AngelicinCAS# 523-50-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 523-50-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10658 | Appearance | White powder |
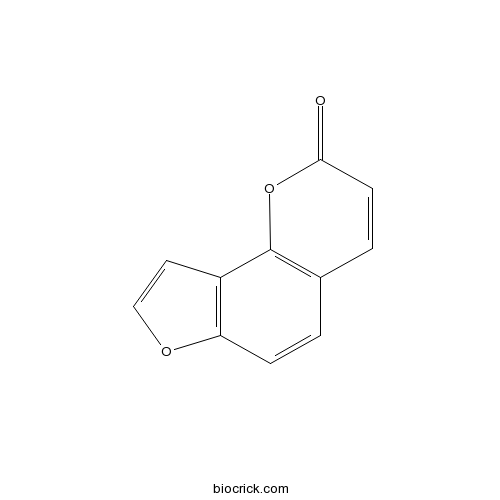
| Formula | C11H6O3 | M.Wt | 186.2 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Isopsoralen | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (179.04 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | furo[2,3-h]chromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=CO2)C3=C1C=CC(=O)O3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XDROKJSWHURZGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Angelicin has anti-cancer, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities; it regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Angelicin is a powerful inducer of erythroid differentiation and -globin mRNA accumulation of human leukemia K562 cells, it is a potential therapeutic approach in hematological disorders, including -beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia. |
| Targets | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | p38MAPK | JNK | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | PI3K | Akt | GSK-3 | Antifection | IKK |
| In vitro | Angelicin regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB pathways.[Pubmed: 23816246]J Surg Res. 2013 Nov;185(1):300-9.Angelicin is a furocoumarin found in Psoralea corylifolia L. fruit. The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective ability of Angelicin against inflammation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and LPS-induced in vivo acute lung injury model.
Anti-influenza drug discovery: structure-activity relationship and mechanistic insight into novel angelicin derivatives.[Pubmed: 20092255 ]J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53(4):1519-33.
Accumulation of gamma-globin mRNA in human erythroid cells treated with angelicin.[Pubmed: 12930320]Eur J Haematol. 2003 Sep;71(3):189-95.
The aim of the present study was to determine whether Angelicin is able to increase the expression of gamma-globin genes in human erythroid cells. Angelicin is structurally related to psoralens, a well-known chemical class of photosensitizers used for their antiproliferative activity in treatment of different skin diseases (i.e., psoriasis and vitiligo).
|
| Cell Research | Angelicin induces apoptosis through intrinsic caspase-dependent pathway in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.[Pubmed: 22766766]Antiviral activity of angelicin against gammaherpesviruses.[Pubmed: 23892155]Antiviral Res. 2013 Oct;100(1):75-83.Human gammaherpesviruses including Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) are important pathogens as they persist in the host and cause various malignancies. However, few antiviral drugs are available to efficiently control gammaherpesvirus replication. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Oct;369(1-2):95-104.Angelicin is structurally related to psoralens, a well-known chemical class of photosensitizers used for its antiproliferative activity in treatment of different skin diseases. To verify the activity of Angelicin, we employed human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells to investigate its cytotoxicity, although its mechanism of action has not yet been fully elucidated.
|

Angelicin Dilution Calculator

Angelicin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.3706 mL | 26.8528 mL | 53.7057 mL | 107.4114 mL | 134.2642 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0741 mL | 5.3706 mL | 10.7411 mL | 21.4823 mL | 26.8528 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5371 mL | 2.6853 mL | 5.3706 mL | 10.7411 mL | 13.4264 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1074 mL | 0.5371 mL | 1.0741 mL | 2.1482 mL | 2.6853 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.5371 mL | 1.0741 mL | 1.3426 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Angelicin, a furocoumarin naturally occurring tricyclic aromatic compound, structurally related to psoralens, is reported to have anti-cancer, antiviral, anti-inflammatory activity. IC50 value: 49.56 μM (cellular cytotoxicity); 5.39 μg/ml (28.95 μM) (against MHV-68) Target: In vitro: In human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, angelicin increased cellular cytotoxicity in a dose- and time-dependent manner with IC50 of 49.56 μM at 48 h of incubation. Angelicin dose-dependently downregulated the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins including Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1; Angelicin-induced apoptosis is mediated primarily through the intrinsic caspase-mediated pathway[1]. Angelicin efficiently inhibited 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced lytic replication of human gammaherpresviruses in both EBV- and KSHV-infected cells [2]. Angelicin was potentially advantageous to prevent inflammatory diseases by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways [3]. In vivo:
References:
[1]. Md. Ataur Rahman, Angelicin induces apoptosis through intrinsic caspase-dependent pathway in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry October 2012, Volume 369, Issue 1-2, pp 95-104
[2]. Hye-Jeong Cho, et al. Antiviral activity of angelicin against gammaherpesviruses. Antiviral Research Volume 100, Issue 1, October 2013, Pages 75–83
[3]. Fang Liu, et al. Angelicin regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Journal of Surgical Research Volume 185, Issue 1, November 2013, Pages 300–309
- 4-Amino-2,5-dimethoxy-N-phenylbenzenesulphonamide
Catalog No.:BCC8676
CAS No.:52298-44-9
- Ginsenoside Rg2
Catalog No.:BCN1067
CAS No.:52286-74-5
- Ginsenoside Re
Catalog No.:BCN1073
CAS No.:52286-59-6
- Ginsenoside Rf
Catalog No.:BCN1075
CAS No.:52286-58-5
- 3,5-Diprenyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN4624
CAS No.:52275-04-4
- CGP 57380
Catalog No.:BCC5279
CAS No.:522629-08-9
- Isomucronulatol
Catalog No.:BCN1428
CAS No.:52250-35-8
- Parathyroid hormone (1-34) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1046
CAS No.:52232-67-4
- Kaempferol-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8130
CAS No.:52222-74-9
- Ciprofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC2266
CAS No.:52214-84-3
- 3-Epicorosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5666
CAS No.:52213-27-1
- Lamalbid
Catalog No.:BCN3750
CAS No.:52212-87-0
- Evolitrine
Catalog No.:BCN8350
CAS No.:523-66-0
- Flavoglaucin
Catalog No.:BCN6398
CAS No.:523-73-9
- Anisatin
Catalog No.:BCC8118
CAS No.:5230-87-5
- Vindorosine
Catalog No.:BCN5668
CAS No.:5231-60-7
- p,p-hydroxy-curucumin
Catalog No.:BCC8890
CAS No.:52328-96-8
- Tetramethylcurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2746
CAS No.:52328-97-9
- Dimethylcurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2748
CAS No.:52328-98-0
- 6alpha-Chloro-5beta-hydroxywithaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN8007
CAS No.:52329-20-1
- Alnusone
Catalog No.:BCN8108
CAS No.:52330-11-7
- 2-Benzoyl-1,3,4,4a,5,8a-hexahydro-6(2H)-isoquinolinone
Catalog No.:BCC8559
CAS No.:52346-14-2
- Erysotramidine
Catalog No.:BCN5670
CAS No.:52358-58-4
- Epistephamiersine
Catalog No.:BCN5671
CAS No.:52389-15-8
Angelicin induces apoptosis through intrinsic caspase-dependent pathway in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.[Pubmed:22766766]
Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Oct;369(1-2):95-104.
Angelicin is structurally related to psoralens, a well-known chemical class of photosensitizers used for its antiproliferative activity in treatment of different skin diseases. To verify the activity of Angelicin, we employed human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells to investigate its cytotoxicity, although its mechanism of action has not yet been fully elucidated. Here, we examined the cellular cytotoxicity of Angelicin by cell viability assay, DNA fragmentation by DNA ladder assay, and activation of caspases and Bcl-2 family proteins by western blot analyses. The results of our investigation suggest that Angelicin increased cellular cytotoxicity in a dose- and time-dependent manner with IC(50) of 49.56 muM at 48 h of incubation. In addition, Angelicin dose-dependently downregulated the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins including Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 suggesting the involvement of the intrinsic mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway which did not participate in Fas/FasL-induced caspase-8-mediated extrinsic, MAP kinases, and PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta pathway. Furthermore, we clarified the dose-dependent upregulation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 which indicated that Angelicin-induced apoptosis is mediated primarily through the intrinsic caspase-mediated pathway. In particular, the caspase-3 inhibitor, DEVD-fmk, induced a reduction in Angelicin-induced cytotoxicity which confirmed that the intrinsic caspase-dependent pathway during this apoptosis which did not prevent cytotoxicity using MAP kinases and GSK-3 inhibitor. Taken together, our data shows that Angelicin is an effective apoptosis-inducing natural compound of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells which suggests that this compound may have a role in future therapies for human neuroblastoma cancer.
Anti-influenza drug discovery: structure-activity relationship and mechanistic insight into novel angelicin derivatives.[Pubmed:20092255]
J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1519-33.
By using a cell-based high throughput screening campaign, a novel Angelicin derivative 6a was identified to inhibit influenza A (H1N1) virus induced cytopathic effect in Madin-Darby canine kidney cell culture in low micromolar range. Detailed structure-activity relationship studies of 6a revealed that the Angelicin scaffold is essential for activity in pharmacophore B, while meta-substituted phenyl/2-thiophene rings are optimal in pharmacophore A and C. The optimized lead 4-methyl-9-phenyl-8-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-furo[2,3-h]chromen-2-one (8g, IC(50) = 70 nM) showed 64-fold enhanced activity compared to the high throughput screening (HTS) hit 6a. Also, 8g was found effective in case of influenza A (H3N2) and influenza B virus strains similar to approved anti-influenza drug zanamivir (4). Preliminary mechanistic studies suggest that these compounds act as anti-influenza agents by inhibiting ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex associated activity and have the potential to be developed further, which could form the basis for developing additional defense against influenza pandemics.
Accumulation of gamma-globin mRNA in human erythroid cells treated with angelicin.[Pubmed:12930320]
Eur J Haematol. 2003 Sep;71(3):189-95.
The aim of the present study was to determine whether Angelicin is able to increase the expression of gamma-globin genes in human erythroid cells. Angelicin is structurally related to psoralens, a well-known chemical class of photosensitizers used for their antiproliferative activity in treatment of different skin diseases (i.e., psoriasis and vitiligo). To verify the activity of Angelicin, we employed two experimental cell systems, the human leukemic K562 cell line and the two-phase liquid culture of human erythroid progenitors isolated from normal donors. The results of our investigation suggest that Angelicin, compared with cytosine arabinoside, mithramycin and cisplatin, is a powerful inducer of erythroid differentiation and gamma-globin mRNA accumulation of human leukemia K562 cells. In addition, when normal human erythroid precursors were cultured in the presence of Angelicin, increases of gamma-globin mRNA accumulation and fetal hemoglobin (HbF) production, even higher than those obtained using hydroxyurea, were detected. These results could have practical relevance, as pharmacologically-mediated regulation of the expression of human gamma-globin genes, leading to HbF induction, is considered a potential therapeutic approach in hematological disorders, including beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia.
Antiviral activity of angelicin against gammaherpesviruses.[Pubmed:23892155]
Antiviral Res. 2013 Oct;100(1):75-83.
Human gammaherpesviruses including Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) are important pathogens as they persist in the host and cause various malignancies. However, few antiviral drugs are available to efficiently control gammaherpesvirus replication. Here we identified the antiviral activity of Angelicin against murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68), genetically and biologically related to human gammaherpesviruses. Angelicin, a furocoumarin naturally occurring tricyclic aromatic compound, efficiently inhibited lytic replication of MHV-68 in a dose-dependent manner following the virus entry. The IC50 of Angelicin antiviral activity was estimated to be 28.95muM, while the CC50 of Angelicin was higher than 2600muM. Furthermore, incubation with Angelicin efficiently inhibited 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced lytic replication of human gammaherpresviruses in both EBV- and KSHV-infected cells. Taken together, these results suggest that MHV-68 can be a useful tool to screen novel antiviral agents against human gammaherepsviruses and that Angelicin may provide a lead structure for the development of antiviral drug against gammaherpesviruses.
Angelicin regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-kappaB pathways.[Pubmed:23816246]
J Surg Res. 2013 Nov;185(1):300-9.
BACKGROUND: Angelicin is a furocoumarin found in Psoralea corylifolia L. fruit. The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective ability of Angelicin against inflammation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and LPS-induced in vivo acute lung injury model. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin (IL)-6 in the culture supernatants of RAW 264.7 cells were determined 24 h after LPS administration. ALI was induced by intratracheal instillation of LPS. Six hours after LPS inhalation, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and lung tissue samples were obtained for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, histologic, and Western blotting analyses. RESULTS: The results showed that pretreatment with Angelicin markedly downregulated TNF-alpha and IL-6 levels in vitro and in vivo, and significantly decreased the amount of inflammatory cells, lung wet-to-dry weight ratio, and myeloperoxidase activity in LPS-induced ALI mice. Furthermore, Western blotting analysis results demonstrated that Angelicin blocked the phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha, NF-kappaBp65, p38 MAPK, and JNK in LPS-induced ALI. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that Angelicin was potentially advantageous to prevent inflammatory diseases by inhibiting NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. Our data indicated that Angelicin might be a potential new agent for prevention of inflammatory reactions and diseases in the clinic.


