FPL 64176Potent activator of Ca2+ channels (L-type) CAS# 120934-96-5 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Fumonisin B1
Catalog No.:BCC2461
CAS No.:116355-83-0
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 120934-96-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3423 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H21NO3 | M.Wt | 347.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in ethanol and to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
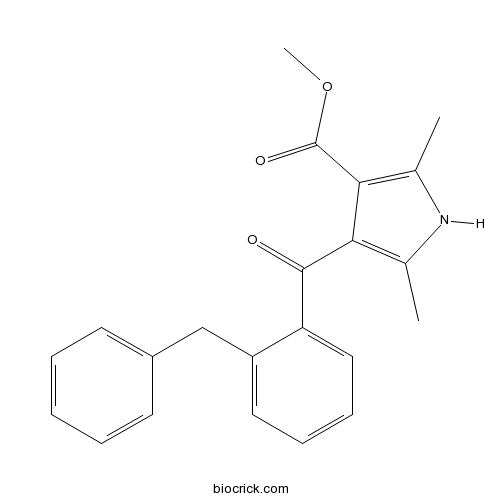
| Chemical Name | methyl 4-(2-benzylbenzoyl)-2,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C(N1)C)C(=O)OC)C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MDMWHKZANMNXTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H21NO3/c1-14-19(20(15(2)23-14)22(25)26-3)21(24)18-12-8-7-11-17(18)13-16-9-5-4-6-10-16/h4-12,23H,13H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent activator of L-type Ca2+ channels (EC50 = 16 nM). 40-fold more potent than Bay K 8644 as a positive inotrope in guinea pig atria. |

FPL 64176 Dilution Calculator

FPL 64176 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8784 mL | 14.3922 mL | 28.7844 mL | 57.5689 mL | 71.9611 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5757 mL | 2.8784 mL | 5.7569 mL | 11.5138 mL | 14.3922 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2878 mL | 1.4392 mL | 2.8784 mL | 5.7569 mL | 7.1961 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0576 mL | 0.2878 mL | 0.5757 mL | 1.1514 mL | 1.4392 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0288 mL | 0.1439 mL | 0.2878 mL | 0.5757 mL | 0.7196 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isoliquiritin apioside
Catalog No.:BCN2914
CAS No.:120926-46-7
- PF-03394197(Oclacitinib)
Catalog No.:BCC6474
CAS No.:1208319-26-9
- N6022
Catalog No.:BCC4127
CAS No.:1208315-24-5
- Ketone Ester
Catalog No.:BCC1677
CAS No.:1208313-97-6
- VU 0365114
Catalog No.:BCC6164
CAS No.:1208222-39-2
- CaMKII-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5530
CAS No.:1208123-85-6
- Quassidine B
Catalog No.:BCN7022
CAS No.:1207862-37-0
- Gynosaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN4078
CAS No.:1207861-69-5
- Huperzine A
Catalog No.:BCN1058
CAS No.:120786-18-7
- 3,2'-Epilarixinol
Catalog No.:BCN6496
CAS No.:1207671-28-0
- LDV FITC
Catalog No.:BCC6229
CAS No.:1207610-07-8
- 5-OMe-UDP trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6153
CAS No.:1207530-98-0
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3604
CAS No.:120964-45-6
- Vanillin
Catalog No.:BCN2605
CAS No.:121-33-5
- Vanillic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6105
CAS No.:121-34-6
- (-)-Terreic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7051
CAS No.:121-40-4
- Benzethonium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4635
CAS No.:121-54-0
- N-Acetylsulfanilyl chloride
Catalog No.:BCC9084
CAS No.:121-60-8
- 2-Amino-5-nitrothiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8538
CAS No.:121-66-4
- Propyl gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8431
CAS No.:121-79-9
- 3'-Nitroacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN2256
CAS No.:121-89-1
- ST 1936 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7919
CAS No.:1210-81-7
- N-Acetyl-5-Hydroxytryptamine
Catalog No.:BCC9080
CAS No.:1210-83-9
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
Activation of cardiac ryanodine receptors by the calcium channel agonist FPL-64176.[Pubmed:12063306]
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002 Jul;283(1):H331-8.
We investigated the possibility that the Ca(2+) channel agonist FPL-64176 (FPL) might also activate the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) release channel ryanodine receptor (RyR). The effects of FPL were tested on single channel activity of purified and crude vesicular RyR (RyR2) isolated from human and dog hearts using the planar lipid bilayer technique. FPL (100-200 microM) increased single channel open probability (P(o)) when added to the cytoplasmic side of the channel (P(o) = 0.070 +/- 0.021 in control RyR2; 0.378 +/- 0.086 in 150 microM FPL, n = 9, P < 0.01) by prolonging open times and decreasing closed times without changing current magnitude. FPL had no effect on P(o) when added to the trans (luminal) side of the bilayer (P(o) = 0.079 +/- 0.036 in control and 0.103 +/- 0.066 in FPL, n = 4, no significant difference). The bell-shaped [Ca(2+)] dependence of [(3)H]ryanodine binding and of P(o) was altered by FPL, suggesting that the mechanism by which FPL increases channel activity is by an increase in Ca(2+)-induced activation at low [Ca(2+)] (without a change in threshold) and suppression of Ca(2+)-induced inactivation at high [Ca(2+)]. However, the fact that inactivation was restored at elevated [Ca(2+)] suggests a competitive interaction between Ca(2+) and FPL on inactivation. FPL had no effect on RyR skeletal channels (RyR1), where P(o) was 0.039 +/- 0.005 in control versus 0.030 +/- 0.006 in 150 microM FPL (no significant difference). These results suggest that, in addition to its ability to activate the L-type Ca(2+) channels, FPL activates cardiac RyR2 primarily by reducing the Ca(2+) sensitivity of inactivation.
FPL 64176 modification of Ca(V)1.2 L-type calcium channels: dissociation of effects on ionic current and gating current.[Pubmed:15501945]
Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88(1):211-23.
FPL 64176 (FPL) is a nondihydropyridine compound that dramatically increases macroscopic inward current through L-type calcium channels and slows activation and deactivation. To understand the mechanism by which channel behavior is altered, we compared the effects of the drug on the kinetics and voltage dependence of ionic currents and gating currents. Currents from a homogeneous population of channels were obtained using cloned rabbit Ca(V)1.2 (alpha1C, cardiac L-type) channels stably expressed in baby hamster kidney cells together with beta1a and alpha2delta1 subunits. We found a striking dissociation between effects of FPL on ionic currents, which were modified strongly, and on gating currents, which were not detectably altered. Inward ionic currents were enhanced approximately 5-fold for a voltage step from -90 mV to +10 mV. Kinetics of activation and deactivation were slowed dramatically at most voltages. Curiously, however, at very hyperpolarized voltages (< -250 mV), deactivation was actually faster in FPL than in control. Gating currents were measured using a variety of inorganic ions to block ionic current and also without blockers, by recording gating current at the reversal potential for ionic current (+50 mV). Despite the slowed kinetics of ionic currents, FPL had no discernible effect on the fundamental movements of gating charge that drive channel gating. Instead, FPL somehow affects the coupling of charge movement to opening and closing of the pore. An intriguing possibility is that the drug causes an inactivated state to become conducting without otherwise affecting gating transitions.
FPL-64176 alters both charge movement and Ca2+ release properties in amphibian muscle fibres.[Pubmed:15061146]
Pflugers Arch. 2004 Mar;447(6):922-7.
A number of recent reports have suggested that ryanodine receptor (RyR)-Ca2+ release channels are gated by tubular depolarization in skeletal muscle through their direct coupling to intramembrane dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR)-voltage sensors. The qgama charge movement, which is inhibited by DHPR antagonists, is often regarded as the electrical signature for the voltage sensing process, yet pharmacological modifications of the RyR produce reciprocal upstream kinetic effects on an otherwise conserved qgamma charge. This study investigates the effect of DHPR-specific agonists upon intramembrane charge and the release of intracellularly stored Ca2+. We empirically demonstrate kinetic effects of FPL-64176 upon charge movements that closely resemble the consequences of previous interventions directed instead at the RyR. Increases in extracellular FPL-64176 concentration from 10 to 40 microM converted delayed qgamma transients to monotonic decays indistinguishable from the exponential qbeta current component. Yet total steady-state intramembrane charge and the steepness of its dependence upon test potential closely resembled previous reports from untreated fibres. These changes accompanied an appearance of transient cytosolic [Ca2+] elevations in confocal line-scans in fluo-3-loaded fibres studied in 10mM K+ and 40, but not 10 microM, FPL-64176 that resembled elementary Ca2+ release events ('sparks'). Pharmacological manipulations of the DHPR whose effects on intramembrane charge resembled those from manoeuvres directed at the RyR can thus produce downstream effects upon Ca2+ release.
The calcium channel ligand FPL 64176 enhances L-type but inhibits N-type neuronal calcium currents.[Pubmed:12842134]
Neuropharmacology. 2003 Aug;45(2):281-92.
One strategy for isolating neuronal L-type calcium (Ca(2+)) currents, which typically comprise a minority of the whole cell current in neurons, has been to use pharmacological agents that increase channel activity. This study examines the effects of the benzoyl pyrrole FPL 64176 (FPL) on L-type Ca(2+) currents and compares them to those of the dihydropyridine (+)-202-791. At micromolar concentrations, both agonists increased whole cell current amplitude in PC12 cells. However, FPL also significantly slowed the rate of activation and elicited a longer-lasting slow component of the tail current compared to (+)-202-791. In single channel cell-attached patch recordings, FPL increased open probability, first latency, mean closed time and mean open time more than (+)-202-791, with no difference in unitary conductance. These gating differences suggest that, compared to (+)-202-791, FPL decreases transition rates between open and closed conformations. Where examined, the actions of FPL and (+)-202-791 on whole cell L-type currents in sympathetic neurons appeared similar to those in PC12 cells. In contrast to its effects on L-type current, 10 microM FPL inhibited the majority of the whole cell current in HEK cells expressing a recombinant N-type Ca(2+) channel, raising caution concerning the use of FPL as a selective L-type Ca(2+) channel agonist in neurons.
Discovery and synthesis of methyl 2,5-dimethyl-4-[2- (phenylmethyl)benzoyl]-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate (FPL 64176) and analogues: the first examples of a new class of calcium channel activator.[Pubmed:7692047]
J Med Chem. 1993 Sep 17;36(19):2739-44.
Methyl 2,5-dimethyl-4-[2-(phenylmethyl)benzoyl]-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, FPL 64176 (1), is the first example of a new class of calcium channel activator (CCA) that does not act on any of the well-defined calcium channel modulator receptor sites, as typified by verapamil, diltiazem, and the dihydropyridines. The potent activity of 1, having the 2-(phenylmethyl)benzoyl substituent, was predicted using QSAR on an initial set of less potent benzoylpyrroles. When compared to the CCA Bay K 8644, 1 has similar potency on calcium uptake into GH3 cells (both have EC50 approximately 0.015 microM) but is appreciably more potent functionally at increasing contractility in a guinea pig atria preparation (1 has EC50 = 0.049 microM vs Bay K 8644 EC50 = 1.95 microM). 1 is an achiral, pharmacologically clean agonist with no demonstrable partial agonist properties and possesses appreciably higher efficacy than Bay K 8644. It should therefore become a useful biochemical and pharmacological tool for the study of calcium channels in many cell types.
Comparison of the in vitro and in vivo cardiovascular effects of two structurally distinct Ca++ channel activators, BAY K 8644 and FPL 64176.[Pubmed:7685384]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jun;265(3):1125-30.
We compared the cardiovascular effects of two structurally distinct L-type Ca++ channel activators, the 1,4-dihydropyridine Bay K 8644 and the benzoylpyrrole FPL 64176. Both compounds prolonged action potential duration and enhanced contractility in guinea pig papillary muscle with these responses being greater in the presence of FPL 64176 compared to (S)-Bay K 8644. (S)-Bay K 8644 (300 nM) and FPL 64176 (300 nM) increased whole-cell Ca++ channel current amplitude in neonatal rat ventricular cells by 249 +/- 14 and 484 +/- 100%, respectively. (S)-Bay K 8644 had little effect on Ca++ channel activation but significantly enhanced the rate of Ca++ channel current inactivation. FPL 64176 significantly slowed Ca++ channel current activation and inactivation. Tail current decay at -50 mV was monoexponential in the presence of (S)-Bay K 8644 and had a time constant of 4.59 +/- 0.16 msec. FPL 64176 produced biexponential tail current decays at -50 mV with fast and slow time constants of 4.30 +/- 0.30 and 44.52 +/- 4.56 msec, respectively. Intravenous administration (1-100 micrograms/kg) of Bay K 8644 and FPL 64176 produced large increases in cardiac contractile force and diastolic blood pressure in anesthetized dogs. Pretreatment with nifedipine attenuated the blood pressure response to FPL 64176 but not the effects on cardiac contractility. This study demonstrates that the benzoylpyrrole FPL 64176 defines a new and potent class of Ca++ channel agonist molecule and that this compound has pharmacological activity that differs, at least in some respects, from the 1,4-dihydropyridine group of agonists.
Pharmacological, radioligand binding, and electrophysiological characteristics of FPL 64176, a novel nondihydropyridine Ca2+ channel activator, in cardiac and vascular preparations.[Pubmed:1719369]
Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):734-41.
The pharmacological, radioligand binding, and electrophysiological properties of FPL 64176, a new nondihydropyridine Ca2+ channel activator, were studied in rat tail artery, cardiac membranes, and A7r5 smooth muscle cells. FPL 64176 induced a contractile response, with an EC50 value of 2.11 x 10(-7) M. The maximum tension response to FPL 64176 was approximately 2-fold higher than that to (S)-Bay K 8644. FPL 64176 showed no significant inhibitory activity at concentrations up to 10(-5) M. The Ca2+ channel antagonists nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem noncompetitively antagonized and completely relaxed the responses induced by FPL 64176. IC50 values of these three drugs were 5.22 x 10(-9), 1.31 x 10(-7), and 1.95 x 10(-7) M, respectively, for relaxing submaximum contractile responses to FPL 64176 (5 x 10(-7) M). The washout time for FPL 64176 was about 40 min, which was much longer than that for (S)-Bay K 8644 (within 1 min). FPL 64176 weakly inhibited (+)-[3H]PN 200-110, [3H]D888, and [3H]TA-3090 binding in rat cardiac membranes, with IC50 values of 1.04 x 10(-5) M and 7.03 x 10(-6) M for inhibition of (+)-[3H]PN 200-110 and [3H]TA-3090 binding, respectively, and with 23% inhibition of [3H]D888 binding at a FPL 64176 concentration of 1 x 10(-5) M. Dissociation kinetics of the three radioligands were allosterically accelerated by FPL 64176. Electrophysiological studies on the A7r5 smooth muscle cell line directly confirmed a large (approximately 14-fold) stimulatory effect on L-type Ca2+ current amplitude. The results suggest that FPL 64176 is a new type of Ca2+ channel activator with higher efficacy and a mechanism and site of action that are distinct from those for (S)-Bay K 8644.


