Bacopaside ICAS# 382148-47-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 382148-47-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21599442 | Appearance | Off-white powder |
| Formula | C46H74O20S | M.Wt | 979.13 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol and methanol; insoluble in chloroform | ||
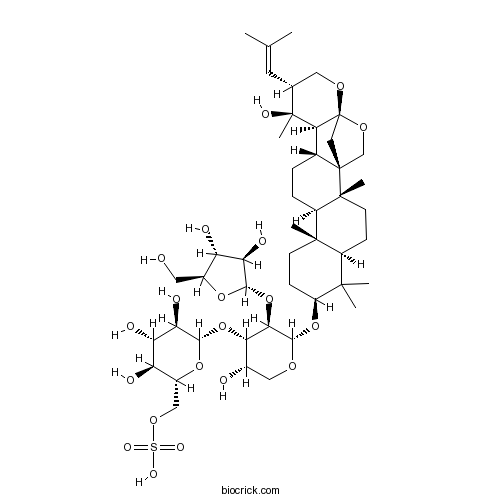
| Chemical Name | [(2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-5-hydroxy-2-[[(1S,2R,5R,7S,10R,11R,14R,15S,16S,17R,20R)-16-hydroxy-2,6,6,10,16-pentamethyl-17-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)-19,21-dioxahexacyclo[18.2.1.01,14.02,11.05,10.015,20]tricosan-7-yl]oxy]oxan-4-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen sulfate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CC1COC23CC4(CO2)C(C3C1(C)O)CCC5C4(CCC6C5(CCC(C6(C)C)OC7C(C(C(CO7)O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)COS(=O)(=O)O)O)O)O)OC9C(C(C(O9)CO)O)O)C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SKFWOYHZBNAJGA-YAOMZRCFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C46H74O20S/c1-21(2)14-22-16-59-46-19-45(20-60-46)23(37(46)44(22,7)54)8-9-28-42(5)12-11-29(41(3,4)27(42)10-13-43(28,45)6)64-40-36(66-38-33(52)30(49)25(15-47)62-38)35(24(48)17-58-40)65-39-34(53)32(51)31(50)26(63-39)18-61-67(55,56)57/h14,22-40,47-54H,8-13,15-20H2,1-7H3,(H,55,56,57)/t22-,23-,24+,25+,26-,27+,28-,29+,30+,31-,32+,33-,34-,35+,36-,37+,38+,39+,40+,42+,43-,44+,45+,46-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Bacopaside I has neuroprotective functions. 2. Bacopaside I exhibits an obvious antidepressant-like effect in mouse model of CUMS-induced depression that was mediated, at least in part, by modulating HPA hyperactivity and activating BDNF signaling pathway. 3. Bacopaside I is a modulator of Aquaporin-1 channel. 4. Bacopaside I has anti-Alzheimer's disease, it ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via immune-mediated clearance of β-amyloid. |
| Targets | NMDAR | GABA Receptor | cAMP |

Bacopaside I Dilution Calculator

Bacopaside I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0213 mL | 5.1066 mL | 10.2131 mL | 20.4263 mL | 25.5329 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2043 mL | 1.0213 mL | 2.0426 mL | 4.0853 mL | 5.1066 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1021 mL | 0.5107 mL | 1.0213 mL | 2.0426 mL | 2.5533 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0204 mL | 0.1021 mL | 0.2043 mL | 0.4085 mL | 0.5107 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0102 mL | 0.0511 mL | 0.1021 mL | 0.2043 mL | 0.2553 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Vinaginsenoside R4
Catalog No.:BCN8659
CAS No.:156009-80-2
- Nuezhenidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8658
CAS No.:183238-67-7
- Kanzonol C
Catalog No.:BCN8657
CAS No.:151135-82-9
- Ginsenoside Rh7
Catalog No.:BCN8656
CAS No.:343780-68-7
- 5-Ethoxy-10-Gingerol
Catalog No.:BCN8655
CAS No.:121771-98-0
- Angelicolide
Catalog No.:BCN8654
CAS No.:90826-58-7
- 11alpha-Methoxysaikosaponin F
Catalog No.:BCN8653
CAS No.:104109-37-7
- Daidzein diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN8652
CAS No.:3682-01-7
- 1-Methyl-6-oxopyridine-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8651
CAS No.:3719-45-7
- Nortracheloside
Catalog No.:BCN8650
CAS No.:33464-78-7
- Euphorbia factor L7b
Catalog No.:BCN8649
CAS No.:93550-95-9
- Bryodulcosigenin
Catalog No.:BCN8648
CAS No.:4965-97-3
- Glicoricone
Catalog No.:BCN8661
CAS No.:161099-37-2
- Angelicide
Catalog No.:BCN8662
CAS No.:92935-94-9
- Aromadendrene
Catalog No.:BCN8663
CAS No.:489-39-4
- Parvisoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN8664
CAS No.:49776-79-6
- Lappaol F
Catalog No.:BCN8665
CAS No.:69394-17-8
- 4''-methyloxy-Daidzin
Catalog No.:BCN8667
CAS No.:1195968-02-5
- 4''-methyloxy-Genistin
Catalog No.:BCN8668
CAS No.:950910-16-4
- Ophiopogonanone B
Catalog No.:BCN8669
CAS No.:1316759-83-7
- Moscatin
Catalog No.:BCN8670
CAS No.:108335-06-4
- Epimagnolin B
Catalog No.:BCN8671
CAS No.:1134188-26-3
- Resveratroloside
Catalog No.:BCN8672
CAS No.:38963-95-0
- Pomiferin
Catalog No.:BCN8673
CAS No.:572-03-2
Antidepressant-like Effect of Bacopaside I in Mice Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress by Modulating the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Function and Activating BDNF Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:28758176]
Neurochem Res. 2017 Nov;42(11):3233-3244.
Preliminary studies conducted in our laboratory have confirmed that Bacopaside I (BS-I), a saponin compound isolated from Bacopa monnieri, displayed antidepressant-like activity in the mouse behavioral despair model. The present investigation aimed to verify the antidepressant-like action of BS-I using a mouse model of behavioral deficits induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) and further probe its underlying mechanism of action. Mice were exposed to CUMS for a period of 5 consecutive weeks to induce depression-like behavior. Then, oral gavage administrations with vehicle (model group), fluoxetine (12 mg/kg, positive group) or BS-I (5, 15, 45 mg/kg, treated group) once daily were started during the last two weeks of CUMS procedure. The results showed that BS-I significantly ameliorated CUMS-induced depression-like behaviors in mice, as characterized by an elevated sucrose consumption in the sucrose preference test and reduced immobility time without affecting spontaneous locomotor activity in the forced swimming test, tail suspension test and open field test. It was also found that BS-I treatment reversed the increased level of plasma corticosterone and decreased mRNA and protein expressions of glucocorticoid receptor induced by CUMS exposure, indicating that hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis hyperactivity of CUMS-exposed mice was restored by BS-I treatment. Furthermore, chronic administration of BS-I elevated expression levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (mRNA and protein) and activated the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and cAMP response element-binding protein in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in mice subjected to CUMS procedure. Taken together, these results indicated that BS-I exhibited an obvious antidepressant-like effect in mouse model of CUMS-induced depression that was mediated, at least in part, by modulating HPA hyperactivity and activating BDNF signaling pathway.
Bacopaside I ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via immune-mediated clearance of beta-amyloid.[Pubmed:26946062]
Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Mar;8(3):521-33.
Standardized extracts of Bacopa monniera (BME) have been shown to exert a neuroprotective effect against mental diseases, such as depression, anxiety and Alzheimer's disease (AD), in chronic administration studies. However, its mechanism of action has remained unclear. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effect of Bacopaside I (BS-I), a major triterpenoid saponin of BME, on the cognitive impairment and neuropathology in APP/PS1 transgenic mice and explored the possible mechanism from a biological systems perspective. We found that BS-I treatment significantly ameliorated learning deficits, improved long-term spatial memory, and reduced plaque load in APP/PS1 mice. We constructed BS-I's therapeutic effect network by mapping the nodes onto the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network constructed according to their functional categories based on genomic and proteomic data. Because many of the top enrichment categories related to the processes of the immune system and phagocytosis were detected, we proposed that BS-I promotes amyloid clearance via the induction of a suitable degree of innate immune stimulation and phagocytosis. Our research may help to clarify the neuroprotective effect of BME and indicated that natural saponins target the immune system, which may offer new research avenues to discover novel treatments for AD.
Differential Inhibition of Water and Ion Channel Activities of Mammalian Aquaporin-1 by Two Structurally Related Bacopaside Compounds Derived from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri.[Pubmed:27474162]
Mol Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;90(4):496-507.
Aquaporin-1 (AQP1) is a major intrinsic protein that facilitates flux of water and other small solutes across cell membranes. In addition to its function as a water channel in maintaining fluid homeostasis, AQP1 also acts as a nonselective cation channel gated by cGMP, a property shown previously to facilitate rapid cell migration in a AQP1-expressing colon cancer cell line. Here we report two new modulators of AQP1 channels, Bacopaside I and Bacopaside II, isolated from the medicinal plant Bacopa monnieri Screening was conducted in the Xenopus oocyte expression system, using quantitative swelling and two-electrode voltage clamp techniques. Results showed Bacopaside I blocked both the water (IC50 117 muM) and ion channel activities of AQP1 but did not alter AQP4 activity, whereas Bacopaside II selectively blocked the AQP1 water channel (IC50 18 muM) without impairing the ionic conductance. These results fit with predictions from in silico molecular modeling. Both bacopasides were tested in migration assays using HT29 and SW480 colon cancer cell lines, with high and low levels of AQP1 expression, respectively. Bacopaside I (IC50 48 muM) and Bacopaside II (IC50 14 muM) impaired migration of HT29 cells but had minimal effect on SW480 cell migration. Our results are the first to identify differential AQP1 modulators isolated from a medicinal plant. Bacopasides could serve as novel lead compounds for pharmaceutic development of selective aquaporin modulators.
Insights into the molecular aspects of neuroprotective Bacoside A and Bacopaside I.[Pubmed:29676230]
Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Apr 19. pii: CN-EPUB-89845.
Bacopa monnieri, commonly known as Brahmi, has been extensively used as a neuromedicine for various disorders such as anxiety, depression and memory loss. Chemical characterization studies revealed the major active constituents of the herb as the triterpenoid saponins, bacosides. Bacoside A, the vital neuroprotective constituent, is composed of four constituents viz., bacoside A3, Bacopaside II, jujubogenin isomer of bacopasaponin C (bacopaside X) and bacopasaponin C. B. monnieri extracts as well as bacosides successfully establish a healthy antioxidant environment in various tissues especially in liver and brain. Free radical scavenging, suppression of lipid peroxidation and activation of antioxidant enzymes by bacosides help to attain a physiological state of minimized oxidative stress. The molecular basis of neuroprotective activity of bacosides is attributed to the regulation of mRNA translation and surface expression of neuroreceptors such as AMPAR, NMDAR and GABAR in the various parts of the brain. Bioavailability as well as binding of neuroprotective agents (such as bacosides) to these receptors is controlled by the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB). However, nano conversion of these drug candidates easily resolves the BBB restriction and carries a promising role in future therapies. This review summarizes the neuroprotective functions of the B. monnieri extracts as well as its active compounds (bacoside A, Bacopaside I) and the molecular mechanisms responsible for these pharmacological activities.


