AlendronateBone resorption inhibitor CAS# 121268-17-5 |
- GW1929
Catalog No.:BCC1611
CAS No.:196808-24-9
- Balaglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1395
CAS No.:199113-98-9
- Inolitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1652
CAS No.:223132-37-4
- Inolitazone dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1653
CAS No.:223132-38-5
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 121268-17-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23681107 | Appearance | Powder |
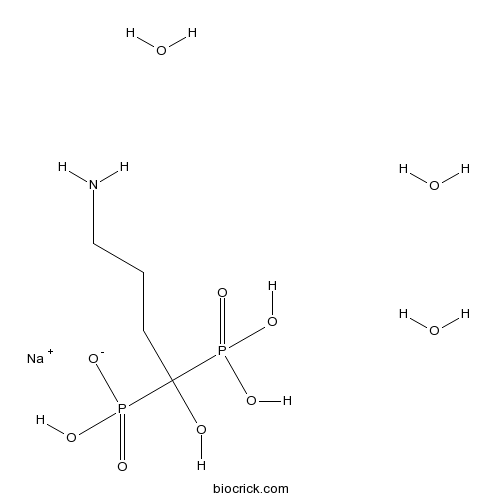
| Formula | C4H18NNaO10P2 | M.Wt | 325.12 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Alendronate; MK 217; G-704650 Adronat | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 28.57 mg/mL (87.88 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;(4-amino-1-hydroxy-1-phosphonobutyl)-hydroxyphosphinate;trihydrate | ||
| SMILES | C(CC(O)(P(=O)(O)O)P(=O)(O)[O-])CN.O.O.O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DCSBSVSZJRSITC-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C4H13NO7P2.Na.3H2O/c5-3-1-2-4(6,13(7,8)9)14(10,11)12;;;;/h6H,1-3,5H2,(H2,7,8,9)(H2,10,11,12);;3*1H2/q;+1;;;/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alendronate (sodium hydrate) is a farnesyl diphosphate synthase inhibitor with IC50 of 460 nM.In Vitro:Alendronate, acting directly on osteoclasts, inhibits a rate-limiting step in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, essential for osteoclast function[1]. Alendronate inhibits the isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway and interferes with protein prenylation, as a result of reduced geranylgeranyl diphosphate levels. Alendronate inhibits the incorporation of [3H]mevalonolactone into proteins of 18-25 kDa and into nonsaponifiable lipids, including sterols in osteoclasts[2]. Alendronate causes a dose-dependent inhibition of [3H]MVA incorporation into sterols and a concomitant increase in incorporation of radiolabel into IPP and DMAPP[3].In Vivo:Alendronate causes erosions in the rabbit stomach, but not antral ulceration in rats. Alendronate increases the incidence and size of indomethacin-induced antral ulcers. Alendronate also enhances indomethacin-induced gastricdamage in the rat, and delays gastric ulcer healing[4]. Alendronate (0.04-0.1 mg/kg twice weekly or 0.1 mg/kg weekly) partially blocks the establishment of bone metastases by human PC-3 ML cells and results in tumor formation in the peritoneum and other soft tissues. Alendronate pretreatment of mice (0.1 mg/kg twice weekly or weekly) and dosing along with taxol (10-50 mg/kg/day, twice weekly, or weekly) blocks the growth of PC-3 ML tumors in the bone marrow and soft tissues in a statistically significant manner and improves survival rates significantly by 4-5 weeks[5]. References: | |||||

Alendronate Dilution Calculator

Alendronate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0758 mL | 15.3789 mL | 30.7579 mL | 61.5157 mL | 76.8947 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6152 mL | 3.0758 mL | 6.1516 mL | 12.3031 mL | 15.3789 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3076 mL | 1.5379 mL | 3.0758 mL | 6.1516 mL | 7.6895 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0615 mL | 0.3076 mL | 0.6152 mL | 1.2303 mL | 1.5379 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0308 mL | 0.1538 mL | 0.3076 mL | 0.6152 mL | 0.7689 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Alendronate is an inhibitor of bone resorption with IC50 value of 2nM [1].
Alendronate is a bisphosphonate. It is developed as a therapeutic agent in many bone disorders such as osteoporosis as well as Paget's disease and tumoral bone disease. Alendronate inhibits the bone resorption through binding to bone mineral and subsequently preventing the osteoclasts from ingesting them. It not only affects the function of osteoclasts but also alter the morphology of the cells. In the in vitro assay, alendronate shows effective antiresorbing potency with IC50 value of 2nM when treated with osteoclast suspension. In organ culture, alendronate inhibits resorption by embryonic long bones and cultured calvaria [1, 2].
References:
[1] Sahni M, Guenther H L, Fleisch H, et al. Bisphosphonates act on rat bone resorption through the mediation of osteoblasts. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 1993, 91(5): 2004.
[2] Bell N H, Johnson R H. Bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis. Endocrine, 1997, 6(2): 203-206.
- ICI 204,448 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6806
CAS No.:121264-04-8
- Calphostin C
Catalog No.:BCC7131
CAS No.:121263-19-2
- Secodihydro-hydramicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN4783
CAS No.:1212148-58-7
- [Ala1,3,11,15]-Endothelin
Catalog No.:BCC5731
CAS No.:121204-87-3
- TC-N 1752
Catalog No.:BCC6179
CAS No.:1211866-85-1
- Rauvoyunine C
Catalog No.:BCN4833
CAS No.:1211543-01-9
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
- LEE011
Catalog No.:BCC3926
CAS No.:1211441-98-3
- Cefprozil hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4951
CAS No.:121123-17-9
- EG00229
Catalog No.:BCC5376
CAS No.:1210945-69-9
- L-670,596
Catalog No.:BCC5857
CAS No.:121083-05-4
- 3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3184
CAS No.:121072-40-0
- RWJ 21757
Catalog No.:BCC7460
CAS No.:121288-39-9
- 1-Hydroxybisabola-2,10-dien-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN7297
CAS No.:1213251-45-6
- WZ4002
Catalog No.:BCC1074
CAS No.:1213269-23-8
- Fmoc-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3489
CAS No.:121343-82-6
- SR 33805 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7181
CAS No.:121346-33-6
- Bernardioside A
Catalog No.:BCN7862
CAS No.:121368-52-3
- N6-Benzyladenine
Catalog No.:BCC9076
CAS No.:1214-39-7
- POM 1
Catalog No.:BCC7454
CAS No.:12141-67-2
- WZ3146
Catalog No.:BCC4004
CAS No.:1214265-56-1
- WZ8040
Catalog No.:BCC1075
CAS No.:1214265-57-2
- WZ4003
Catalog No.:BCC4363
CAS No.:1214265-58-3
- Ajugapantin A
Catalog No.:BCN3663
CAS No.:121449-67-0
Targeting to the Bone: Alendronate-Directed Combretastatin A-4 Bearing Antiangiogenic Polymer-Drug Conjugates.[Pubmed:28358515]
Mol Pharm. 2017 May 1;14(5):1373-1383.
Selective targeting of tumor site with chemotherapeutic agents appears to be one of the most effective methods to address many of the problems encountered with conventional chemotherapy. In this work, poly(oligoethylene glycol)methacrylate (POEGMA) based bone-targeting polymers bearing an antiangiogenic drug combretastatin A4 (CA4) were synthesized using free radical polymerization. Targeted and nontargeting copolymers were evaluated for their bone targeting efficiency, cytotoxicities against endothelial cells, namely, HUVECs and U2-OS and Saos-2 cancerous cell lines, as well as their antiangiogenic activity against endothelial cell tube formation by HUVECs. It is observed that the drug conjugated polymers conjugated with the bisphosphonate groups containing drug Alendronate (ALN) have remarkably high affinity for bone mineral when compared to the polymer-drug conjugates devoid of the bisphosphonate groups. Both targeted and nontargeted polymer-drug conjugates show a sustained drug release in rat plasma with an overall release of 80-93% over 5 days. In vitro studies revealed high levels of cytotoxicity of the polymer-drug conjugates against HUVECs and U2-OS, and moderate cytotoxicity toward Saos-2. Importantly, the CA4 conjugated copolymers displayed excellent level of antiangiogenic activity as deduced from in vitro endothelial cell tube formation assay using HUVECs. Overall, a novel bone-targeting antiangiogenic polymer-drug conjugate that can be further elaborated to carry additional anticancer drugs is disclosed.
Raloxifene but not alendronate can compensate the impaired osseointegration in osteoporotic rats.[Pubmed:28357643]
Clin Oral Investig. 2018 Jan;22(1):255-265.
OBJECTIVES: Alendronate and raloxifene, a bisphosphonate and a selective estrogen modulator, respectively, are established osteoporosis therapies. Current evidence suggests that simultaneous application of osteoporosis therapies modulates osseointegration. However, Alendronate shows inconsistent findings and raloxifene has not been studied comprehensively. This study aimed to evaluate the bone dynamics and molecular and microstructural features at the peri-implant bone interface in osteoporotic rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty female rats underwent ovariectomy and were fed a diet low in calcium and phosphate and treated with Alendronate or raloxifene for 30 days or underwent fictional ovariectomy surgery (SHAM) prior to implant insertion in the tibia; osteoporosis therapies continued thereafter. After 42 days, peri-implant bone was evaluated by histometric and micro-CT analysis. Fluorochrome incorporation and gene expression was determined to evaluate bone turnover. RESULTS: We report here that Alendronate had no impact on bone-to-implant contacts and the mineral apposition rate. The RANKL/OPG ratio and local bone volume, however, were increased compared to the untreated osteoporotic rats. Even though signaling to bone resorption activity through RANKL production was observed in the Alendronate group, the blockade of bone resorption activity that occurs in decorrence to Alendronate activity took place and resulted in an increase in bone volume. Raloxifene significantly increased osseointegration in osteoporotic rats, as indicated by bone-to-implant contacts, mineral apposition, and local bone volume. Raloxifene, however, had no considerable impact on the RANKL/OPG ratio compared to untreated osteoporotic rats. As expected, the SH group showed higher bone-to-implant contacts and mineral apposition rates than the untreated osteoporotic rats. CONCLUSIONS: These findings suggest that raloxifene but not Alendronate can compensate for the impaired osseointegration in osteoporotic rats. CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Regarding the superiority of raloxifene observed in the improvement of bone dynamics response, this statement suggests that raloxifene could be a good option for osteoporosis patients in oral rehabilitation procedures.
Effects of alendronate on osteoporosis treatment and levels of related cytokines.[Pubmed:28362987]
Genet Mol Res. 2017 Mar 16;16(1). pii: gmr-16-01-gmr.16019485.
Alendronate regulates the activity of osteoclasts and healing of osteoporosis. This study investigated the effect of Alendronate on bone healing and changes in the levels of cytokines. Bilateral ovaries of 10 adult female rabbits were removed surgically in aseptic condition to establish the animal model of osteoporosis. Five rabbits in group A were treated with Alendronate (1.15 mg.kg(-1).week(-1)) once a week by a stomach tube, whereas the remaining 5 in group B were treated with physiological saline. The success of the animal model establishment and the efficacy of Alendronate treatment were evaluated by the sports ability score and the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) score; the healing degree of osteoporosis was determined by X-ray analysis and measurement of biomechanical properties; the changes in the levels of related cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunohistochemical staining. Treatment improved dyskinesia of the animals in group A than that in group B, with significant improvement occurring in the 4th week of treatment. The BBB score of the group A animals revealed movements similar to normal, but that of the group B animals exhibited significant motor disturbance (P < 0.01). X-ray examination showed that with time, the X-ray ratings increased. Measurement of the biomechanical properties further showed that Alendronate had a positive effect on osteoporosis healing. The results of ELISA and immunohistochemistry showed that the levels of ALP, BMP-2, bFGF, and IGF-1 were upregulated in group A. In conclusion, Alendronate accelerated osteoporosis healing probably via certain cytokine-related mechanism.
Role of local alendronate delivery on the osseointegration of implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.[Pubmed:28366449]
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Jul;46(7):912-921.
There is controversy regarding whether locally delivered Alendronate enhances osseointegration. The aim of this systematic review was to assess the role of local Alendronate delivery (topical, or as a coating on implant surfaces) in the osseointegration of implants. The focused question was, "Does the local delivery of Alendronate affect osseointegration around implants?". To address this question, indexed databases were searched, without time or language restriction, up to and including January 2017. Various combinations of the following key words were used: "Alendronate", "bisphosphonates", "osseointegration", and "topical administration". letters to the editor, historic reviews, commentaries, case series, and case reports were excluded. In total, 18 experimental studies were included: Alendronate-coated implants were used in 13 of these studies and local delivery in five studies. The results of 11 of the studies showed that Alendronate coating increased new bone formation, the bone volume fraction, or bone-to-implant contact (BIC) and biomechanical properties. Results from two studies in which Alendronate was administered topically indicated impaired BIC and/or biomechanical fixation around implants. On experimental grounds, local Alendronate delivery seems to promote osseointegration. From a clinical perspective, the results in animal models support phase 1 studies in healthy humans (without co-morbidities other than edentulism).


