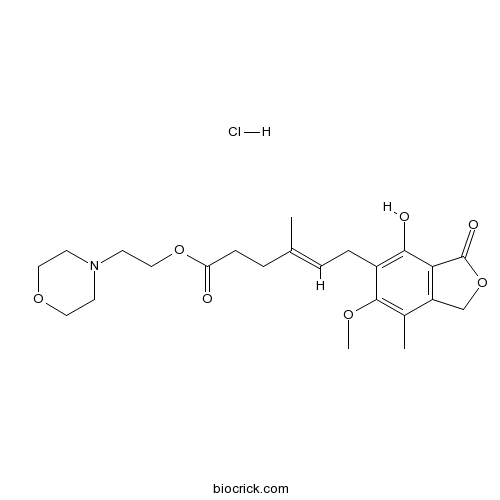
Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochlorideCAS# 116680-01-4 |
- PSI-7977
Catalog No.:BCC1871
CAS No.:1190307-88-0
- Trovafloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC3931
CAS No.:147059-75-4
- Capecitabine
Catalog No.:BCN2168
CAS No.:154361-50-9
- Viomycin
Catalog No.:BCC3930
CAS No.:32988-50-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 116680-01-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6441022 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H32ClNO7 | M.Wt | 469.96 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >83.3mg/mL in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-morpholin-4-ylethyl (E)-6-(4-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-1H-2-benzofuran-5-yl)-4-methylhex-4-enoate;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C(C2=C1COC2=O)O)CC=C(C)CCC(=O)OCCN3CCOCC3)OC.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OWLCGJBUTJXNOF-HDNKIUSMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H31NO7.ClH/c1-15(5-7-19(25)30-13-10-24-8-11-29-12-9-24)4-6-17-21(26)20-18(14-31-23(20)27)16(2)22(17)28-3;/h4,26H,5-14H2,1-3H3;1H/b15-4+; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1278 mL | 10.6392 mL | 21.2784 mL | 42.5568 mL | 53.196 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4256 mL | 2.1278 mL | 4.2557 mL | 8.5114 mL | 10.6392 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2128 mL | 1.0639 mL | 2.1278 mL | 4.2557 mL | 5.3196 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0426 mL | 0.2128 mL | 0.4256 mL | 0.8511 mL | 1.0639 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0213 mL | 0.1064 mL | 0.2128 mL | 0.4256 mL | 0.532 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Mycophenolate Mofetil is a non-competitive, selective and reversible inhibitor of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase I/II with IC50 of 39 nM and 27 nM, respectively.
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- 3-Methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8636
CAS No.:116539-55-0
- Dehydroalisol B 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9240
CAS No.:
- Aflatoxin G1
Catalog No.:BCC9214
CAS No.:1165-39-5
- 9alpha,13alpha-Epidioxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1611
CAS No.:116499-73-1
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6043
CAS No.:116498-58-9
- ML 145
Catalog No.:BCC7876
CAS No.:1164500-72-4
- Sal 003
Catalog No.:BCC2465
CAS No.:1164470-53-4
- Curcumadione
Catalog No.:BCN3525
CAS No.:116425-36-6
- Aerugidiol
Catalog No.:BCN3529
CAS No.:116425-35-5
- AZD7687
Catalog No.:BCC1394
CAS No.:1166827-44-6
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- H-9 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5656
CAS No.:116700-36-8
- Glycyrrhisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2930
CAS No.:116709-70-7
- Novaluron
Catalog No.:BCC5466
CAS No.:116714-46-6
- 9'-Methyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2824
CAS No.:1167424-31-8
- 9'''-Methyl salvianolate B
Catalog No.:BCN2923
CAS No.:1167424-32-9
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-pyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1610
CAS No.:1167483-18-2
- 4',5,6,7-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8256
CAS No.:1168-42-9
- GDC-0623
Catalog No.:BCC4150
CAS No.:1168091-68-6
- 5-Formamide-1-(2-formyloxyethl)pyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8747
CAS No.:116856-18-9
- Fmoc-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3547
CAS No.:116861-26-8
Renal Transplant Acute Rejection with Lower Mycophenolate Mofetil Dosing and Proton Pump Inhibitors or Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists.[Pubmed:28976570]
Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Dec;37(12):1507-1515.
BACKGROUND: Pharmacokinetic data show reduced mycophenolic acid levels in renal transplant recipients taking mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) concomitantly. This reduced exposure could increase rejection risk. The typical initial MMF dose post renal transplantation is 2 g/day, which often requires dose reduction secondary to side effects. Existing studies have not shown significant acute rejection differences for patients taking MMF-PPI versus patients taking MMF-ranitidine. OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to evaluate clinical outcomes in renal transplant recipients receiving a lower MMF dose than previously studied (1.5 g/day) and either a PPI or histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2RA). METHODS: This retrospective cohort study included adult subjects receiving a renal transplant between January 1, 2009, and June 30, 2013. Comparison groups were defined based on acid-suppressing therapy class prescribed at discharge from transplantation. The primary outcome was acute rejection incidence within 1 year posttransplantation. RESULTS: Of 728 renal transplant recipients screened, 522 were included: 183 taking a PPI and 339 taking an H2RA. There was no significant difference in acute rejection within 1 year (H2RA 19% versus PPI 14%, p=0.12) or 3 months (4% vs 5%, p=0.44, respectively) posttransplantation. Maintenance immunosuppression (MMF dose and tacrolimus troughs) was similar between groups at 3 months and 1 year. Graft and patient survivals were favorable (> 95%), and graft function at 1 year was stable and similar between groups. CONCLUSION: Despite taking lower MMF doses than previously studied, subjects on a PPI compared to an H2RA were not at increased risk of acute rejection within 1 year posttransplantation.
Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolic acid using the prospective data in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.[Pubmed:28991252]
Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018 Jan;53(1):44-51.
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), a prodrug of mycophenolic acid (MPA), is used to suppress GvHD in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT). The purpose of this study was to construct a population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model in HCT patients for individualized MPA therapy. Blood samples were obtained from 49 HCT patients after starting MMF therapy. Population pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters were obtained using the program NONMEM. MPA was described via a one-compartment model with a first-order elimination, and 30.9% of MPA glucuronide (MPAG) was found in the enterohepatic circulation. Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) activity was modeled as a maximal inhibitory model with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 3.59 mug/mL against MPA concentrations. Simulations based on the obtained pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters revealed that decreased creatinine clearance increases the MPAG concentration followed by an increased MPA concentration; therefore, IMPDH activity decreases. Diarrhea decreases the enterohepatic circulation of MPAG and consequently reduces MPA concentration. The IC50 for MPA exhibited a positive association with C-reactive protein. Dosage adjustment based on plasma MPA concentration is required especially for patients with renal dysfunction and/or diarrhea.
Limited sampling strategy for the estimation of mycophenolic acid area under the curve in Tunisian renal transplant patients.[Pubmed:28958670]
Nephrol Ther. 2017 Nov;13(6):460-462.
Mycophenolate mofetil is a prodrug widely used in renal transplantation to prevent organ rejection. It is hydrolyzed to its active compound mycophenolic acid (MPA). MPA area under the curve (AUC0-12h) is considered the best pharmacokinetic parameter for the estimation of MPA exposition and for prediction of rejection. MPA-AUC requires several blood samples, making it impractical for clinical practice. Therefore, development of a limited sampling strategy (LSS) to estimate MPA AUC0-12h using three blood samples is very helpful for MPA individual dose adjustment. Results of LSS differ according to the patient background and to the drug formulation. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to develop a LSS for the estimation of MPA AUC0-12h in Tunisian renal transplant patients treated with the generic formulation of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF((R)), MEDIS). The best correlation was achieved by a profile based on three time points C0.5h, C1.5h, and C4h after drug intake: AUC0-12h = 0.414 + 1.210 x C0.5 + 2.256 x C1.5 + 4.134 x C4 (mei = 1.65% and rmse = 5.81%). The correlation between full AUC0-12h and abbreviated AUC0-12h was 0.917. In conclusion, this model provides a reliable and simple equation to estimate MPA AUC0-12h for the generic formulation of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF((R))).
In Vitro Study on Influences of UGT1A8 Gene Polymorphisms on Mycophenolate Mofetil Metabolism.[Pubmed:29025387]
Exp Clin Transplant. 2018 Aug;16(4):466-472.
OBJECTIVES: Mycophenolate mofetil is a first-line drug after organ transplant, but there are differences in metabolism of mycophenolate mofetil among individuals. The UDP glucuronosyltransferase enzyme is the key metabolic enzyme for mycophenolate mofetil, and UGT1A8 gene polymorphisms may affect the elimination of mycophenolate mofetil in patients. Here, we conducted an in vitro study to explore the relation between UGT1A8 gene polymorphisms and mycophenolate mofetil metabolism. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five mutant loci overexpression vectors (UGT1A8 128C>T, 157C>A, 431C>T, 518C>G, and 830G>A) were constructed by genetic recombination and site-directed mutagenesis. We used Lipo2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to transfect the vectors into HEK293 cells. Mycophenolic acid, the active ingredient of mycophenolate mofetil, was added to different groups of cells. We then used the liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry technique to detect production of the metabolite 7-O-mycophenolic acid glucuronide and to evaluate activity of the UDP glucuronosyltransferase enzyme in cells with different overexpression vectors. RESULTS: Mutations of UGT1A8 157C>A and 518C>G vectors can lead to increased activity of UDP glucuronosyltransferase enzymes and increased production of the 7-O-mycophenolic acid glucuronide metabolite, which showed 116% (P < .001) and 107% (P = .0191) production changes of 157C>A and 518C>G mutations, respectively, relative to wild-type UGT1A8. However, mutations of UGT1A8 431C>T and 830G>A loci resulted in decreased activity of UDP glucuronosyltransferase enzymes and decreased production of the metabolite, respectively showing 62.9% (P < .001) and 9.05% (P < .001) activity relative to wild-type UGT1A8. UGT1A8 128C>T had little effect on enzyme activity, with 96.8% activity relative to wild-type UGT1A8 (P = .0569). CONCLUSIONS: Our results showed that UGT1A8 gene polymorphisms can affect the activity of UDP glucuronosyltransferase enzyme, which may influence the elimination of mycophenolate mofetil in different patients.
[Late-onset rheumatoid arthritis in a patient with successfully treated IgA nephropathy].[Pubmed:28914855]
Ter Arkh. 2017;89(8):77-79.
The paper describes a rare clinical case of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that developed in a patient 9 years after diagnosing IgA nephropathy. Kidney disease was characterized by a stable course with moderate urinary syndrome, hypertension, and reduced renal function. Immunosuppressive therapy using glucocorticosteroids and then mycophenolic acid led to remission of nephritis and recovery of renal function. However, the absence of nephritis activity and discontinuation of immunosuppressants was responsible for articular syndrome. The diagnosis of RA is based on its characteristic radiological patterns and immunological characteristics after ruling out a number of systemic diseases and infections. The common pathogenetic components of IgA nephropathy and RA, including the role of rheumatoid factor IgA, are discussed.


