Secretin (rat)Gastrointestinal peptide CAS# 121028-49-7 |
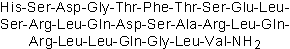
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
- (24S)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1291
CAS No.:112849-14-6
- 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxy VD2-D6
Catalog No.:BCC1299
CAS No.:216244-04-1
- 1alpha, 24, 25-Trihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1298
CAS No.:457048-34-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 121028-49-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488725 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C129H216N42O42 | M.Wt | 3027.38 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O Peptide Solubility and Storage Guidelines: 1. Calculate the length of the peptide. 2. Calculate the overall charge of the entire peptide according to the following table: 3. Recommended solution: | ||
| Sequence | HSDGTFTSELSRLQDSARLQRLLQGLV (Modifications: Val-27 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC2=CNC=N2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LKHWQEXKRMDFFJ-NEMWHCQRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C129H216N42O42/c1-58(2)40-78(119(206)170-99(64(13)14)102(134)189)149-94(181)51-145-105(192)74(29-33-91(131)178)153-113(200)81(43-61(7)8)161-116(203)82(44-62(9)10)159-108(195)72(27-22-38-143-128(137)138)151-110(197)75(30-34-92(132)179)154-114(201)79(41-59(3)4)157-107(194)71(26-21-37-142-127(135)136)150-103(190)65(15)148-121(208)87(53-172)166-118(205)86(49-98(187)188)163-111(198)76(31-35-93(133)180)155-115(202)80(42-60(5)6)158-109(196)73(28-23-39-144-129(139)140)152-122(209)89(55-174)167-117(204)83(45-63(11)12)160-112(199)77(32-36-96(183)184)156-123(210)90(56-175)168-126(213)101(67(17)177)171-120(207)84(46-68-24-19-18-20-25-68)164-125(212)100(66(16)176)169-95(182)52-146-106(193)85(48-97(185)186)162-124(211)88(54-173)165-104(191)70(130)47-69-50-141-57-147-69/h18-20,24-25,50,57-67,70-90,99-101,172-177H,21-23,26-49,51-56,130H2,1-17H3,(H2,131,178)(H2,132,179)(H2,133,180)(H2,134,189)(H,141,147)(H,145,192)(H,146,193)(H,148,208)(H,149,181)(H,150,190)(H,151,197)(H,152,209)(H,153,200)(H,154,201)(H,155,202)(H,156,210)(H,157,194)(H,158,196)(H,159,195)(H,160,199)(H,161,203)(H,162,211)(H,163,198)(H,164,212)(H,165,191)(H,166,205)(H,167,204)(H,168,213)(H,169,182)(H,170,206)(H,171,207)(H,183,184)(H,185,186)(H,187,188)(H4,135,136,142)(H4,137,138,143)(H4,139,140,144)/t65-,66+,67+,70-,71-,72-,73-,74-,75-,76-,77-,78-,79-,80-,81-,82-,83-,84-,85-,86-,87-,88-,89-,90-,99-,100-,101-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Gastrointestinal peptide that stimulates pancreatic and biliary secretion. Also thought to play a role in the regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. |

Secretin (rat) Dilution Calculator

Secretin (rat) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- 3'-Nitroacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN2256
CAS No.:121-89-1
- Propyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8431
CAS No.:121-79-9
- 2-Amino-5-nitrothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8538
CAS No.:121-66-4
- N-Acetylsulfanilyl chloride
Catalog No.:BCC9084
CAS No.:121-60-8
- Benzethonium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4635
CAS No.:121-54-0
- (-)-Terreic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7051
CAS No.:121-40-4
- Vanillic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6105
CAS No.:121-34-6
- Vanillin
Catalog No.:BCN2605
CAS No.:121-33-5
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3604
CAS No.:120964-45-6
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- IEM 1460
Catalog No.:BCC7135
CAS No.:121034-89-7
- PF-04971729
Catalog No.:BCC1852
CAS No.:1210344-57-2
- Abiesadine I
Catalog No.:BCN6104
CAS No.:1210347-50-4
- Melanotan II
Catalog No.:BCC7414
CAS No.:121062-08-6
- 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4724
CAS No.:121064-78-6
- 3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3184
CAS No.:121072-40-0
- L-670,596
Catalog No.:BCC5857
CAS No.:121083-05-4
- EG00229
Catalog No.:BCC5376
CAS No.:1210945-69-9
- Cefprozil hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4951
CAS No.:121123-17-9
- LEE011
Catalog No.:BCC3926
CAS No.:1211441-98-3
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
Circulating secretin activates supraoptic nucleus oxytocin and vasopressin neurons via noradrenergic pathways in the rat.[Pubmed:20332196]
Endocrinology. 2010 Jun;151(6):2681-8.
Secretin is a 27-amino acid brain-gut peptide from duodenal S-cells. We tested the effects of systemic administration of secretin to simulate its postprandial release on neuroendocrine neurons of the supraoptic nucleus (SON) in urethane-anesthetized female rats. Secretin dose-dependently increased the firing rate of oxytocin neurons, more potently than cholecystokinin, and dose-dependently increased plasma oxytocin concentration. The effect of secretin on SON vasopressin neurons was also predominantly excitatory, in contrast to the inhibitory actions of cholecystokinin. To explore the involvement of noradrenergic inputs in secretin-induced excitation, benoxathian, an alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonist, was infused intracerebroventricularly. Benoxathian intracerebroventricular infusion blocked the excitation by secretin of both oxytocin and vasopressin neurons. To test the role of local noradrenaline release in the SON, benoxathian was microdialyzed onto the SON. The basal firing rate of oxytocin neurons was slightly reduced and the secretin-induced excitation was attenuated during benoxathian microdialysis. Hence, noradrenergic pathways mediate the excitation by systemic secretin of oxytocin neurons via alpha1-adrenoceptors in the SON. As both systemic secretin and oxytocin are involved in regulating gastrointestinal functions and natriuresis, systemically released secretin might act partly through oxytocin.
Distribution of secretin receptors in the rat central nervous system: an in situ hybridization study.[Pubmed:23065333]
J Mol Neurosci. 2013 May;50(1):172-8.
Secretin shows a wide distribution in the brain. Functional significance of central secretin is stressed since it has been associated with autism and schizophrenia. The presence of the secretin receptor was previously demonstrated in the brain by different methods. Neurons in the cerebellum, hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei, and in the vascular organ of lamina terminalis were shown to express secretin receptor mRNA by using in situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled probe. In this work, we used a very sensitive radioactive in situ hybridization technique and systematically mapped the expression of secretin receptor mRNA in the brain. The densest labeling was observed in the nucleus of solitary tract and in the laterodorsal thalamic nucleus, where decreasing number of receptors was seen in the vascular organ of lamina terminalis, and the lateral habenular complex, and then in the supraoptic nucleus. Only a few scattered labeled cells were observed in the median frontal gyrus, entorhinal cortex, hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, perifornical region, lateral hypothalamic area, head of the caudate nucleus, spinal trigeminal nucleus, and cerebellum. Secretin receptor mRNA showed a far wider distribution than was known before, suggesting a more significant functional relevance than thought earlier.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is conjugated with taurine to promote secretin-stimulated biliary hydrocholeresis in the normal rat.[Pubmed:22194894]
PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28717.
BACKGROUND & AIMS: Secretin induces bicarbonate-rich hydrocholeresis in healthy individuals, but not in untreated patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)--the first choice treatment for PBC--restores the secretin response. Compared with humans, secretin has poor effect in experimental normal-rat models with biliary drainage, although it may elicit hydrocholeresis when the bile-acid pool is maintained. In view of the benefits of UDCA in PBC, we used normal-rat models to unravel the acute contribution of UDCA (and/or taurine-conjugated TUDCA) for eliciting the biliary secretin response. METHODS: Intravascular and/or intrabiliary administration of agonists and inhibitors was performed in normal rats with biliary monitoring. Secretin/bile-acid interplay was analyzed in 3D cultured rat cholangiocytes that formed expansive cystic structures with intralumenal hydroionic secretion. RESULTS: In vivo, secretin stimulates hydrocholeresis upon UDCA/TUDCA infusion, but does not modify the intrinsic hypercholeretic effect of dehydrocholic acid (DHCA). The former effect is dependent on microtubule polymerization, and involves PKCalpha, PI3K and MEK pathways, as shown by colchicine (i.p.) and retrograde biliary inhibitors. In vitro, while secretin alone accelerates the spontaneous expansion of 3D-cystic structures, this effect is enhanced in the presence of TUDCA, but not UDCA or DHCA. Experiments with inhibitors and Ca(2+)-chelator confirmed that the synergistic effect of secretin plus TUDCA involves microtubules, intracellular Ca(2+), PKCalpha, PI3K, PKA and MEK pathways. Gene silencing also demonstrated the involvement of the bicarbonate extruder Ae2. CONCLUSIONS: UDCA is conjugated in order to promote secretin-stimulated hydrocholeresis in rats through Ae2, microtubules, intracellular Ca(2+), PKCalpha, PI3K, PKA, and MEK.
Secretin as a neuropeptide.[Pubmed:12392059]
Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Aug;26(1):97-107.
The role of secretin as a classical hormone in the gastrointestinal system is well-established. The recent debate on the use of secretin as a potential therapeutic treatment for autistic patients urges a better understanding of the neuroactive functions of secretin. Indeed, there is an increasing body of evidence pointing to the direction that, in addition to other peptides in the secretin/glucagon superfamily, secretin is also a neuropeptide. The purpose of this review is to discuss the recent data for supporting the neurocrine roles of secretin in rodents. By in situ hybridization and immunostaining, secretin was found to be expressed in distinct neuronal populations within the cerebellum and cerebral cortex, whereas the receptor transcript was found throughout the brain. In the rat cerebellum, secretin functions as a retrograde messenger to facilitate GABA transmission, indicating that it can modulate motor and other functions. In summary, the recent data support strongly the neuropeptide role of secretin, although the secretin-autism link remains to be clarified in the future.
Secretin, glucagon, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, parathyroid hormone, and related peptides in the regulation of the hypothalamus- pituitary-adrenal axis.[Pubmed:10764961]
Peptides. 2000 Feb;21(2):309-24.
Secretin, glucagon, gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), and parathyroid hormone (PTH) belong, together with vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase (AC)-activating polypeptide, to a family of peptides (the VIP-secretin-glucagon family), which also includes growth hormone-releasing hormone and exendins. All the members of this peptide family possess a remarkable amino-acid sequence homology, and bind to G-protein-coupled receptors, whose signaling mechanism primarily involves AC/protein kinase A and phospholipase C/protein kinase C cascades. VIP and pituitary AC-activating polypeptide play a role in the regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and in this review we survey findings that also other members of the VIP-secretin-glucagon family may have the same function. Secretin and secretin receptors are expressed in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, and secretin inhibits adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) release. No evidence is available for the presence of secretin receptors in adrenal glands, but secretin selectively depresses the glucocorticoid response to ACTH of dispersed zona fasciculata-reticularis (ZF/R) cells. Glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 are contained in the hypothalamus, and all the components of the HPA axis are provided with glucagon and glucagons-like-1 receptors. These peptides exert a short-term inhibitory effect on stress-induced pituitary ACTH release and depress the ZF/R cell response to ACTH by inhibiting the AC/protein kinase A cascade; they also stimulate hypothalamic arginine-vasopressin release. GIP receptors are present in the ZF/R of the normal adrenals, and are particularly abundant in some types of adrenocortical adenomas and hyperplasias. GIP, through the activation of the AC/protein kinase A cascade, evokes a sizeable glucocorticoid secretagogue effect, leading to the identification of a food/GIP-dependent Cushing's syndrome. PTH and PTH-related protein are expressed in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, and PTH and PTH-related protein receptors in all the components of the HPA axis. Both peptides enhance ACTH and arginine-vasopressin release, as well as stimulate aldosterone and glucocorticoid secretion of dispersed zona glomerulosa and ZF/R cells, respectively. The involvement of growth hormone-releasing hormone and exendins in the functional regulation of the HPA axis has not yet been extensively investigated.
The origin and function of the pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)/glucagon superfamily.[Pubmed:11133067]
Endocr Rev. 2000 Dec;21(6):619-70.
The pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP)/ glucagon superfamily includes nine hormones in humans that are related by structure, distribution (especially the brain and gut), function (often by activation of cAMP), and receptors (a subset of seven-transmembrane receptors). The nine hormones include glucagon, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), GLP-2, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), GH-releasing hormone (GRF), peptide histidine-methionine (PHM), PACAP, secretin, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). The origin of the ancestral superfamily members is at least as old as the invertebrates; the most ancient and tightly conserved members are PACAP and glucagon. Evidence to date suggests the superfamily began with a gene or exon duplication and then continued to diverge with some gene duplications in vertebrates. The function of PACAP is considered in detail because it is newly (1989) discovered; it is tightly conserved (96% over 700 million years); and it is probably the ancestral molecule. The diverse functions of PACAP include regulation of proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis in some cell populations. In addition, PACAP regulates metabolism and the cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems, although the physiological event(s) that coordinates PACAP responses remains to be identified.


