CGP 57380MNK1 inhibitor, specific and selective CAS# 522629-08-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 522629-08-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11644425 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H9FN6 | M.Wt | 244.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 6 mg/mL (24.57 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-N-(4-fluorophenyl)-2H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-3,4-diamine | ||
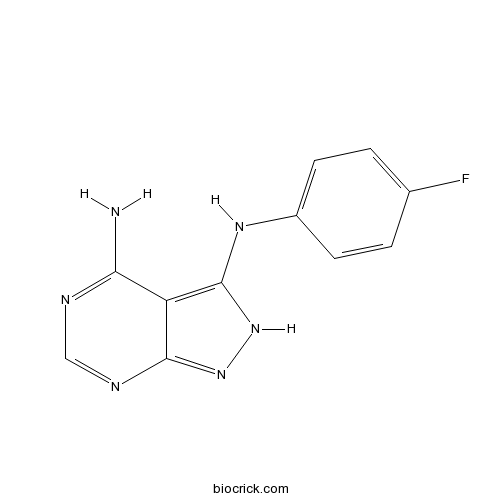
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1NC2=C3C(=NC=NC3=NN2)N)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UQPMANVRZYYQMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H9FN6/c12-6-1-3-7(4-2-6)16-11-8-9(13)14-5-15-10(8)17-18-11/h1-5H,(H4,13,14,15,16,17,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of MAP-kinase interacting kinase-1 (Mnk1, MKNK1) (IC50 = 2.2 μM) that displays selectivity over p38, JNK1, ERK1, ERK2, PKC and c-src family kinases. Blocks phosphorylation of eIF4E in cellular assays (IC50 = 3 μM) and inhibits LPS-induced TNFα expression in macrophages. |

CGP 57380 Dilution Calculator

CGP 57380 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0945 mL | 20.4725 mL | 40.945 mL | 81.89 mL | 102.3625 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8189 mL | 4.0945 mL | 8.189 mL | 16.378 mL | 20.4725 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4095 mL | 2.0473 mL | 4.0945 mL | 8.189 mL | 10.2363 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0819 mL | 0.4095 mL | 0.8189 mL | 1.6378 mL | 2.0473 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0409 mL | 0.2047 mL | 0.4095 mL | 0.8189 mL | 1.0236 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CGP 57380 is a specific and selective inhibitor of MNK1 with IC50 value of 2.2 μM [1].
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase interacting kinases 1 (MNK1) is a serine/threonine kinase and is able to integrate signal from MAP kinase pathway and phosphorylate eIF4E [1].
CGP 57380 is a specific and selective MNK1 inhibitor. In 293 cells, CGP 57380 (10 μM) inhibited eIF4E phosphorylation in response to fetal calf serum (FCS), arsenite, anisomycin, PMA or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Also, CGP 57380 increased the cap-dependent reporter rluc. In cellular assays, CGP 57380 inhibited eIF4E phosphorylation with IC50 value of 3 μM [1]. In rat vascular smooth muscle cells, CGP 57380 inhibited eIF4E phosphorylation, protein synthesis and VSMC hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II in a dose dependent way [2]. In mouse macrophages, CGP 57380 concentration-dependently inhibited TNFα production stimulated by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) through posttranscriptional regulation. Also, CGP 57380 inhibited eIF4E phosphorylation. These results suggested that adenine/uridine-rich elements (ARE)-containing TNFα mRNA required eIF4E phosphorylation for initiation of translation [3]. In bone marrow-derived macrophages, CGP 57380 significantly inhibited the production of proinflammatory cytokines monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, TNF and IL-6 [4].
References:
[1]. Knauf U, Tschopp C, Gram H. Negative regulation of protein translation by mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting kinases 1 and 2. Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 21(16): 5500-5511.
[2]. Ishida M, Ishida T, Nakashima H, et al. Mnk1 is required for angiotensin II-induced protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res, 2003, 93(12): 1218-1224.
[3]. Andersson K, Sundler R. Posttranscriptional regulation of TNFalpha expression via eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) phosphorylation in mouse macrophages. Cytokine, 2006, 33(1): 52-57.
[4]. Rowlett RM, Chrestensen CA, Nyce M, et al. MNK kinases regulate multiple TLR pathways and innate proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2008, 294(2): G452-459.
- Isomucronulatol
Catalog No.:BCN1428
CAS No.:52250-35-8
- Parathyroid hormone (1-34) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1046
CAS No.:52232-67-4
- Kaempferol-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8130
CAS No.:52222-74-9
- Ciprofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC2266
CAS No.:52214-84-3
- 3-Epicorosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5666
CAS No.:52213-27-1
- Lamalbid
Catalog No.:BCN3750
CAS No.:52212-87-0
- Tetrahydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2648
CAS No.:522-97-4
- Allo-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3487
CAS No.:522-94-1
- Dequalinium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4998
CAS No.:522-51-0
- Tetrahydrozoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4339
CAS No.:522-48-5
- Lochnerine
Catalog No.:BCN5667
CAS No.:522-47-4
- Norsanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN3714
CAS No.:522-30-5
- 3,5-Diprenyl-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN4624
CAS No.:52275-04-4
- Ginsenoside Rf
Catalog No.:BCN1075
CAS No.:52286-58-5
- Ginsenoside Re
Catalog No.:BCN1073
CAS No.:52286-59-6
- Ginsenoside Rg2
Catalog No.:BCN1067
CAS No.:52286-74-5
- 4-Amino-2,5-dimethoxy-N-phenylbenzenesulphonamide
Catalog No.:BCC8676
CAS No.:52298-44-9
- Angelicin
Catalog No.:BCN5669
CAS No.:523-50-2
- Evolitrine
Catalog No.:BCN8350
CAS No.:523-66-0
- Flavoglaucin
Catalog No.:BCN6398
CAS No.:523-73-9
- Anisatin
Catalog No.:BCC8118
CAS No.:5230-87-5
- Vindorosine
Catalog No.:BCN5668
CAS No.:5231-60-7
- p,p-hydroxy-curucumin
Catalog No.:BCC8890
CAS No.:52328-96-8
- Tetramethylcurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2746
CAS No.:52328-97-9
Effect of GABAB receptor antagonists (CGP 35348 and CGP 55845) on serum interleukin 6 and 18 concentrations in albino mice following neonatal hypoxia ischemia insult.[Pubmed:27731803]
Pak J Pharm Sci. 2016 Sep;29(5):1503-1508.
Interleukin (IL) 6 and 18 plays an important role in inflammatory response following hypoxia ischemia encephalopathy (HIE). Present study was designed to demonstrate the effect of two GABAB receptor antagonists (CGP 35348 and 55845), respectively, on the serum IL6 and IL 18 concentrations in albino mice. Albino mice pups (of both genders) were subjected to Murine model of hypoxia-ischemia encephalopathy on postnatal day 10 (right common carotid artery was ligated followed by 8% hypoxia for 25 minutes). After neonatal brain damage and following weaning, mice were divided in three groups, in gender specific manner, and fed on normal rodent diet till they were 13 week old. At this time point, group 1 received intraperitonial saline solution (control group), group 2 was supplemented with CGP 35348 (1mg/ml solvent/Kg body weight) and group 3 with CGP 55845 (1mg/ml solvent/Kg body weight), intraperitonially, for 12 days and IL 6 and 18 concentrations were determined in serum by ELISA. It was observed that CGP 35348 supplementation resulted in reduced interlukin-6 and interlukin-18 concentrations in male albino mice. While CGP 55845 supplementation increased IL-6 and IL-18 concentrations in female albino mice following HIE. Our results are indicating that GABAB receptor antagonist's supplementation affects IL concentrations in albino mice in a gender specific manner following neonatal brain damage and can be further explored for the treatments of hypoxia ischemia associated neurological ailments.
Comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) of ovarian clear cell carcinomas (OCCC) identifies clinically relevant genomic alterations (CRGA) and targeted therapy options.[Pubmed:28349114]
Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2017 Mar 1;20:62-66.
*MTOR pathway genes are often mutated in ovarian clear cell carcinomas (OCCC).*11.2% of OCCC have targetable alterations only in the mTOR pathway.*MTOR pathway mutations in OCCC can underlie robust, lasting responses to everolimus.
Gender-specific effects of CGP 55845, GABAB receptor antagonist, on neuromuscular coordination, learning and memory formation in albino mouse following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia insult.[Pubmed:25847084]
Neurol Sci. 2015 Jun;36(6):961-9.
GABAB receptor antagonists are experimentally proved as spatial memory enhancers in mouse models but their role has not been described following hypoxic-ischemic insult. 10-day-old albino mice were subjected to Murine model of hypoxia and ischemia. Following brain damage, mice were fed on normal rodent diet till they were 13 weeks old. At this time point, mice were divided into two groups. Group 1 received saline and group 2 received intraperitoneally CGP 55845 (1 mg/ml solvent/Kg body weight) for 12 days. Behavioural observations were made during rota rod, open field and Morris water maze test along with brain infarct measurement in both CGP 55845 treated and untreated groups. It was observed that application of GABAB receptor antagonist improved the over all motor function in male and female albino mice but effects were more pronounced in males. In open field, CGP 55845-treated female mice showed poor performance. CGP 55845 had no significant effect on learning and memory formation during Morris water maze test and also on brain infract size in both genders following hypoxia ischemia encephalopathy. Effects of CGP 55845 can be further explored in a dose and duration dependent manner to improve the learning and memory in albino mice following neonatal brain damage.
Posttranscriptional regulation of TNFalpha expression via eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) phosphorylation in mouse macrophages.[Pubmed:16431125]
Cytokine. 2006 Jan 7;33(1):52-7.
Resident mouse macrophages secrete Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) upon challenge with LPS. The production of TNFalpha is controlled not only at the transcription of the gene, but also by strong posttranscriptional regulation. When macrophages are stimulated with LPS different signal transduction pathways become activated. Here we show that the combination of the 2 kinases p38 and MEK and presumably ERK1/2 regulate translation of TNFalpha, through the downstream kinase Mnk1. TNFalpha production is inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner by CGP57380 (Mnk1 inhibitor). The corresponding mRNA results show that the inhibition targets posttranscriptional regulation and is paralleled by inhibition of the phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). Unexpectedly, the activation/inhibition of MAPKAP kinase-2 (MK2) does not parallel TNFalpha production, arguing against a direct/immediate role for this kinase. On the basis of the present and previous results we propose that ARE-containing TNFalpha mRNA requires phosphorylation of eIF4E for initiation of translation.
Mnk1 is required for angiotensin II-induced protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:14605021]
Circ Res. 2003 Dec 12;93(12):1218-24.
Angiotensin II (Ang II) stimulates protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), possibly secondary to regulatory changes at the initiation of mRNA translation. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signal-integrating kinase-1 (Mnk1), a substrate of ERK and p38 MAP kinase, phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), an important factor in translation. The goal of the present study was to investigate the role of Mnk1 in Ang II-induced protein synthesis and to characterize the molecular mechanisms by which Mnk1 and eIF4E is activated in rat VSMCs. Ang II treatment resulted in increased Mnk1 activity and eIF4E phosphorylation. Expression of a dominant-negative Mnk1 mutant abolished Ang II-induced eIF4E phosphorylation. PD98059 or introduction of kinase-inactive MEK1/MKK1, but not SB202190 or kinase-inactive p38 MAP kinase, inhibited Ang II-induced Mnk1 activation and eIF4E phosphorylation, suggesting that ERK, but not p38 MAP kinase, is required for Ang II-induced Mnk1-eIF4E activation. Further, dominant-negative constructs for Ras, but not for Rho, Rac, or Cdc42, abolished Ang II-induced Mnk1 activation. Finally, treatment of VSMCs with CGP57380, a novel specific kinase inhibitor of Mnk1, resulted in dose-dependent decreases in Ang II-stimulated phosphorylation of eIF4E, protein synthesis, and VSMC hypertrophy. In summary, these data demonstrated that (1) Ang II-induced Mnk1 activation is mediated by the Ras-ERK cascade in VSMCs, and (2) Mnk1 is involved in Ang II-mediated protein synthesis and hypertrophy, presumably through the activation of translation-initiation. The Mnk1-eIF4E pathway may provide new insights into molecular mechanisms involved in vascular hypertrophy and other Ang II-mediated pathological states.
Negative regulation of protein translation by mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting kinases 1 and 2.[Pubmed:11463832]
Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(16):5500-11.
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) is a key component of the translational machinery and an important modulator of cell growth and proliferation. The activity of eIF4E is thought to be regulated by interaction with inhibitory binding proteins (4E-BPs) and phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-interacting kinase (MNK) on Ser209 in response to mitogens and cellular stress. Here we demonstrate that phosphorylation of eIF4E via MNK1 is mediated via the activation of either the Erk or p38 pathway. We further show that expression of active mutants of MNK1 and MNK2 in 293 cells diminishes cap-dependent translation relative to cap-independent translation in a transient reporter assay. The same effect on cap-dependent translation was observed when MNK1 was activated by the Erk or p38 pathway. In line with these findings, addition of recombinant active MNK1 to rabbit reticulocyte lysate resulted in a reduced protein synthesis in vitro, and overexpression of MNK2 caused a decreased rate of protein synthesis in 293 cells. By using CGP 57380, a novel low-molecular-weight kinase inhibitor of MNK1, we demonstrate that eIF4E phosphorylation is not crucial to the formation of the initiation complex, mitogen-stimulated increase in cap-dependent translation, and cell proliferation. Our results imply that activation of MNK by MAP kinase pathways does not constitute a positive regulatory mechanism to cap-dependent translation. Instead, we propose that the kinase activity of MNKs, eventually through phosphorylation of eIF4E, may serve to limit cap-dependent translation under physiological conditions.


