ArundoinCAS# 4555-56-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 4555-56-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12308619.0 | Appearance | Powder |
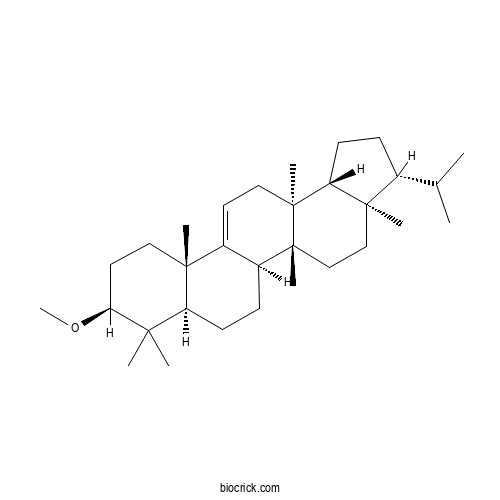
| Formula | C31H52O | M.Wt | 440.76 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3R,3aR,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aS,13aS,13bR)-9-methoxy-3a,5a,8,8,11a,13a-hexamethyl-3-propan-2-yl-1,2,3,4,5,5b,6,7,7a,9,10,11,13,13b-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]chrysene | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C1CCC2C1(CCC3(C2(CC=C4C3CCC5C4(CCC(C5(C)C)OC)C)C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MRNPHCMRIQYRFU-KXUMSINMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H52O/c1-20(2)21-10-13-25-29(21,6)18-19-30(7)23-11-12-24-27(3,4)26(32-9)15-16-28(24,5)22(23)14-17-31(25,30)8/h14,20-21,23-26H,10-13,15-19H2,1-9H3/t21-,23+,24+,25-,26+,28-,29-,30-,31+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Arundoin Dilution Calculator

Arundoin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2688 mL | 11.344 mL | 22.6881 mL | 45.3762 mL | 56.7202 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4538 mL | 2.2688 mL | 4.5376 mL | 9.0752 mL | 11.344 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2269 mL | 1.1344 mL | 2.2688 mL | 4.5376 mL | 5.672 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.2269 mL | 0.4538 mL | 0.9075 mL | 1.1344 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0227 mL | 0.1134 mL | 0.2269 mL | 0.4538 mL | 0.5672 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- γ-Linolenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1388
CAS No.:506-26-3
- Linoleic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCX1387
CAS No.:822-17-3
- Methyl Eicosapentaenoate
Catalog No.:BCX1386
CAS No.:2734-47-6
- Eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1385
CAS No.:86227-47-6
- Docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1384
CAS No.:2566-90-7
- Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1383
CAS No.:84494-72-4
- Ethyl oleate
Catalog No.:BCX1382
CAS No.:111-62-6
- Methyl arachidonate
Catalog No.:BCX1381
CAS No.:2566-89-4
- Ethyl Arachidonate
Catalog No.:BCX1380
CAS No.:1808-26-0
- Arachidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1379
CAS No.:506-30-9
- Palmitoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1378
CAS No.:373-49-9
- Ethyl palmitoleate
Catalog No.:BCX1377
CAS No.:56219-10-4
- Flaccidoside II
Catalog No.:BCX1390
CAS No.:140694-19-5
- Peruvoside
Catalog No.:BCX1391
CAS No.:1182-87-2
- Thevetin A
Catalog No.:BCX1392
CAS No.:37933-66-7
- 3-O-Acetylbufotalin
Catalog No.:BCX1393
CAS No.:4029-69-0
- Smilagenin
Catalog No.:BCX1394
CAS No.:126-18-1
- Elaidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1395
CAS No.:112-79-8
- 7-Hydroxyisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1396
CAS No.:13057-72-2
- 7α-Hydroxysarsasapogenin
Catalog No.:BCX1397
CAS No.:220832-70-2
- Tapinarof
Catalog No.:BCX1398
CAS No.:79338-84-4
- Senecionine acetate
Catalog No.:BCX1399
CAS No.:126642-77-1
- 4,3',5'-Trihydroxyresveratrol
Catalog No.:BCX1400
CAS No.:637776-83-1
- 7β-Hydroxyganoderenic acid F
Catalog No.:BCX1401
CAS No.:1245946-62-6
[Chemical constituents from Imperata cylindrica].[Pubmed:23189737]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;37(15):2296-300.
Chemical investigation of Imperata cylindrica led to the isolation of thirteen compounds using various chromatographic techniques. The structure of these compounds were identified as: three phenylpropanoids, 1-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-1,2,3-propanetriol ( 1 ), 1-O-p-coumaroylglycerol (2), 4-methoxy-5-methyl coumarin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3); four organic acids, 4-hydroxybenzene carboxylic acid(4), 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (5), vanillic acid (6), 3, 4-dihydroxybutyric acid (7); one phenolic compound, salicin (8); and five triterpenes, namely, Arundoin (9), cylindrin (10), fernenol (11), simiarenol (12), glutinone (13) by their physicochemical properties and spectral data analysis. Among them, compounds 1-8 were isolated from the genus Imperata for the first time.
[Chemical constituents of rhizoma imperatae and their anti-complementary activity].[Pubmed:21548362]
Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Dec;33(12):1871-4.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents of Rhizoma Imperatae and their anti-complementary activity. METHODS: By the hemolysis test, the petroleum extraction, ethyl acetate extraction, n-butanol extraction and the water extraction was tested for anti-complementary activity. Compounds were isolated and purified by silica gel column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20 and reversed-phase column chromatography. The structures were identified by the various spectroscopic data of ESI-MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR. The compounds were evaluated for anti-complementary activity in vitro. RESULTS: The petroleum extraction, ethyl acetate extraction showed significant anti-complementary activity. Ten compounds were isolated from the petroleum and EtOAc soluble fractions and identified as cylindrin (1), Arundoin (2), friedelin (3), beta-sitosterol (4), siderin (5), ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate (6), 5-methoxyflavone (7), vanillic acid (8), trans-p-coumaric acid (9), 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (10). CONCLUSION: Compounds 6, 7, 8, and 10 are isolated from the genus for the first time, and compounds 3, 8 and 9 inhibited the complement system towards the classical pathway.
Occurrence and sources of triterpenoid methyl ethers and acetates in sediments of the cross-river system, southeast Nigeria.[Pubmed:20414350]
Int J Anal Chem. 2010;2010:502076.
Pentacyclic triterpenol methyl ethers (PTMEs), germanicol methyl ether (miliacin), 3-methoxyfern-9(11)-ene (Arundoin), beta-amyrin methyl ether (iso-sawamilletin), and 3-methoxytaraxer-14-ene (sawamilletin or crusgallin) were characterized in surface sediments of the Cross-River system using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Triterpenol esters (mainly alpha- and beta-amyrinyl acetates and hexanoates, and lupeyl acetate and hexanoate) were also found. These distinct compounds are useful for assessing diagenesis that can occur during river transport of organic detritus. Poaceae, mainly Gramineae and Elaeis guineensis higher plant species, are proposed as primary sources for the PTMEs and esters in the sediments. PTMEs are biomarkers of specific higher plant subspecies, while the triterpenol esters are indicators of early diagenetic alteration of higher plant detritus.


