AZD7687DGAT inhibitor,potent and selective CAS# 1166827-44-6 |
- GDC-0623
Catalog No.:BCC4150
CAS No.:1168091-68-6
- Trametinib DMSO solvate
Catalog No.:BCC2013
CAS No.:1187431-43-1
- Pimasertib (AS-703026)
Catalog No.:BCC2529
CAS No.:1236699-92-5
- SL-327
Catalog No.:BCC1123
CAS No.:305350-87-2
- MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162)
Catalog No.:BCC1148
CAS No.:606143-89-9
- Arctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN6291
CAS No.:7770-78-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1166827-44-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 42636350 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H25N3O3 | M.Wt | 367.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (136.08 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
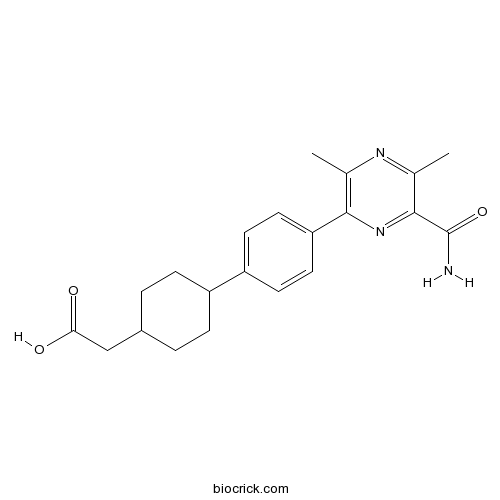
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[4-(6-carbamoyl-3,5-dimethylpyrazin-2-yl)phenyl]cyclohexyl]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(N=C(C(=N1)C)C(=O)N)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3CCC(CC3)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YXFNPRHZMOGREC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25N3O3/c1-12-19(24-20(21(22)27)13(2)23-12)17-9-7-16(8-10-17)15-5-3-14(4-6-15)11-18(25)26/h7-10,14-15H,3-6,11H2,1-2H3,(H2,22,27)(H,25,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD7687 is a potent and selective DGAT1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 80 nM (hDGAT1).
IC50 value: 80 nM [1]
Target: DGAT1
in vitro: Plasma AZD7687 exposure was measured repeatedly. Postprandial serum TAG excursion was measured during 8 h after a standardized mixed meal with fat energy content of 60% (SMM 60%; five cohorts, 1-20 mg), before (baseline) and after dosing, to assess effects on gut DGAT1 activity. AZD7687 markedly reduced postprandial TAG excursion with a steep concentration-effect relationship [2].
in vivo: Multiple doses of AZD7687 (1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20 mg/day, n=6 or n=12 for each) or placebo (n=20) were administered for 1 week. Dose-dependent reductions in postprandial serum TAG were demonstrated with AZD7687 doses ≥5mg compared with placebo (p<0.01). Significant (p<0.001) increases in plasma GLP-1 and PYY levels were seen at these doses, but no clear effect on gastric emptying was demonstrated at the end of treatment. With AZD7687 doses >5 mg/day, gastrointestinal (GI) side effects increased; 11/18 of these participants discontinued treatment owing to diarrhoea [3]. References: | |||||

AZD7687 Dilution Calculator

AZD7687 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7215 mL | 13.6077 mL | 27.2153 mL | 54.4307 mL | 68.0383 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5443 mL | 2.7215 mL | 5.4431 mL | 10.8861 mL | 13.6077 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2722 mL | 1.3608 mL | 2.7215 mL | 5.4431 mL | 6.8038 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0544 mL | 0.2722 mL | 0.5443 mL | 1.0886 mL | 1.3608 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0272 mL | 0.1361 mL | 0.2722 mL | 0.5443 mL | 0.6804 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD7687 is a potent and selective inhibitor of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) with IC50 value of 80 nM [1].
DGAT1 is a diacylglycerol acyltransferase that found to be an important target in treatment for metabolic syndrome such as obesity and diabetes. As a highly potent and selective inhibitor of DGAT1, AZD7687 inhibited the activity of human DGAT1 with IC50 value of 0.8 μM. AZD7687 showed more less inhibitory effects on ACAT1with IC50 value of 34 μM, thus causing no toxicological side effects. Besides that, AZD7687 had no significant effects on human DGAT2, ACAT2 and other enzymes involved in metabolism including PDE10A1 (IC50 value of 5.5 μM), muscarinic M2 receptor (IC50 value of 80.5 μM) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (IC50 value of 3.7 μM) [1].
AZD7687 displayed similar inhibitory effects on recombinant human DGAT1 and DGAT1 expressed in human liver microsome with IC50 values of 80 and 70 nM, respectively. In human intestinal HuTu80 cells, AZD7687 exerted higher potency with IC50 value of 10 nM which was the same as that tested in human adipose tissue [1].
In the OLLT assay tested in rats, administration of AZD7687 was found to inhibit the appearance of TAG in plasma potently with IC50 value of 42 nM. In adipose tissue, AZD7687 also dose-dependently reduced the formation of TAG with IC50 value of 132 nM. In some models of preclinical metabolic diseases, administration of AZD7687 showed various positive effects including improving insulin sensitivity, enhancing GLP-1 secretion, reducing atherosclerosis and delaying gastric emptying. However, AZD7687 exerted some degree of adverse skin changes in animal experiments. Oral administration of AZD7687 caused sebaceous glandatrophy in the skin both in mice and in dogs [1 and 2].
References:
[1] Barlind JG, Bauer UA, Birch AM, Birtles S, Buckett LK, Butlin RJ, Davies RD, Eriksson JW, Hammond CD, Hovland R, Johannesson P, Johansson MJ, Kemmitt PD, Lindmark BT, Morentin Gutierrez P, Noeske TA, Nordin A, O'Donnell CJ, Petersson AU, Redzic A, Turnbull AV, Vinblad J. Design and optimization of pyrazinecarboxamide-based inhibitors of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) leading to a clinical candidate dimethylpyrazinecarboxamide phenylcyclohexylacetic acid (AZD7687). J Med Chem. 2012 Dec 13;55(23):10610-29.
[2] Floettmann E, Lees D2, Seeliger F3, Jones HB2. Pharmacological Inhibition of DGAT1 Induces Sebaceous Gland Atrophy in Mouse and Dog Skin While Overt Alopecia Is Restricted to the Mouse. Toxicol Pathol. 2014 Aug 11.
- Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4117
CAS No.:116680-01-4
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- 3-Methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8636
CAS No.:116539-55-0
- Dehydroalisol B 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9240
CAS No.:
- Aflatoxin G1
Catalog No.:BCC9214
CAS No.:1165-39-5
- 9alpha,13alpha-Epidioxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1611
CAS No.:116499-73-1
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6043
CAS No.:116498-58-9
- ML 145
Catalog No.:BCC7876
CAS No.:1164500-72-4
- Sal 003
Catalog No.:BCC2465
CAS No.:1164470-53-4
- Curcumadione
Catalog No.:BCN3525
CAS No.:116425-36-6
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- H-9 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5656
CAS No.:116700-36-8
- Glycyrrhisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN2930
CAS No.:116709-70-7
- Novaluron
Catalog No.:BCC5466
CAS No.:116714-46-6
- 9'-Methyl lithospermate B
Catalog No.:BCN2824
CAS No.:1167424-31-8
- 9'''-Methyl salvianolate B
Catalog No.:BCN2923
CAS No.:1167424-32-9
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2,3-dihydro-4H-pyran-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1610
CAS No.:1167483-18-2
- 4',5,6,7-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8256
CAS No.:1168-42-9
- GDC-0623
Catalog No.:BCC4150
CAS No.:1168091-68-6
- 5-Formamide-1-(2-formyloxyethl)pyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8747
CAS No.:116856-18-9
- Fmoc-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3547
CAS No.:116861-26-8
- 20-Hydroxyaflavinine
Catalog No.:BCN7283
CAS No.:116865-08-8
Design and optimization of pyrazinecarboxamide-based inhibitors of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) leading to a clinical candidate dimethylpyrazinecarboxamide phenylcyclohexylacetic acid (AZD7687).[Pubmed:23116186]
J Med Chem. 2012 Dec 13;55(23):10610-29.
A new series of pyrazinecarboxamide DGAT1 inhibitors was designed to address the need for a candidate drug with good potency, selectivity, and physical and DMPK properties combined with a low predicted dose in man. Rational design and optimization of this series led to the discovery of compound 30 (AZD7687), which met the project objectives for potency, selectivity, in particular over ACAT1, solubility, and preclinical PK profiles. This compound showed the anticipated excellent pharmacokinetic properties in human volunteers.
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibition with AZD7687 alters lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut with intolerable side effects: a randomized clinical trial.[Pubmed:24118885]
Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Apr;16(4):334-43.
AIM: Inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) is a potential treatment modality for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity, based on preclinical data suggesting it is associated with insulin sensitization and weight loss. This randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 1 study in 62 overweight or obese men explored the effects and tolerability of AZD7687, a reversible and selective DGAT1 inhibitor. METHODS: Multiple doses of AZD7687 (1, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20 mg/day, n = 6 or n = 12 for each) or placebo (n = 20) were administered for 1 week. Postprandial serum triacylglycerol (TAG) was measured for 8 h after a standardized 45% fat meal. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY) were measured and a paracetamol challenge was performed to assess gastric emptying. RESULTS: Dose-dependent reductions in postprandial serum TAG were demonstrated with AZD7687 doses >/=5 mg compared with placebo (p < 0.01). Significant (p < 0.001) increases in plasma GLP-1 and PYY levels were seen at these doses, but no clear effect on gastric emptying was demonstrated at the end of treatment. With AZD7687 doses >5 mg/day, gastrointestinal (GI) side effects increased; 11/18 of these participants discontinued treatment owing to diarrhoea. CONCLUSIONS: Altered lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut were demonstrated during 1-week treatment with the DGAT1 inhibitor AZD7687. However, the apparent lack of therapeutic window owing to GI side effects of AZD7687, particularly diarrhoea, makes the utility of DGAT1 inhibition as a novel treatment for diabetes and obesity questionable.
Proof of mechanism for the DGAT1 inhibitor AZD7687: results from a first-time-in-human single-dose study.[Pubmed:22950654]
Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Feb;15(2):136-43.
AIMS: Inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1), which catalyses the final step in triacylglycerol (TAG) assembly, is suggested as a treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity based on animal data indicating insulin sensitization and weight reduction. This first-time-in-human single ascending dose study explored the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the selective DGAT1 inhibitor AZD7687. METHODS: Eighty healthy male subjects were enrolled. In each of 10 cohorts, six subjects received the same dose of AZD7687 orally (range across cohorts 1-60 mg) and two placebo. Plasma AZD7687 exposure was measured repeatedly. Postprandial serum TAG excursion was measured during 8 h after a standardized mixed meal with fat energy content of 60% (SMM 60%; five cohorts, 1-20 mg), before (baseline) and after dosing, to assess effects on gut DGAT1 activity. RESULTS: AZD7687 markedly reduced postprandial TAG excursion with a steep concentration-effect relationship. Incremental TAG AUC (area under the serum concentration vs. time curve) following SMM 60% was decreased >75% from baseline at doses >/=5 mg (p < 0.0001 vs. placebo). Serum levels of diacylglycerol, specifically measured with mass spectrometry, did not increase after AZD7687 administration. Nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea were reported with increasing doses and they limited dose escalation. Lowering of SMM fat content to 45 or 30% in five cohorts gradually reduced the frequency of gastrointestinal symptoms at a given dose of AZD7687. CONCLUSIONS: The attenuating effect of AZD7687 on postprandial TAG excursion provides proof of mechanism with respect to gut DGAT1 inhibition. However, dose and diet-related gastrointestinal side effects may impact further development of DGAT1 inhibitors.


