EG00229Nrp1 inhibitor CAS# 1210945-69-9 |
- Tenofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2500
CAS No.:147127-20-6
- Nelfinavir
Catalog No.:BCC4138
CAS No.:159989-64-7
- Nelfinavir Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1794
CAS No.:159989-65-8
- Tenofovir hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4261
CAS No.:206184-49-8
- Dapivirine (TMC120)
Catalog No.:BCC3882
CAS No.:244767-67-7
- Zidovudine
Catalog No.:BCC5024
CAS No.:30516-87-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1210945-69-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 45142253 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H20F3N7O7S3 | M.Wt | 611.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 41.4 mg/mL (67.69 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
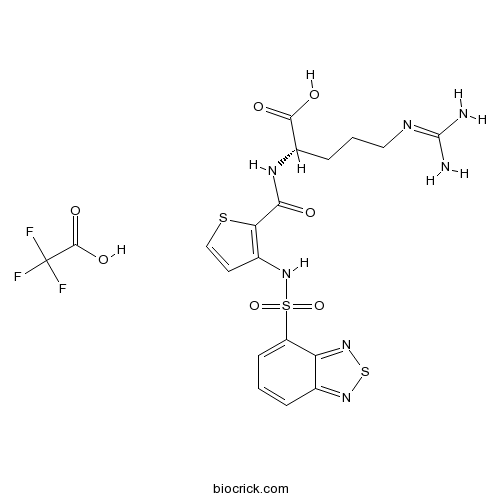
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[3-(2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-ylsulfonylamino)thiophene-2-carbonyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid;2,2,2-trifluoroacetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=NSN=C2C(=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC3=C(SC=C3)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)O.C(=O)(C(F)(F)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZYQBITUOSRZDTG-MERQFXBCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H19N7O5S3.C2HF3O2/c18-17(19)20-7-2-4-11(16(26)27)21-15(25)14-10(6-8-30-14)24-32(28,29)12-5-1-3-9-13(12)23-31-22-9;3-2(4,5)1(6)7/h1,3,5-6,8,11,24H,2,4,7H2,(H,21,25)(H,26,27)(H4,18,19,20);(H,6,7)/t11-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | EG00229 is the first small molecule inhibitor of the neuropilin-1 and VEGF-A interaction with an IC50 of inhibition of 8 uM(125I-VEGF binding to PAE/NRP1 cells).
IC50 value: 8 uM [1]
Target: NRP1/VEGF-A inhibitor
EG00229 reduced VEGF-A-induced VEGFR2 tyrosine phosphorylation in HUVECs in a dose-dependent fashion, with a maximum inhibition of 34% at 100 μM. EG00229 also significantly reduced VEGF-A induced migration of HUVECs. caused a partial inhibition of VEGF receptor activity and biological function, consistent with the current model for the role of NRP1 in VEGF function, in which NRP1 is required for optimal signaling and certain biological functions downstream of VEGFR2, particularly migration [1]. References: | |||||

EG00229 Dilution Calculator

EG00229 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6351 mL | 8.1753 mL | 16.3506 mL | 32.7011 mL | 40.8764 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.327 mL | 1.6351 mL | 3.2701 mL | 6.5402 mL | 8.1753 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1635 mL | 0.8175 mL | 1.6351 mL | 3.2701 mL | 4.0876 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0327 mL | 0.1635 mL | 0.327 mL | 0.654 mL | 0.8175 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0164 mL | 0.0818 mL | 0.1635 mL | 0.327 mL | 0.4088 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
EG00229 is a small molecule inhibitor of neuropilin-1(Nrp1) with an IC50 of 3μM [1].
EG00229 has been reported to inhibit VEGF-A binding to PAE/NRP1 in the Nrp1and bt-VEGF-A binding to purified Nrp1 b1 domain in a cell-free assay with an IC50 value of 8μM and 3μM, respectively. In addition, EG00229 has also shown the inhibition of VEGF-A binding to VEGFR2, VEGFR1 and Nrp1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 23μM [1]. Besides, EG00229 has been revealed to prevent tuftsin binding to the Nrp1 which is at the cell surface. Moreover, EG00229 has been noted to suppress the anti-inflammatory M2 shift in microglia induced by tuftsin and thus potently prevent tuftsin’s action [2].
References:
[1] Jarvis A1, Allerston CK, Jia H, Herzog B, Garza-Garcia A, Winfield N, Ellard K, Aqil R, Lynch R, Chapman C, Hartzoulakis B, Nally J, Stewart M, Cheng L, Menon M, Tickner M, Djordjevic S, Driscoll PC, Zachary I, Selwood DL.Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction. J Med Chem. 2010 Mar 11;53(5):2215-26.
[2] Nissen JC1, Selwood DL, Tsirka SE. Tuftsin signals through its receptor neuropilin-1 via the transforming growth factor beta pathway. J Neurochem. 2013 Nov;127(3):394-402.
- L-670,596
Catalog No.:BCC5857
CAS No.:121083-05-4
- 3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3184
CAS No.:121072-40-0
- 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4724
CAS No.:121064-78-6
- Melanotan II
Catalog No.:BCC7414
CAS No.:121062-08-6
- Abiesadine I
Catalog No.:BCN6104
CAS No.:1210347-50-4
- PF-04971729
Catalog No.:BCC1852
CAS No.:1210344-57-2
- IEM 1460
Catalog No.:BCC7135
CAS No.:121034-89-7
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Secretin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5848
CAS No.:121028-49-7
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- Cefprozil hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4951
CAS No.:121123-17-9
- LEE011
Catalog No.:BCC3926
CAS No.:1211441-98-3
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
- Rauvoyunine C
Catalog No.:BCN4833
CAS No.:1211543-01-9
- TC-N 1752
Catalog No.:BCC6179
CAS No.:1211866-85-1
- [Ala1,3,11,15]-Endothelin
Catalog No.:BCC5731
CAS No.:121204-87-3
- Secodihydro-hydramicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN4783
CAS No.:1212148-58-7
- Calphostin C
Catalog No.:BCC7131
CAS No.:121263-19-2
- ICI 204,448 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6806
CAS No.:121264-04-8
- Alendronate
Catalog No.:BCC4885
CAS No.:121268-17-5
- RWJ 21757
Catalog No.:BCC7460
CAS No.:121288-39-9
- 1-Hydroxybisabola-2,10-dien-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN7297
CAS No.:1213251-45-6
Small Molecule Neuropilin-1 Antagonists Combine Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Activity with Immune Modulation through Reduction of Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFbeta) Production in Regulatory T-Cells.[Pubmed:29648813]
J Med Chem. 2018 May 10;61(9):4135-4154.
We report the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of some potent small-molecule neuropilin-1 (NRP1) antagonists. NRP1 is implicated in the immune response to tumors, particularly in Treg cell fragility, required for PD1 checkpoint blockade. The design of these compounds was based on a previously identified compound EG00229. The design of these molecules was informed and supported by X-ray crystal structures. Compound 1 (EG01377) was identified as having properties suitable for further investigation. Compound 1 was then tested in several in vitro assays and was shown to have antiangiogenic, antimigratory, and antitumor effects. Remarkably, 1 was shown to be selective for NRP1 over the closely related protein NRP2. In purified Nrp1(+), FoxP3(+), and CD25(+) populations of Tregs from mice, 1 was able to block a glioma-conditioned medium-induced increase in TGFbeta production. This comprehensive characterization of a small-molecule NRP1 antagonist provides the basis for future in vivo studies.
Ablation of Neuropilin 1 from glioma-associated microglia and macrophages slows tumor progression.[Pubmed:26755653]
Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):9801-14.
Gliomas are the most commonly diagnosed primary tumors of the central nervous system (CNS). Median times of survival are dismal regardless of the treatment approach, underlying the need to develop more effective therapies. Modulation of the immune system is a promising strategy as innate and adaptive immunity play important roles in cancer progression. Glioma associated microglia and macrophages (GAMs) can comprise over 30% of the cells in glioma biopsies. Gliomas secrete cytokines that suppress the anti-tumorigenic properties of GAMs, causing them to secrete factors that support the tumor's spread and growth. Neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) is a transmembrane receptor that in mice both amplifies pro-angiogenic signaling in the tumor microenvironment and affects behavior of innate immune cells. Using a Cre-lox system, we generated mice that lack expression of Nrp1 in GAMs. We demonstrate, using an in vivo orthotopic glioma model, that tumors in mice with Nrp1-deficient GAMs exhibit less vascularity, grow at a slower pace, and are populated by increased numbers of anti-tumorigenic GAMs. Moreover, glioma survival times in mice with Nrp1-deficient GAMs were significantly longer. Treating wild-type mice with a small molecule inhibitor of Nrp1's b1 domain, EG00229, which we show here is selective for Nrp1 over Nrp2, yielded an identical outcome. Nrp1-deficient or EG00229-treated wild-type microglia exhibited a shift towards anti-tumorigenicity as evident by altered inflammatory marker profiles in vivo and decreased SMAD2/3 activation when conditioned in the presence of glioma-derived factors. These results provide support for the proposal that pharmacological inhibition of Nrp1 constitutes a potential strategy for suppressing glioma progression.
Tuftsin signals through its receptor neuropilin-1 via the transforming growth factor beta pathway.[Pubmed:24033337]
J Neurochem. 2013 Nov;127(3):394-402.
Tuftsin (Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg) is a natural immunomodulating peptide found to stimulate phagocytosis in macrophages/microglia. Tuftsin binds to the receptor neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) on the surface of cells. Nrp1 is a single-pass transmembrane protein, but its intracellular C-terminal domain is too small to signal independently. Instead, it associates with a variety of coreceptors. Despite its long history, the pathway through which tuftsin signals has not been described. To investigate this question, we employed various inhibitors to Nrp1's coreceptors to determine which route is responsible for tuftsin signaling. We use the inhibitor EG00229, which prevents tuftsin binding to Nrp1 on the surface of microglia and reverses the anti-inflammatory M2 shift induced by tuftsin. Furthermore, we demonstrate that blockade of transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) signaling via TbetaR1 disrupts the M2 shift similar to EG00229. We report that tuftsin promotes Smad3 phosphorylation and reduces Akt phosphorylation. Taken together, our data show that tuftsin signals through Nrp1 and the canonical TGFbeta signaling pathway. Despite the 40-year history of the tetrapeptide tuftsin (TKPR), a macrophage and microglial activator, its mechanism of action has not been defined. Here, we report that the tuftsin-mediated anti-inflammatory M2 shift in microglia is caused specifically by tuftsin binding to the receptor neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) and signaling through TGFbeta receptor-1, a coreceptor of Nrp1. We further show that tuftsin signals via the canonical TGFbeta pathway and promotes TGFbeta release from target cells.
Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction.[Pubmed:20151671]
J Med Chem. 2010 Mar 11;53(5):2215-26.
We report the molecular design and synthesis of EG00229, 2, the first small molecule ligand for the VEGF-A receptor neuropilin 1 (NRP1) and the structural characterization of NRP1-ligand complexes by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Mutagenesis studies localized VEGF-A binding in the NRP1 b1 domain and a peptide fragment of VEGF-A was shown to bind at the same site by NMR, providing the basis for small molecule design. Compound 2 demonstrated inhibition of VEGF-A binding to NRP1 and attenuated VEGFR2 phosphorylation in endothelial cells. Inhibition of migration of endothelial cells was also observed. The viability of A549 lung carcinoma cells was reduced by 2, and it increased the potency of the cytotoxic agents paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil when given in combination. These studies provide the basis for design of specific small molecule inhibitors of ligand binding to NRP1.


