4',5,6,7-TetramethoxyflavoneCAS# 1168-42-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1168-42-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 96118 | Appearance | Powder |
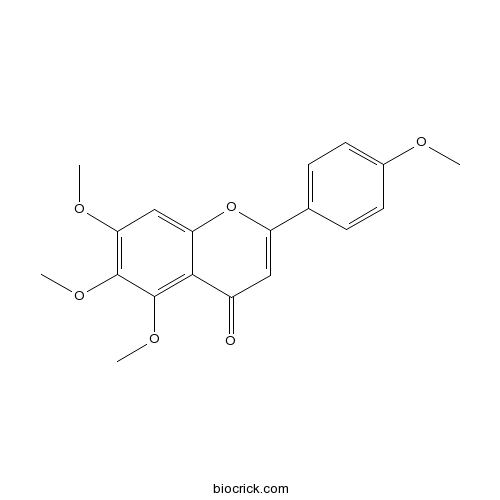
| Formula | C19H18O6 | M.Wt | 342.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)OC)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | URSUMOWUGDXZHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H18O6/c1-21-12-7-5-11(6-8-12)14-9-13(20)17-15(25-14)10-16(22-2)18(23-3)19(17)24-4/h5-10H,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 4',5,6,7-Tetramethoxyflavone has a hemostatic effect. |
| Targets | PAFR |

4',5,6,7-Tetramethoxyflavone Dilution Calculator

4',5,6,7-Tetramethoxyflavone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9206 mL | 14.6028 mL | 29.2056 mL | 58.4112 mL | 73.014 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5841 mL | 2.9206 mL | 5.8411 mL | 11.6822 mL | 14.6028 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2921 mL | 1.4603 mL | 2.9206 mL | 5.8411 mL | 7.3014 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0584 mL | 0.2921 mL | 0.5841 mL | 1.1682 mL | 1.4603 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0292 mL | 0.146 mL | 0.2921 mL | 0.5841 mL | 0.7301 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-pyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1610
CAS No.:1167483-18-2
- 9'''-Methyl salvianolate B
Catalog No.:BCN2923
CAS No.:1167424-32-9
- 9'-Methyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2824
CAS No.:1167424-31-8
- Novaluron
Catalog No.:BCC5466
CAS No.:116714-46-6
- Glycyrrhisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2930
CAS No.:116709-70-7
- H-9 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5656
CAS No.:116700-36-8
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- AZD7687
Catalog No.:BCC1394
CAS No.:1166827-44-6
- Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4117
CAS No.:116680-01-4
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- GDC-0623
Catalog No.:BCC4150
CAS No.:1168091-68-6
- 5-Formamide-1-(2-formyloxyethl)pyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8747
CAS No.:116856-18-9
- Fmoc-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3547
CAS No.:116861-26-8
- 20-Hydroxyaflavinine
Catalog No.:BCN7283
CAS No.:116865-08-8
- Monohydroxyisoaflavinine
Catalog No.:BCN7284
CAS No.:116865-09-9
- XL413
Catalog No.:BCC4241
CAS No.:1169558-38-6
- XL413 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4039
CAS No.:1169562-71-3
- INDY
Catalog No.:BCC6349
CAS No.:1169755-45-6
- Sculponeatin N
Catalog No.:BCN6044
CAS No.:1169805-98-4
- Sculponeatin O
Catalog No.:BCN6045
CAS No.:1169806-00-1
- Sculponeatic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6046
CAS No.:1169806-02-3
- Rubiadin
Catalog No.:BCN6047
CAS No.:117-02-2
Effect of Eupatorium odoratum on blood coagulation.[Pubmed:1783877]
J Med Assoc Thai. 1991 May;74(5):283-7.
The purified compound, 4', 5, 6, 7-tetramethoxyflavone, is an active ingredient isolated from Eupatorium odoratum, a Thai indigenous plant that has long been used to stop bleeding. This compound was studied in vitro for the effect on blood clotting factor activities. It was found that the compound enhanced blood coagulation, the observed APTT being shorter than that observed in the control. The result suggested that the compound accelerated clotting time through the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation which may involve the reaction of factor XII, factor XI, factor IX or factor VIII.
Flavonoids from Praxelis clematidea R.M. King and Robinson modulate bacterial drug resistance.[Pubmed:21666549]
Molecules. 2011 Jun 10;16(6):4828-35.
Chemical studies of Praxelis clematidea R.M. King & Robinson resulted in the isolation of six flavones: Apigenine, genkwanine, 7,4'-dimethylapigenin, trimethylapigenin, cirsimaritin and tetramethylscutellarein, which were tested for their toxicity against Staphylococcus aureus SA-1199B, a strain possessing the NorA efflux pump. Efflux pumps are integral proteins of the bacterial membrane and are recognized as one of the main causes of bacterial drug resistance, since they expel antibiotics from the cell. The inhibition of this transporter is one form of modulating bacterial resistance to antimicrobial drugs. The flavones tested did not show any significant antibacterial activity against the Staphylococcus aureus strain used, but were able to modulate bacterial drug resistance. This property might be related to the degree of lipophilicity of the flavones conferred by the methoxyl groups, since 4',5,6,7 tetramethoxyflavone the most methoxylated compound, reduced the minimal inhibitory concentration of the drug 16-fold.


