BitopertinGlycine reuptake inhibitor(GlyT1) CAS# 845614-11-1 |
- ALX 5407 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7168
CAS No.:200006-08-2
- Bitopertin (R enantiomer)
Catalog No.:BCC1420
CAS No.:845614-12-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 845614-11-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24946690 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H20F7N3O4S | M.Wt | 543.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (92.00 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
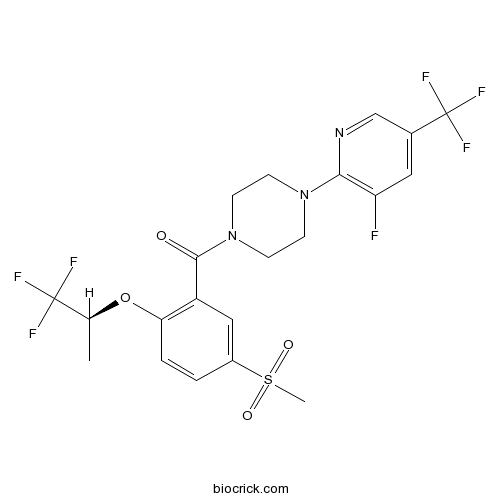
| Chemical Name | [4-[3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]piperazin-1-yl]-[5-methylsulfonyl-2-[(2S)-1,1,1-trifluoropropan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]methanone | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(F)(F)F)OC1=C(C=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)C)C(=O)N2CCN(CC2)C3=C(C=C(C=N3)C(F)(F)F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YUUGYIUSCYNSQR-LBPRGKRZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20F7N3O4S/c1-12(20(23,24)25)35-17-4-3-14(36(2,33)34)10-15(17)19(32)31-7-5-30(6-8-31)18-16(22)9-13(11-29-18)21(26,27)28/h3-4,9-12H,5-8H2,1-2H3/t12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bitopertin is a potent, noncompetitive glycine reuptake inhibitor, inhibits glycine uptake at human GlyT1 with a concentration exhibiting IC50 of 25 nM.In Vitro:Bitopertin (RG1678) competitively blocks [3H]ORG24598 binding sites at human GlyT1b in membranes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Bitopertin potently inhibits [3H]glycine uptake in cells stably expressing hGlyT1b and mGlyT1b, with IC50 values of 25±2 nM and 22±5 nM, respectively (n=6). Conversely, Bitopertin has no effect on hGlyT2-mediated glycine uptake up to 30 μM concentration. Bitopertin has high affinity for the recombinant hGlyT1b transporter. Under equilibrium conditions (1 h at room temperature), Bitopertin displaces [3H]ORG24598 binding with a Ki of 8.1 nM. In hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells, Bitopertin enhances NMDA-dependent long-term potentiation at 100 nM but not at 300 nM[1]. Additional profiling revealed that Bitopertin (RG1678) has an excellent selectivity profile against the GlyT2 isoform (IC50>30 μM) and toward a panel of 86 targets including transmembrane and soluble receptors, enzymes, ion channels, and monoamine transporters (<41% inhibition at 10 μM is measured for all targets)[2].In Vivo:Bitopertin (RG1678) dose-dependently increases cerebrospinal fluid and striatal levels of glycine measured bymicrodialysis in rats. Additionally Bitopertin attenuates hyperlocomotion induced by the psychostimulant D-amphetamine or the NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist L-687,414 in mice. Bitopertin also prevents the hyper-response to D-amphetamine challenge in rats treated chronically with phencyclidine, an NMDA receptor open-channel blocker. Administration of vehicle has no effect on extracellular levels of striatal glycine, which remained constant throughout the experiment. In contrast, p.o. administration of Bitopertin (1-30 mg/kg) produced a dose-dependent increase in extracellular glycine levels. Bitopertin 30 mg/kg produces glycine levels 2.5 times higher than pretreatment levels. A similar dose-dependent increase in glycine concentration is observed in the CSF of rats treated p.o. with Bitopertin (1-10 mg/kg) compared with vehicle-treated animals, 3 h after drug administration. Interestingly, the level of CSF glycine increase 3 h after Bitopertin dosing is very similar to the increase in the microdialysis experiment at the same time point[1]. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies in rat and monkey reveals that Bitopertin (RG1678) has, in both species, a low plasma clearance, an intermediate volume of distribution, a good oral bioavailability (78% for rat, 56% for monkey), and a favorable terminal half-life (5.8 h for rat, 6.4 h for monkey). The plasma protein binding is high in the two preclinical species (97%) and in human (98%). The CNS penetration of Bitopertin in rat (brain/plasma=0.7) is better than that in mouse (brain/plasma=0.5)[2]. References: | |||||

Bitopertin Dilution Calculator

Bitopertin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8401 mL | 9.2003 mL | 18.4006 mL | 36.8012 mL | 46.0015 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.368 mL | 1.8401 mL | 3.6801 mL | 7.3602 mL | 9.2003 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.184 mL | 0.92 mL | 1.8401 mL | 3.6801 mL | 4.6002 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0368 mL | 0.184 mL | 0.368 mL | 0.736 mL | 0.92 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0184 mL | 0.092 mL | 0.184 mL | 0.368 mL | 0.46 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bitopertin, also known as RG1678, is a potent and selective inhibitor of GlyT1 with an EC50 of 30nM. [1]
Abnormal signaling through the N-methyl-D–aspartate (NMDA) receptor has been hypothesized to be a key factor underlying many signs and symptoms of schizophrenia. Increasing NMDA receptor function pharmacologically is thought to compensate for dysfunctional receptor signaling and is a promising approach for the treatment of schizophrenia. Targeting the NMDA receptor allosteric glycine site has been assumed as an approach to enhance NMDA receptor functioning and thus normalize glutamate transmission, which can be achieved by glycine agonists and also by preventing synaptic clearance of glycine through the inhibition of the glycine transporter type 1 (GlyT1). Bitopertin selectively inhibits GlyT1, thus increasing the synaptic level of glycine, an obligatory coagonist at the NMDA receptor, and consequently enhancing NMDA signaling. [1, 2]
Bitopertin was found to possess a high in vitro GlyT1 inhibitory activity with EC50 of 30nM, and a favorable hERG activity with IC50 of 17μM. Moreover, Bitopertin also showed excellent selectivity over GlyT2, as well as a panel of 86 other targets including transmembrane and soluble receptors, enzymes, ion channels, and monoamine transporters. Notwithstanding Bitopertin showed low aqueous solubility, it exhibited a satisfactory solubility characteristics in both fasted state simulated intestinal fluid (20 μg/mL) and fed state simulated intestinal fluid (60 μg/mL). Additionally, by parallel artificial membrane permeation assay it exhibited excellent membrane permeability. [1]
In a phase II RCT study, placebo and different doses of Bitopertin were added to standard antipsychotic treatment for 8 weeks, which revealed that Bitopertin groups had significantly higher response rates and trends towards improved function. Bitopertin inhibiting glycine reuptake is likely to be a new treatment for schizophrenia with negative symptoms. [2]
References:
1.Pinard E, Alanine A, Alberati D, et al. Selective GlyT1 inhibitors: discovery of [4-(3-fluoro-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl) piperazin-1-yl][5-methanesulfonyl-2-((S)-2, 2, 2-trifluoro-1-methylethoxy) phenyl] methanone (RG1678), a promising novel medicine to treat schizophrenia[J]. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2010, 53(12): 4603-4614.
2.Umbricht D, Alberati D, Martin-Facklam M, et al. Effect of bitopertin, a glycine reuptake inhibitor, on negative symptoms of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, proof-of-concept study[J]. JAMA psychiatry, 2014.
- MNI-caged-D-aspartate
Catalog No.:BCC5896
CAS No.:845555-94-4
- Bedaquiline fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC5245
CAS No.:845533-86-0
- ICI 162,846
Catalog No.:BCC6808
CAS No.:84545-30-2
- Sevelamer Carbonate
Catalog No.:BCC4717
CAS No.:845273-93-0
- Varlitinib (ARRY334543)
Catalog No.:BCC3725
CAS No.:845272-21-1
- Sibutramine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5252
CAS No.:84485-00-7
- BTS 54-505 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5901
CAS No.:84484-78-6
- C-1
Catalog No.:BCC6687
CAS No.:84468-24-6
- threo-Guaiacylglycerol-beta-O-4'-dehydrodisinapyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6928
CAS No.:844637-85-0
- β-CCB
Catalog No.:BCC6635
CAS No.:84454-35-3
- A-769662
Catalog No.:BCC2080
CAS No.:844499-71-4
- AT7519
Catalog No.:BCC2541
CAS No.:844442-38-2
- Bitopertin (R enantiomer)
Catalog No.:BCC1420
CAS No.:845614-12-2
- 4-Hydroxycephalotaxine
Catalog No.:BCN4386
CAS No.:84567-08-8
- PHA-767491
Catalog No.:BCC1858
CAS No.:845714-00-3
- Rocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN4387
CAS No.:84573-16-0
- Cleomiscosin C
Catalog No.:BCN4388
CAS No.:84575-10-0
- Bakuchalcone
Catalog No.:BCN3201
CAS No.:84575-13-3
- CP 94253 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7018
CAS No.:845861-39-4
- 2-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5663
CAS No.:845861-49-6
- Serrin A
Catalog No.:BCN6985
CAS No.:845959-98-0
- 5α-Androstanedione
Catalog No.:BCC8752
CAS No.:846-46-8
- Boldenone
Catalog No.:BCC8892
CAS No.:846-48-0
- Lorazepam
Catalog No.:BCC5970
CAS No.:846-49-1
Bitopertin in Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia-Results From the Phase III FlashLyte and DayLyte Studies.[Pubmed:28117049]
Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Jul 1;82(1):8-16.
BACKGROUND: There is currently no standard of care for treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia, although some previous results with glutamatergic agonists have been promising. METHODS: Three (SunLyte [WN25308], DayLyte [WN25309], and FlashLyte [NN25310]) phase III, multicenter, randomized, 24-week, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled studies evaluated the efficacy and safety of adjunctive Bitopertin in stable patients with persistent predominant negative symptoms of schizophrenia treated with antipsychotics. SunLyte met the prespecified criteria for lack of efficacy and was declared futile. Key inclusion criteria were age >/=18 years, DSM-IV-TR diagnosis of schizophrenia, score >/=40 on the sum of the 14 Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale negative symptoms and disorganized thought factors, unaltered antipsychotic treatment, and clinical stability. Following a 4-week prospective stabilization period, patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to Bitopertin (5 mg and 10 mg [DayLyte] and 10 mg and 20 mg [FlashLyte]) or placebo once daily for 24 weeks. The primary efficacy end point was mean change from baseline in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale negative symptom factor score at week 24. RESULTS: The intent-to-treat population in DayLyte and FlashLyte included 605 and 594 patients, respectively. At week 24, mean change from baseline showed improvement in all treatment arms but no statistically significant separation from placebo in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale negative symptom factor score and all other end points. Bitopertin was well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS: These studies provide no evidence for superior efficacy of adjunctive Bitopertin in any of the doses tested over placebo in patients with persistent predominant negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Efficacy and safety of adjunctive bitopertin versus placebo in patients with suboptimally controlled symptoms of schizophrenia treated with antipsychotics: results from three phase 3, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicentre studies in the SearchLyte clinical trial programme.[Pubmed:27816567]
Lancet Psychiatry. 2016 Dec;3(12):1115-1128.
BACKGROUND: Many patients with schizophrenia require high doses of medication for their ongoing psychotic symptoms. Glutamate theories and findings from studies showing efficacy of sarcosine, an endogenous, non-selective glycine-reuptake inhibitor mediated by GlyT1, offer an alternative approach. We undertook the SearchLyte trial programme to examine the efficacy of Bitopertin, a selective GlyT1-mediated glycine-reuptake inhibitor, as an adjunctive treatment to ongoing antipsychotic treatment. METHODS: SearchLyte consisted of three phase 3, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicentre studies done in outpatient clinics in Asia, Europe, and North and South America (TwiLyte done at 109 sites, NightLyte at 84, and MoonLyte at 87). Participants were male and female outpatients, aged at least 18 years, meeting DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia with suboptimally controlled positive symptoms despite treatment with antipsychotics. Inclusion criteria included a Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score of at least 70 and antipsychotic treatment stability for the past 12 weeks before randomisation. Key exclusion criteria included meeting criteria for symptomatic remission or previous treatment with a GlyT1 inhibitor or any other investigational drug. After a screening or 4-week prospective stabilisation period, we randomly assigned participants (1:1:1) to a 12-week, double-blind treatment of either placebo or one of two fixed doses of oral, once-daily Bitopertin (10 or 20 mg in TwiLyte and NightLyte; 5 or 10 mg in MoonLyte) added to their current antipsychotic medicine. After completion of 12 weeks' treatment, the study design allowed for additional double-blind treatment for 40 weeks to assess maintenance of the effect, followed by a randomised 4-week washout period to assess withdrawal effects. Subsequently, all patients were offered the opportunity to receive Bitopertin treatment in a 3-year follow-up. The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean change from baseline in the PANSS Positive Symptom Factor Score (PSFS) at week 12, analysed in the modified intention-to-treat population. The trials were registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (numbers NCT01235520 [TwiLyte], NCT01235585 [MoonLyte], and NCT01235559 [NightLyte]). FINDINGS: Between Nov 19, 2010, and Dec 12, 2014, we randomly assigned 1794 patients to treatment, of whom 1772 were treated and analysed. MoonLyte was discontinued in September, 2014, on the basis of results from futility analyses. Across studies and treatment arms, most patients completed 12 weeks of treatment (505 in TwiLyte, 517 in NightLyte, and 506 in MoonLyte). Only one study, NightLyte, met the primary endpoint where the PANSS PSFS significantly differed from placebo at week 12, and only in the 10-mg arm: mean difference in score -1.37, 95% CI -2.27 to -0.47; p=0.0028. Improvements from baseline for the Bitopertin 20-mg arm in Nightlyte were not significant compared with placebo: -3.77, 95% CI -4.40 to -3.14; p=0.3142. Results from the other two studies also did not differ from placebo (TwiLyte 0.58, 95% CI -0.34 to 1.50, p=0.22 for 10 mg and 0.43, -0.49 to 1.36, p=0.36 for 20 mg; MoonLyte 0.06, 95% CI -0.79 to 0.92, p=0.88 for 5 mg and 0.44, -0.41 to 1.28, p=0.31 for 10 mg). Placebo responses varied across studies and might have contributed to the differences in efficacy between studies. Four deaths occurred during the 12-week treatment period, three in NightLyte (upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage, alcohol poisoning and related head injury, and a completed suicide) and one in MoonLyte (myocardial infarction in a patient with pre-existing risk factors). Only the death by suicide was deemed related to the study drug. The incidence of serious adverse events was low across treatment groups in all three studies; psychiatric disorders were the most frequently reported serious adverse events and the most frequent cause of adverse events leading to discontinuation. INTERPRETATION: Only one of six active treatment arms across the three studies offered an advantage of adjunctive Bitopertin over placebo for the treatment of suboptimally controlled symptoms of schizophrenia. The small improvement associated with Bitopertin together with the varying placebo response suggests that adjunctive Bitopertin treatment might offer only modest benefit to suboptimal responders to antipsychotics, if any. FUNDING: F Hoffmann-La Roche.
Efficacy and Safety of Bitopertin in Patients with Schizophrenia and Predominant Negative Symptoms: Subgroup Analysis of Japanese Patients from the Global Randomized Phase 2 Trial.[Pubmed:28096877]
Psychiatry Investig. 2017 Jan;14(1):63-73.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of the present study was to perform a subgroup analysis of data from a phase II global, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Bitopertin, a glycine reuptake inhibitor that activates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by increasing the concentration of glycine in the synaptic cleft, in Japanese and non-Japanese patients with schizophrenia and predominant negative symptoms. METHODS: Patients with schizophrenia and predominant negative symptoms on one or two antipsychotic drugs, including atypical antipsychotic drugs (olanzapine, risperidone, quetiapine, aripiprazole, and paliperidone) as the primary treatment, received Bitopertin (10, 30, or 60 mg/day) or placebo once daily for 8 weeks as an add-on treatment. Efficacy was assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) negative symptom factor score (NSFS). RESULTS: The efficacy of Bitopertin (10 mg and 30 mg) was similar between Japanese and non-Japanese patients. In the Bitopertin 60-mg group, no difference from the placebo group was observed in Japanese or non-Japanese patients. The response to placebo was lower in Japanese patients, and there was a trend towards a greater difference in the change in PANSS NSFS between the placebo group and the 10-mg and 30-mg groups among Japanese patients. The safety profile of Bitopertin was favorable in Japanese and non-Japanese patients. CONCLUSION: According to this subgroup analysis from a global phase II study of Bitopertin, there was no difference in terms of efficacy and safety between Japanese and non-Japanese patients.


