Astin BCAS# 151201-76-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 151201-76-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15233656 | Appearance | Powder |
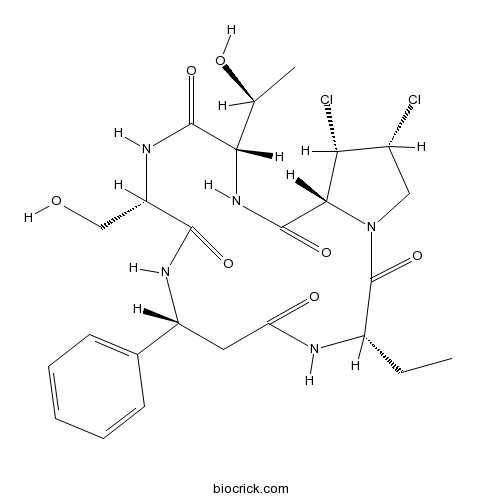
| Formula | C25H33N5O7Cl2 | M.Wt | 586.5 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S,7R,10S,13S,16R,17S,18R)-17,18-dichloro-3-ethyl-13-[(1S)-1-hydroxyethyl]-10-(hydroxymethyl)-7-phenyl-1,4,8,11,14-pentazabicyclo[14.3.0]nonadecane-2,5,9,12,15-pentone | ||
| SMILES | CCC1C(=O)N2CC(C(C2C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N1)C3=CC=CC=C3)CO)C(C)O)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DQILVZOWLYBPKT-FKOMMSEQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H33Cl2N5O7/c1-3-15-25(39)32-10-14(26)19(27)21(32)24(38)31-20(12(2)34)23(37)30-17(11-33)22(36)29-16(9-18(35)28-15)13-7-5-4-6-8-13/h4-8,12,14-17,19-21,33-34H,3,9-11H2,1-2H3,(H,28,35)(H,29,36)(H,30,37)(H,31,38)/t12-,14+,15-,16+,17-,19+,20-,21-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Astin B has antitumor activity. |
| Structure Identification | J Sep Sci. 2015 Feb;38(4):571-5.Simultaneous separation and determination of phenolic acids, pentapeptides, and triterpenoid saponins in the root of Aster tataricus by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[Pubmed: 25491750 ]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1996 May;44(5):1026-32.Cyclic peptides from higher plants. XXVIII. Antitumor activity and hepatic microsomal biotransformation of cyclic pentapeptides, astins, from Aster tataricus.[Pubmed: 8689717 ]
|

Astin B Dilution Calculator

Astin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.705 mL | 8.5251 mL | 17.0503 mL | 34.1006 mL | 42.6257 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.341 mL | 1.705 mL | 3.4101 mL | 6.8201 mL | 8.5251 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1705 mL | 0.8525 mL | 1.705 mL | 3.4101 mL | 4.2626 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0341 mL | 0.1705 mL | 0.341 mL | 0.682 mL | 0.8525 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0171 mL | 0.0853 mL | 0.1705 mL | 0.341 mL | 0.4263 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Astin A
Catalog No.:BCN8851
CAS No.:151201-75-1
- Hydroxy-γ-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8849
CAS No.:78886-66-5
- Loureiriol
Catalog No.:BCN8843
CAS No.:479195-44-3
- (3R)-5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-(4'-hydroxybenzyl)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN8842
CAS No.:84638-48-2
- Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside-1-2-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8820
CAS No.:55696-57-6
- Syringetin-3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8819
CAS No.:53430-50-5
- 6-Hydroxykaempferol 3-beta-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8807
CAS No.:205527-00-0
- (+)-δ-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCN8805
CAS No.:119-13-1
- Silyamandin
Catalog No.:BCN8804
CAS No.:1009565-36-9
- Benzoylgomisin P
Catalog No.:BCN8803
CAS No.:129445-43-8
- Sanguisorbigenin
Catalog No.:BCN8876
CAS No.:6812-98-2
- N-trans-Sinapoyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCN8875
CAS No.:200125-11-7
- Neochlorogenic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN8860
CAS No.:123410-65-1
- Astin C
Catalog No.:BCN8877
CAS No.:148057-23-2
- Bergaptol-beta-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8878
CAS No.:131623-13-7
- Orthosiphol A
Catalog No.:BCN8879
CAS No.:142741-25-1
- Gypenoside XIII
Catalog No.:BCN8927
CAS No.:80325-22-0
- Tigloylgomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN8880
CAS No.:130855-74-2
- Trachelogenin 4'-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN8881
CAS No.:106647-13-6
- Geoside
Catalog No.:BCN8882
CAS No.:585-90-0
- 3-O-methylellagic acid 4'-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8884
CAS No.:51768-39-9
- Pieceid-2''-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN8885
CAS No.:105304-51-6
- Isolappaol A
Catalog No.:BCN8886
CAS No.:131400-96-9
- Isovalerylshikonin
Catalog No.:BCN8887
CAS No.:52387-14-1
Simultaneous separation and determination of phenolic acids, pentapeptides, and triterpenoid saponins in the root of Aster tataricus by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:25491750]
J Sep Sci. 2015 Feb;38(4):571-5.
We established a qualitative method to analyze the main chemical compositions of the root of Aster tataricus. Most of the peaks were separated on a C(18) column packed with 5.0 mum particles, and 28 compounds were identified, including 11 chlorogenic acids, ten astins/asterinins, and seven astersaponins, four of which were reported for the first time from A. tataricus. Furthermore, we developed a reliable method for the simultaneous quantification of 3-caffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, astin A, Astin B, astin C, astersaponin A, and astersaponin C, and the qualified separations were achieved only on a C18 column packed with 2.7 mum particles. The method was used to measure the concentrations of eight components in samples from two major producing areas in China, and the average contents in samples from Bozhou (Anhui) were higher than those in samples from Anguo (Hebei).
Astin B, a cyclic pentapeptide from Aster tataricus, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatic L-02 cells.[Pubmed:25219577]
Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Nov 5;223:1-9.
Astins (including Astin B) are a class of halogenated cyclic pentapeptides isolated from the medicinal herb of Aster tataricus. However, our previous works showed that the herbal medicine was hepatotoxic in vivo, and a toxicity-guided isolation method led to the identification of a cyclopeptide Astin B. Astin B is structurally similar to cyclochlorotine, a well-known hepatotoxic mycotoxin. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine the potential cytotoxic effects and the underlying mechanism of Astin B on human normal liver L-02 cells. We found that Astin B has hepatotoxic effects in vitro and in vivo and that hepatic injury was primarily mediated by apoptosis in a mitochondria/caspase-dependent manner. Astin B provoked oxidative stress-associated inflammation in hepatocytes as evidenced by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), reduced contents of intracellular glutathione (GSH), and enhanced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Furthermore, the mitochondria-dependent apoptosis was evidenced by the depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane potential, the release of cytochrome c into cytosol, the increased ratio of Bax/Bcl-2, and the increased activities of caspases-9 and -3. Interestingly, Astin B treatment also induces autophagy in L-02 cells, characterized by acidic-vesicle fluorescence, increased LC3-II and decreased p62 expression. Autophagy is a protective mechanism that is used to protect cells from apoptosis. The presence of autophagy is further supported by the increased cytotoxicity and the enhanced cleaved caspase-3 after co-treatment of cells with an autophagy inhibitor, also by increased LC3-II and decreased p62 after co-treatment with a caspase inhibitor. Taken together, Astin B, most likely together with other members of astins, is the substance that is primarily responsible for the hepatotoxicity of A.tataricus.
Structural and conformational analysis of hydroxycyclochlorotine and cyclochlorotine, chlorinated cyclic peptides from Penicillium islandicum.[Pubmed:18558744]
J Nat Prod. 2008 Jul;71(7):1297-300.
A new chlorinated cyclic pentapeptide, hydroxycyclochlorotine (1), has been isolated from Penicillium islandicum, and the structure including absolute stereochemistry of 1 and conformational properties of 1 and cyclochlorotine (2) in DMSO-d6 were elucidated by using extensive 2D NMR and chemical means. Hydroxycyclochlorotine (1) and Astin B (3) from Aster tataricus, each containing an allo threonine at residue 2, have a cis proline configuration, whereas cyclochlorotine (2) has two conformational states in solution, which may be produced from cis-trans isomerization of the proline amide bond. The presence of an intramolecular hydrogen bond between Ser (3)-NH and a hydroxyl oxygen atom of alloThr (2) may serve to maintain the backbone conformation with a cis proline amide bond.
Solution forms of antitumor cyclic pentapeptides with 3,4-dichlorinated proline residues, astins A and C, from Aster tataricus.[Pubmed:7553986]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1995 Aug;43(8):1395-7.
Conformational analysis of antitumor cyclic pentapeptides, astins A (1) and C (3), was made by a combination of NMR and computational techniques. These results indicated that the backbone conformations of 1 and 3, with lower activity than Astin B (2), were different from that of 2. The backbone conformation together with a cis 3,4-dichlorinated proline residue was considered to play an important role in the antitumor activities of astins.


