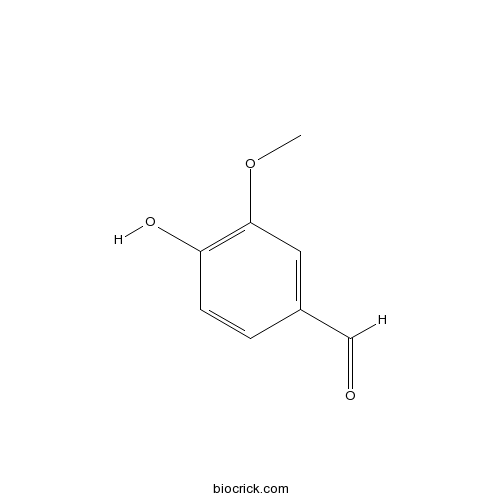
VanillinCAS# 121-33-5 |
- ZM323881
Catalog No.:BCC2073
CAS No.:193001-14-8
- BIBX 1382
Catalog No.:BCC1418
CAS No.:196612-93-8
- Ki8751
Catalog No.:BCC1116
CAS No.:228559-41-9
- KRN 633
Catalog No.:BCC2544
CAS No.:286370-15-8
- Brivanib (BMS-540215)
Catalog No.:BCC1231
CAS No.:649735-46-6
- Golvatinib (E7050)
Catalog No.:BCC4423
CAS No.:928037-13-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 121-33-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1183 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C8H8O3 | M.Wt | 152.14 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 4-Hydroxy 3-methoxybenzaldehyde; Vanillic aldehyde | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (657.25 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MWOOGOJBHIARFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H8O3/c1-11-8-4-6(5-9)2-3-7(8)10/h2-5,10H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Vanillin is a single molecule extracted from vanilla beans and also a popular odor used widely in perfume, food and medicine.Vanillin can reversibly and non-competitively inhibit the cellulase activity at appropriate concentrations and the value of IC50 was estimated to be 30 g/L.Vanillin protects KSC from UVB irradiation and its effects may occur through the suppression of downstream step of MDM2 in UVB irradiation-induced p53 activation. Vanillin also inhibits yeast growth and fermentation. |
| Targets | Chk | p53 | p38MAPK | JNK | Mdm2 | NADPH-oxidase |
| In vitro | Vanillin protects human keratinocyte stem cells against ultraviolet B irradiation.[Pubmed: 24184596]Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:30-7.Ultraviolet-B (UVB) irradiation is one of major factors which induce cellular damages in the epidermis. Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) for vanillin tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.[Pubmed: 24725964]J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Sep;118(3):263-9.Vanillin is derived from lignocellulosic biomass and, as one of the major biomass conversion inhibitors, inhibits yeast growth and fermentation. Vanillin was recently shown to induce the mitochondrial fragmentation and formation of mRNP granules such as processing bodies and stress granules in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Furfural, another major biomass conversion inhibitor, also induces oxidative stress and is reduced in an NAD(P)H-dependent manner to its less toxic alcohol derivative. Therefore, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), through which most NADPH is generated, plays a role in tolerance to furfural. Although Vanillin also induces oxidative stress and is reduced to vanillyl alcohol in a NADPH-dependent manner, the relationship between Vanillin and PPP has not yet been investigated. |
| Kinase Assay | Vanillin causes the activation of Yap1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.[Pubmed: 23850265]Inhibitory effect of vanillin on cellulase activity in hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass.[Pubmed: 24997375]Bioresour Technol. 2014 Sep;167:324-30.Pretreatment of lignocellulosic material produces a wide variety of inhibitory compounds, which strongly inhibit the following enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass. Vanillin is a kind of phenolics derived from degradation of lignin. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Jan;117(1):33-8.Vanillin and furfural are derived from lignocellulosic biomass and inhibit yeast growth and fermentation as biomass conversion inhibitors. Furfural has been shown to induce oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |

Vanillin Dilution Calculator

Vanillin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5729 mL | 32.8645 mL | 65.7289 mL | 131.4579 mL | 164.3223 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3146 mL | 6.5729 mL | 13.1458 mL | 26.2916 mL | 32.8645 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6573 mL | 3.2864 mL | 6.5729 mL | 13.1458 mL | 16.4322 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1315 mL | 0.6573 mL | 1.3146 mL | 2.6292 mL | 3.2864 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3286 mL | 0.6573 mL | 1.3146 mL | 1.6432 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3604
CAS No.:120964-45-6
- FPL 64176
Catalog No.:BCC7050
CAS No.:120934-96-5
- Isoliquiritin apioside
Catalog No.:BCN2914
CAS No.:120926-46-7
- PF-03394197(Oclacitinib)
Catalog No.:BCC6474
CAS No.:1208319-26-9
- N6022
Catalog No.:BCC4127
CAS No.:1208315-24-5
- Ketone Ester
Catalog No.:BCC1677
CAS No.:1208313-97-6
- VU 0365114
Catalog No.:BCC6164
CAS No.:1208222-39-2
- CaMKII-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5530
CAS No.:1208123-85-6
- Quassidine B
Catalog No.:BCN7022
CAS No.:1207862-37-0
- Gynosaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN4078
CAS No.:1207861-69-5
- Huperzine A
Catalog No.:BCN1058
CAS No.:120786-18-7
- 3,2'-Epilarixinol
Catalog No.:BCN6496
CAS No.:1207671-28-0
- Vanillic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6105
CAS No.:121-34-6
- (-)-Terreic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7051
CAS No.:121-40-4
- Benzethonium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4635
CAS No.:121-54-0
- N-Acetylsulfanilyl chloride
Catalog No.:BCC9084
CAS No.:121-60-8
- 2-Amino-5-nitrothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8538
CAS No.:121-66-4
- Propyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8431
CAS No.:121-79-9
- 3'-Nitroacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN2256
CAS No.:121-89-1
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- Secretin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5848
CAS No.:121028-49-7
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
Vanillin protects human keratinocyte stem cells against ultraviolet B irradiation.[Pubmed:24184596]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:30-7.
Ultraviolet-B (UVB) irradiation is one of major factors which induce cellular damages in the epidermis. We investigated protective effects and mechanisms of Vanillin, a main constituent of vanilla beans, against UVB-induced cellular damages in keratinocyte stem cells (KSC). Here, Vanillin significantly attenuated UVB irradiation-induced cytotoxicity. The Vanillin effects were also demonstrated by the results of the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase and alkaline comet assays. In addition, Vanillin induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Attempts to elucidate a possible mechanism underlying the Vanillin-mediated effects revealed that Vanillin significantly reduced UVB-induced phosphorylation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM), serine threonine kinase checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2), tumor suppressor protein 53 (p53), p38/mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38), c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK), S6 ribosomal protein (S6RP), and histone 2A family member X (H2A.X). UVB-induced activation of p53 luciferase reporter was also significantly inhibited by Vanillin. In addition, while ATM inhibitor had no effect on the Vanillin effects, mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) inhibitor significantly attenuated suppressive effects of Vanillin on UVB-induced activation of p53 reporter in KSC. Taken together, these findings suggest that Vanillin protects KSC from UVB irradiation and its effects may occur through the suppression of downstream step of MDM2 in UVB irradiation-induced p53 activation.
Inhibitory effect of vanillin on cellulase activity in hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass.[Pubmed:24997375]
Bioresour Technol. 2014 Sep;167:324-30.
Pretreatment of lignocellulosic material produces a wide variety of inhibitory compounds, which strongly inhibit the following enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass. Vanillin is a kind of phenolics derived from degradation of lignin. The effect of Vanillin on cellulase activity for the hydrolysis of cellulose was investigated in detail. The results clearly showed that Vanillin can reversibly and non-competitively inhibit the cellulase activity at appropriate concentrations and the value of IC50 was estimated to be 30 g/L. The inhibition kinetics of cellulase by Vanillin was studied using HCH-1 model and inhibition constants were determined. Moreover, investigation of three compounds with similar structure of Vanillin on cellulase activity demonstrated that aldehyde group and phenolic hydroxyl groups of Vanillin had inhibitory effect on cellulase. These results provide valuable and detailed information for understanding the inhibition of lignin derived phenolics on cellulase.
Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) for vanillin tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.[Pubmed:24725964]
J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Sep;118(3):263-9.
Vanillin is derived from lignocellulosic biomass and, as one of the major biomass conversion inhibitors, inhibits yeast growth and fermentation. Vanillin was recently shown to induce the mitochondrial fragmentation and formation of mRNP granules such as processing bodies and stress granules in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Furfural, another major biomass conversion inhibitor, also induces oxidative stress and is reduced in an NAD(P)H-dependent manner to its less toxic alcohol derivative. Therefore, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), through which most NADPH is generated, plays a role in tolerance to furfural. Although Vanillin also induces oxidative stress and is reduced to vanillyl alcohol in a NADPH-dependent manner, the relationship between Vanillin and PPP has not yet been investigated. In the present study, we examined the importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), which catalyzes the rate-limiting NADPH-producing step in PPP, for yeast tolerance to Vanillin. The growth of the null mutant of G6PDH gene (zwf1Delta) was delayed in the presence of Vanillin, and Vanillin was efficiently reduced in the culture of wild-type cells but not in the culture of zwf1Delta cells. Furthermore, zwf1Delta cells easily induced the activation of Yap1, an oxidative stress responsive transcription factor, mitochondrial fragmentation, and P-body formation with the Vanillin treatment, which indicated that zwf1Delta cells were more susceptible to Vanillin than wild type cells. These findings suggest the importance of G6PDH and PPP in the response of yeast to Vanillin.
Vanillin causes the activation of Yap1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.[Pubmed:23850265]
J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Jan;117(1):33-8.
Vanillin and furfural are derived from lignocellulosic biomass and inhibit yeast growth and fermentation as biomass conversion inhibitors. Furfural has been shown to induce oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Since there has been no report on the relationship between Vanillin and oxidative stress, we investigated whether Vanillin caused oxidative stress in yeast cells. We showed that Vanillin caused the nuclear accumulation of Yap1, an oxidative stress responsive transcription factor, and subsequent transcriptional activation of Yap1-target genes. The growth of the null mutant of the YAP1 gene (yap1Delta) was delayed in the presence of Vanillin, which indicated that Yap1 plays a role in the acquisition of tolerance to Vanillin. We also demonstrated that Vanillin facilitated the fragmentation of mitochondria. These findings suggest that the toxicity of Vanillin involves damage induced by oxidative stress.


