ML 145GPR35 antagonist CAS# 1164500-72-4 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1164500-72-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2914104 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H22N2O5S2 | M.Wt | 482.57 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
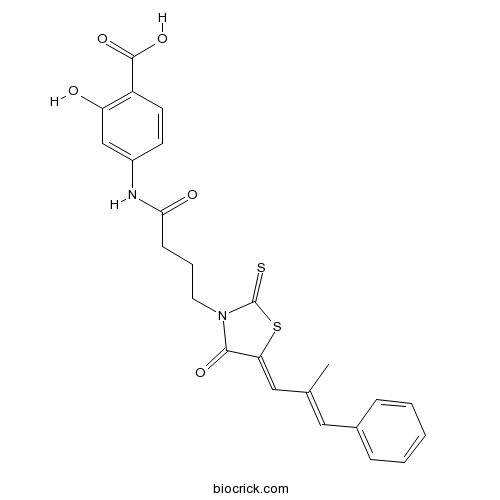
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-4-[4-[5-(2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-enylidene)-4-oxo-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]butanoylamino]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CC1=CC=CC=C1)C=C2C(=O)N(C(=S)S2)CCCC(=O)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | COFMYJWNXSFLKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H22N2O5S2/c1-15(12-16-6-3-2-4-7-16)13-20-22(29)26(24(32)33-20)11-5-8-21(28)25-17-9-10-18(23(30)31)19(27)14-17/h2-4,6-7,9-10,12-14,27H,5,8,11H2,1H3,(H,25,28)(H,30,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective antagonist for the GPR35 orphan receptor GPCR (IC50 = 20.1 nM). Over 1000-fold more selective for GPR35 compared to GPR55 antagonists. |

ML 145 Dilution Calculator

ML 145 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0722 mL | 10.3612 mL | 20.7224 mL | 41.4448 mL | 51.806 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4144 mL | 2.0722 mL | 4.1445 mL | 8.289 mL | 10.3612 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2072 mL | 1.0361 mL | 2.0722 mL | 4.1445 mL | 5.1806 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0414 mL | 0.2072 mL | 0.4144 mL | 0.8289 mL | 1.0361 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0207 mL | 0.1036 mL | 0.2072 mL | 0.4144 mL | 0.5181 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sal 003
Catalog No.:BCC2465
CAS No.:1164470-53-4
- Curcumadione
Catalog No.:BCN3525
CAS No.:116425-36-6
- Aerugidiol
Catalog No.:BCN3529
CAS No.:116425-35-5
- Fargesone B
Catalog No.:BCN6415
CAS No.:116424-70-5
- Fargesone A
Catalog No.:BCN6417
CAS No.:116424-69-2
- 9S-10alpha-Hydroxyepigambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3080
CAS No.:1164201-85-7
- SR 3576
Catalog No.:BCC7999
CAS No.:1164153-22-3
- Androstanolone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8826
CAS No.:1164-91-6
- Z-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2747
CAS No.:1164-16-5
- 3',4',7-Trimethoxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN6042
CAS No.:116384-26-0
- Loureirin C
Catalog No.:BCN3761
CAS No.:116384-24-8
- 2alpha-hydroxy-3beta-acetyloxy-betulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3072
CAS No.:1163728-89-9
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6043
CAS No.:116498-58-9
- 9alpha,13alpha-Epidioxyabiet-8(14)-en-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1611
CAS No.:116499-73-1
- Aflatoxin G1
Catalog No.:BCC9214
CAS No.:1165-39-5
- Dehydroalisol B 23-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9240
CAS No.:
- 3-Methylamino-1-(2-thienyl)-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8636
CAS No.:116539-55-0
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Mycophenolate mofetil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4117
CAS No.:116680-01-4
- AZD7687
Catalog No.:BCC1394
CAS No.:1166827-44-6
- FK 3311
Catalog No.:BCC1576
CAS No.:116686-15-8
- H-9 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5656
CAS No.:116700-36-8
MiR-145 negatively regulates Warburg effect by silencing KLF4 and PTBP1 in bladder cancer cells.[Pubmed:28380435]
Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33064-33077.
The Warburg effect is a well-known feature in cancer-specific metabolism. We previously reported on the role of microRNA (miR)-145 as a tumor-suppressor in human bladder cancer (BC) cells. In this study, we reveal that miR-145 decreases the Warburg effect by silencing KLF4 in BC cells. The expression levels of miR-145 were significantly lower in clinical BC samples and BC cell lines compared to those in normal tissues and HUC cells. Luciferase assay results showed that miR-145 directly bound to 3'UTR of KLF4, which was shown to be overexpressed in the clinical BC samples using Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry. Remarkable growth inhibition and apoptosis were induced by the ectopic expression of miR-145 or by the gene silencing of KLF4 (siR-KLF4). Also, Warburg effect-related genes such as PTBP1/PKMs were regulated by the transfection of BC cells with miR-145 or siR-KLF4. These results thus indicate that the miR-145/KLF4/PTBP1/PKMs axis is one of the critical pathways that maintain the Warburg effect in BC carcinogenesis. MiR-145 perturbed the Warburg effect by suppressing the KLF4/PTBP1/PKMs pathway in BC cells, resulting in significant cell growth inhibition.
MicroRNA-145 inhibits the activation of the mTOR signaling pathway to suppress the proliferation and invasion of invasive pituitary adenoma cells by targeting AKT3 in vivo and in vitro.[Pubmed:28352194]
Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Mar 16;10:1625-1635.
PURPOSE: This study was designed to explore how miR-145 regulates the mTOR signaling pathway in invasive pituitary adenoma (IPA) by targeting AKT3. METHODS: A total of 71 cases of IPA tissues and 66 cases of non-IPA tissues were obtained in this study. In vitro, the IPA cells were assigned into blank control, empty plasmid, miR-145 mimic, miR-145 inhibitor, miR-145 mimic + rapamycin, miR-145 inhibitor + rapamycin and rapamycin groups. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting were performed to detect the protein expressions of PI3K, AKT3, mTOR mRNA and the mRNA expression of miR-145 both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, the S6K and RPS6 mRNA and protein expressions as well as the relative phosphorylation levels were determined in vitro. MTT assay, flow cytometry and transwell assay were used to testify the cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion ability, respectively. RESULTS: The IPA tissues exhibited significantly lower expression of miR-145 but higher PI3K, AKT3 and mTOR mRNA and protein expressions when compared with the non-IPA tissues. Compared with the blank control and empty plasmid groups, the miR-145 mimic group showed significantly decreased PI3K, AKT3, mTOR, S6K and RPS6 mRNA and protein expressions as well as phosphorylation levels; besides, the IPA cell proliferation, migration and invasion ability were strongly inhibited, accompanied with the increased number of apoptotic cells. In the miR-145 inhibitor group, the PI3K, AKT3, mTOR, S6K and RPS6 mRNA and protein expressions as well as the phosphorylation levels were significantly increased; cell proliferation, migration and invasion ability were remarkably elevated, accompanied with reduced apoptotic cell number. CONCLUSION: The study demonstrates that miR-145 inhibits the mTOR signaling pathway to suppress the IPA cell proliferation and invasion and promotes its apoptosis by targeting AKT3.
Plasma miR-145, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-223 as novel biomarkers for screening early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.[Pubmed:28356944]
Oncol Lett. 2017 Feb;13(2):669-676.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the world. Late diagnosis is one of the most significant reasons for the high mortality rate of lung cancer. The identification of microRNAs (miRNAs) has opened a new field for molecular diagnosis of cancer. The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether plasma miRNAs may be used as biomarkers for early-stage NSCLC. A total of 232 participants, including 149 NSCLC patients and 83 healthy controls, were recruited between July 2012 and May 2014. We measured the levels of 10 miRNAs (miR-30d, miR-383, miR-20a, miR-145, miR-221, miR-25, miR-223, miR-21, miR-126 and miR-210) in plasma samples of 40 individuals (20 patients and 20 matched healthy controls) at the point of identification of disease, and 129 NSCLC patients and 83 healthy controls at the validation stage using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves were generated for each possible combination of the miRNAs. We observed that the expression of plasma miR-145, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-223 was significantly increased in the early-stage NSCLC samples compared with controls. miRNAs have significant diagnostic value for early-stage NSCLC. Combined ROC analyses using these four miRNAs revealed an elevated area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.897, with a sensitivity and specificity of 81.8 and 90.1%, respectively. This AUC helped in distinguishing early-stage NSCLC. Furthermore, the levels of the four plasma miRNAs were significantly decreased following surgery (P<0.05). Altered expression of miR-145, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-223 in plasma are of tumor origin, and the four miRNAs may represent potential novel non-invasive biomarkers for early-stage NSCLC.
Antagonists of GPR35 display high species ortholog selectivity and varying modes of action.[Pubmed:22967846]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Dec;343(3):683-95.
Variation in pharmacology and function of ligands at species orthologs can be a confounding feature in understanding the biology and role of poorly characterized receptors. Substantial selectivity in potency of a number of GPR35 agonists has previously been demonstrated between human and rat orthologs of this G protein-coupled receptor. Via a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based assay of induced interactions between GPR35 and beta-arrestin-2, addition of the mouse ortholog to such studies indicated that, as for the rat ortholog, murine GPR35 displayed very low potency for pamoate, whereas potency for the reference GPR35 agonist zaprinast was intermediate between the rat and human orthologs. This pattern was replicated in receptor internalization and G protein activation assays. The effectiveness and mode of action of two recently reported GPR35 antagonists, methyl-5-[(tert-butylcarbamothioylhydrazinylidene)methyl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)p yrazole-4-carboxylate (CID-2745687) and 2-hydroxy-4-[4-(5Z)-5-[(E)-2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-enylidene]-4-oxo-2-sulfanylide ne-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]butanoylamino)benzoic acid (ML-145), were investigated. Both CID-2745687 and ML-145 competitively inhibited the effects at human GPR35 of cromolyn disodium and zaprinast, two agonists that share an overlapping binding site. By contrast, although ML-145 also competitively antagonized the effects of pamoate, CID-2745687 acted in a noncompetitive fashion. Neither ML-145 nor CID-2745687 was able to effectively antagonize the agonist effects of either zaprinast or cromolyn disodium at either rodent ortholog of GPR35. These studies demonstrate that marked species selectivity of ligands at GPR35 is not restricted to agonists and considerable care is required to select appropriate ligands to explore the function of GPR35 in nonhuman cells and tissues.


