LEE011CDK4/6 inhibitor CAS# 1211441-98-3 |
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- CDK4 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4242
CAS No.:1256963-02-6
- R547
Catalog No.:BCC3927
CAS No.:741713-40-6
- PHA-848125
Catalog No.:BCC3839
CAS No.:802539-81-7
- P276-00
Catalog No.:BCC4415
CAS No.:920113-03-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1211441-98-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44631912 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H30N8O | M.Wt | 434.54 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ribociclib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 5.4 mg/mL (12.43 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
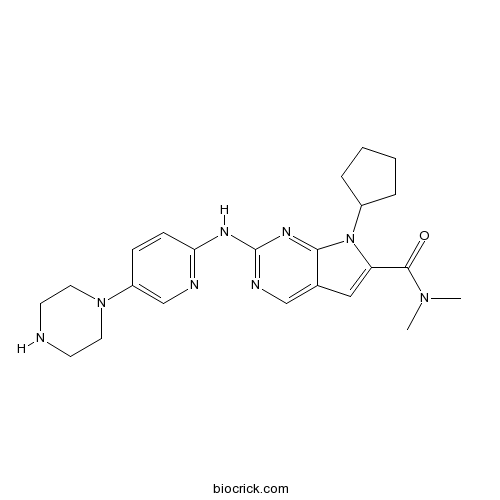
| Chemical Name | 7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C(=O)C1=CC2=CN=C(N=C2N1C3CCCC3)NC4=NC=C(C=C4)N5CCNCC5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RHXHGRAEPCAFML-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H30N8O/c1-29(2)22(32)19-13-16-14-26-23(28-21(16)31(19)17-5-3-4-6-17)27-20-8-7-18(15-25-20)30-11-9-24-10-12-30/h7-8,13-15,17,24H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26,27,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | LEE011 is an orally available and highly specific inhibitor of CDK4/6. | |||||
| Targets | CDK4 | CDK6 | ||||

LEE011 Dilution Calculator

LEE011 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3013 mL | 11.5064 mL | 23.0128 mL | 46.0257 mL | 57.5321 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4603 mL | 2.3013 mL | 4.6026 mL | 9.2051 mL | 11.5064 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2301 mL | 1.1506 mL | 2.3013 mL | 4.6026 mL | 5.7532 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.046 mL | 0.2301 mL | 0.4603 mL | 0.9205 mL | 1.1506 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.023 mL | 0.1151 mL | 0.2301 mL | 0.4603 mL | 0.5753 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
LEE011 (NVP-LEE011) is a highly specific inhibitor of CDK4/CDK6 and functions via decreasing in phosphorylated RB and FOXM1 [1]. When tested with 17 human neuroblastoma cell lines, 12 of them were sensitive to LEE011 treatment with mean IC50=306±68 nM [2].
CDK4/6 could increase G1-S phase cell cycle progression and ultimately cellular proliferation via phosphorylating tumor suppressor protein RB. CDK4/6 signaling also could senescence suppression by regulating FOXM1 transcription[3]. Numerous studies have shown that over-expression of CDK4/CDK6 correlated with tumorigenesis and disease progression [4].
LEE011 is a novel inhibitor for CDK4/CDK6. When subjected to human liposarcoma cell lines, treated with LEE011 could dramatically decrease cell growth via arresting cell cycle G0-G1 [1]. In 12 of 17 human neuroblastoma-derived cell lines, treatment with LEE011 could significantly reduce cell proliferation [2].
In a mouse model with human liposarcoma xerography, continued treating the mouse with LEE011 orally could inhibit tumor growth or induce regression without detrimental effects on mouse weight [1]. In mice xerography with neuroblastoma cells, treated with LEE011 could inhibit the tumor growth [2].
References:
1.Zhang, Y.X., et al., Antiproliferative effects of CDK4/6 inhibition in CDK4-amplified human liposarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther, 2014. 13(9): p. 2184-93.
2.Rader, J., et al., Dual CDK4/CDK6 inhibition induces cell-cycle arrest and senescence in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res, 2013. 19(22): p. 6173-82.
3.Paternot, S., et al., The CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor PD0332991 paradoxically stabilizes activated cyclin D3-CDK4/6 complexes. Cell Cycle, 2014. 13(18): p. 2879-88.
4.Dickson, M.A., Molecular pathways: CDK4 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res, 2014. 20(13): p. 3379-83.
- Cefprozil hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4951
CAS No.:121123-17-9
- EG00229
Catalog No.:BCC5376
CAS No.:1210945-69-9
- L-670,596
Catalog No.:BCC5857
CAS No.:121083-05-4
- 3-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3184
CAS No.:121072-40-0
- 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4724
CAS No.:121064-78-6
- Melanotan II
Catalog No.:BCC7414
CAS No.:121062-08-6
- Abiesadine I
Catalog No.:BCN6104
CAS No.:1210347-50-4
- PF-04971729
Catalog No.:BCC1852
CAS No.:1210344-57-2
- IEM 1460
Catalog No.:BCC7135
CAS No.:121034-89-7
- Nelarabine
Catalog No.:BCC1072
CAS No.:121032-29-9
- Secretin (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5848
CAS No.:121028-49-7
- JZL 195
Catalog No.:BCC7966
CAS No.:1210004-12-8
- LEE011 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4101
CAS No.:1211443-80-9
- Rauvoyunine C
Catalog No.:BCN4833
CAS No.:1211543-01-9
- TC-N 1752
Catalog No.:BCC6179
CAS No.:1211866-85-1
- [Ala1,3,11,15]-Endothelin
Catalog No.:BCC5731
CAS No.:121204-87-3
- Secodihydro-hydramicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN4783
CAS No.:1212148-58-7
- Calphostin C
Catalog No.:BCC7131
CAS No.:121263-19-2
- ICI 204,448 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6806
CAS No.:121264-04-8
- Alendronate
Catalog No.:BCC4885
CAS No.:121268-17-5
- RWJ 21757
Catalog No.:BCC7460
CAS No.:121288-39-9
- 1-Hydroxybisabola-2,10-dien-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN7297
CAS No.:1213251-45-6
- WZ4002
Catalog No.:BCC1074
CAS No.:1213269-23-8
- Fmoc-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3489
CAS No.:121343-82-6
Molecular mechanism of G1 arrest and cellular senescence induced by LEE011, a novel CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor, in leukemia cells.[Pubmed:28286417]
Cancer Cell Int. 2017 Mar 6;17:35.
BACKGROUND: Overexpression of cyclin D1 dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) is a common feature of many human cancers including leukemia. LEE011 is a novel inhibitor of both CDK4 and 6. To date, the molecular function of LEE011 in leukemia remains unclear. METHODS: Leukemia cell growth and apoptosis following LEE011 treatment was assessed through CCK-8 and annexin V/propidium iodide staining assays. Cell senescence was assessed by beta-galactosidase staining and p16(INK4a) expression analysis. Gene expression profiles of LEE011 treated HL-60 cells were investigated using an Arraystar Human LncRNA array. Gene ontology and KEGG pathway analysis were then used to analyze the differentially expressed genes from the cluster analysis. RESULTS: Our studies demonstrated that LEE011 inhibited proliferation of leukemia cells and could induce apoptosis. Hoechst 33,342 staining analysis showed DNA fragmentation and distortion of nuclear structures following LEE011 treatment. Cell cycle analysis showed LEE011 significantly induced cell cycle G1 arrest in seven of eight acute leukemia cells lines, the exception being THP-1 cells. beta-Galactosidase staining analysis and p16(INK4a) expression analysis showed that LEE011 treatment can induce cell senescence of leukemia cells. LncRNA microarray analysis showed 2083 differentially expressed mRNAs and 3224 differentially expressed lncRNAs in LEE011-treated HL-60 cells compared with controls. Molecular function analysis showed that LEE011 induced senescence in leukemia cells partially through downregulation of the transcriptional expression of MYBL2. CONCLUSIONS: We demonstrate for the first time that LEE011 treatment results in inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of G1 arrest and cellular senescence in leukemia cells. LncRNA microarray analysis showed differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in LEE011-treated HL-60 cells and we demonstrated that LEE011 induces cellular senescence partially through downregulation of the expression of MYBL2. These results may open new lines of investigation regarding the molecular mechanism of LEE011 induced cellular senescence.
Ribociclib (LEE011): Mechanism of Action and Clinical Impact of This Selective Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor in Various Solid Tumors.[Pubmed:28351928]
Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 1;23(13):3251-3262.
The cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6-p16-retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway is commonly disrupted in cancer, leading to abnormal cell proliferation. Therapeutics targeting this pathway have demonstrated antitumor effects in preclinical and clinical studies. Ribociclib is a selective, orally bioavailable inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6, which received FDA approval in March 2017 and is set to enter the treatment landscape alongside other CDK4/6 inhibitors, including palbociclib and abemaciclib. Here, we describe the mechanism of action of ribociclib and review preclinical and clinical data from phase I, II, and III trials of ribociclib across different tumor types, within the context of other selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, tolerability, and clinical responses with ribociclib as a single agent or in combination with other therapies are discussed, and an overview of the broad portfolio of ongoing clinical trials with ribociclib across a wide range of indications is presented. On the basis of the available data, ribociclib has a manageable tolerability profile and therapeutic potential for a variety of cancer types. Its high selectivity makes it an important partner drug for other targeted therapies, and it has been shown to enhance the clinical activity of existing anticancer therapies and delay the development of treatment resistance, without markedly increasing toxicity. Ongoing trials of doublet and triplet targeted therapies containing ribociclib seek to identify optimal CDK4/6-based targeted combination regimens for various tumor types and advance the field of precision therapeutics in oncology. Clin Cancer Res; 23(13); 3251-62. (c)2017 AACR.
A Phase I Study of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors and Lymphomas.[Pubmed:27542767]
Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 1;22(23):5696-5705.
PURPOSE: Ribociclib (an oral, highly specific cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor) inhibits tumor growth in preclinical models with intact retinoblastoma protein (Rb(+)). This first-in-human study investigated the MTD, recommended dose for expansion (RDE), safety, preliminary activity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of ribociclib in patients with Rb(+) advanced solid tumors or lymphomas. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Patients received escalating doses of ribociclib (3-weeks-on/1-week-off or continuous). Dose escalation was guided by a Bayesian Logistic Regression Model with overdose control principle. RESULTS: Among 132 patients, 125 received ribociclib 3-weeks-on/1-week-off and 7 were dosed continuously. Nine dose-limiting toxicities were observed among 70 MTD/RDE evaluable patients during cycle 1, most commonly neutropenia (n = 3) and thrombocytopenia (n = 2). The MTD and RDE were established as 900 and 600 mg/day 3-weeks-on/1-week-off, respectively. Common treatment-related adverse events were (all-grade; grade 3/4) neutropenia (46%; 27%), leukopenia (43%; 17%), fatigue (45%; 2%), and nausea (42%; 2%). Asymptomatic Fridericia's corrected QT prolongation was specific to doses >/=600 mg/day (9% of patients at 600 mg/day; 33% at doses >600 mg/day). Plasma exposure increases were slightly higher than dose proportional; mean half-life at the RDE was 32.6 hours. Reduced Ki67 was observed in paired skin and tumor biopsies, consistent with ribociclib-mediated antiproliferative activity. There were 3 partial responses and 43 patients achieved a best response of stable disease; 8 patients were progression-free for >6 months. CONCLUSIONS: Ribociclib demonstrated an acceptable safety profile, dose-dependent plasma exposure, and preliminary signs of clinical activity. Phase I-III studies of ribociclib are under way in various indications. Clin Cancer Res; 22(23); 5696-705. (c)2016 AACR.
The Novel Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) Alone and in Dual-Targeting Approaches Demonstrates Antitumoral Efficacy in Neuroendocrine Tumors in vitro.[Pubmed:28226315]
Neuroendocrinology. 2018;106(1):58-73.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are crucial for cell cycle regulation, and alterations in the cell cycle are often observed in human cancer. CDK4/6 in particular orchestrates G1 phase progression and the G1/S transition. Here, we investigated the in vitro effects of the CDK4/6 inhibitor LEE011 in human neuroendocrine tumor cells. METHODS: The human neuroendocrine tumor cell lines BON1, QGP1, NCI-H727 and GOT1 were treated with different concentrations of LEE011 alone and in combination with 5-fluorouracil and everolimus. RESULTS: Cell viability decreased in a time- and dose-dependent manner in BON1, QGP1, and NCI-H727 cells upon LEE011 treatment, whereas GOT1 cells were treatment resistant. Treatment sensitivity towards LEE011 was associated with the high expression of cyclin D1 and Rb. LEE011 caused the dephosphorylation of Rb and a subsequent G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Combined treatment with LEE011 and 5-fluorouracil or everolimus showed a significant enhancement in the inhibition of cell viability when compared to single-substance treatments due to PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway downregulation and cooperative downregulation of cell cycle components. However, LEE011 also exhibited antagonizing effects with 5-fluorouracil, protecting NET cells from DNA-damaging chemotherapy by blocking PARP cleavage and caspase-3/7 activity. CONCLUSIONS: Our data demonstrate that the CDK 4/6 inhibitor LEE011 exhibits promising anti-tumoral properties alone and in combination treatment approaches with 5-fluorouracil or everolimus in human neuroendocrine tumor cell lines.


