
CAS No.:1164-16-5
- Dehydroalisol B 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9240
CAS No.:
- 3-Methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8636
CAS No.:116539-55-0
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4117
CAS No.:116680-01-4
- AZD7687
Catalog No.:BCC1394
CAS No.:1166827-44-6
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- H-9 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5656
CAS No.:116700-36-8
- Glycyrrhisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2930
CAS No.:116709-70-7
- Novaluron
Catalog No.:BCC5466
CAS No.:116714-46-6
- 9'-Methyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2824
CAS No.:1167424-31-8
Aflatoxin G1 induced TNF-alpha-dependent lung inflammation to enhance DNA damage in alveolar epithelial cells.[Pubmed:30478833]
J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9194-9206.
Aflatoxin G1 (AFG1 ), a member of the AF family with cytotoxic and carcinogenic properties, could cause DNA damage in alveolar type II (AT-II) cells and induce lung adenocarcinoma. Recently, we found AFG1 could induce chronic lung inflammation associated with oxidative stress in the protumor stage. Chronic inflammation plays a critical role in cigarette smoke or benzo[a]pyrene-induced lung tissues damage. However, it is unclear whether and how AFG1 -induced lung inflammation affects DNA damage in AT-II cells. In this study, we found increased DNA damage and cytochrome P450 (CYP2A13) expression in AFG1 -induced inflamed lung tissues. Furthermore, we treated the mice with a soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha receptor and AFG1 and found that TNF-alpha neutralization inhibited the AFG1 -induced chronic lung inflammation in vivo, and then reversed the CYP2A13 expression and DNA damage in AT-II cells. The results suggest that AFG1 induces TNF-alpha-dependent lung inflammation to regulate 2A13 expression and enhance DNA damage in AT-II cells. Then, we treated the primary mice AT-II cells and human AT-II like cells (A549) with AFG1 and TNF-alpha and found that TNF-alpha enhanced the AFG1 -induced DNA damage in mice AT-II cells as well as A549 cells in vitro. In AFG1 -exposed A549 cells, TNF-alpha-enhanced DNA damage and apoptosis were reversed by CYP2A13 small interfering RNA. Blocking NF-kappaB pathway inhibited the TNF-alpha-enhanced CYP2A13 upregulation and DNA damage confirming that the CYP2A13 upregulation by TNF-alpha plays an essential role in the activation of AFG1 under inflammatory conditions. Taken together, our findings suggest that AFG1 induces TNF-alpha-dependent lung inflammation, which upregulates CYP2A13 to promote the metabolic activation of AFG1 and enhance oxidative DNA damage in AT-II cells.


