BufotalineCAS# 471-95-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 471-95-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10119 | Appearance | Powder |
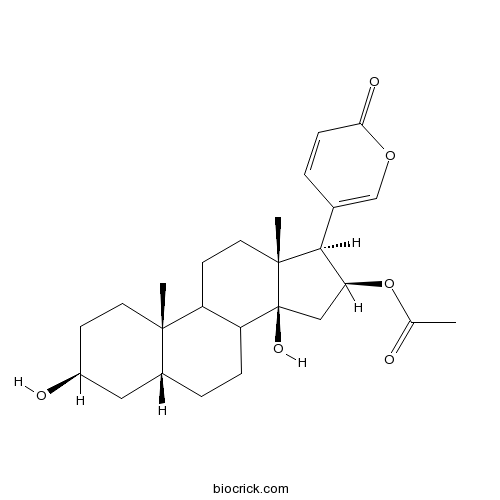
| Formula | C26H36O6 | M.Wt | 444.56 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 4.6 mg/mL (10.35 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(3S,5R,10S,13R,14S,16S,17R)-3,14-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-(6-oxopyran-3-yl)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-16-yl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1CC2(C3CCC4CC(CCC4(C3CCC2(C1C5=COC(=O)C=C5)C)C)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VOZHMAYHYHEWBW-JNUCAMJOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H36O6/c1-15(27)32-21-13-26(30)20-6-5-17-12-18(28)8-10-24(17,2)19(20)9-11-25(26,3)23(21)16-4-7-22(29)31-14-16/h4,7,14,17-21,23,28,30H,5-6,8-13H2,1-3H3/t17-,18+,19?,20?,21+,23+,24+,25-,26+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Bufotalin is a cardiotoxic bufanolide steroid, cardiac glycoside analogue. Bufotalin has anti-cancer activity, it can induce apoptosis in Hep 3B cells, and caspase-8 inhibitor (Z-IETD) or wide-ranging caspase inhibitor (Z-VAD) significantly suppresses the bufotalin-induced apoptosis. Bufotalin is a powerful sensitizer of death receptor-induced apoptosis in cancer cells, it promotes death receptor-mediated cell death, especially TRAIL-induced apoptosis, through activation of caspase-3 and PARP-1. |
| Targets | CDK | p53 | p21 | Caspase | PARP | Akt | Bcl-2/Bax | TNF-α | STAT |
| In vitro | Involvement of caspases and apoptosis-inducing factor in bufotaline-induced apoptosis of Hep 3B cells.[Pubmed: 19055367]J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jan 14;57(1):55-61.Bufotaline is one of the bufadienolides isolated from Formosan Ch'an Su, which is made of the skin and parotid glands of toads. Ingestion of toad venom results in severe morbidity and high mortality. Although Ch'an Su is clinically toxic, it has been used as an important traditional Chinese medicine for heart failure and pains. |
| In vivo | Bufotaline from Venenum Bufonis inhibits growth of multidrug resistant HepG2 cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.[Pubmed: 22841670 ]Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 5;692(1-3):19-28.Venenum Bufonis, a traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the treatment of liver cancer in modern Chinese medical practices. |
| Kinase Assay | Bufotaline sensitizes death receptor-induced apoptosis via Bid- and STAT1-dependent pathways.[Pubmed: 21887462 ]Int J Oncol. 2012 Jan;40(1):203-8.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) are apoptosis-inducing ligands that stimulate death receptors. |

Bufotaline Dilution Calculator

Bufotaline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2494 mL | 11.2471 mL | 22.4942 mL | 44.9883 mL | 56.2354 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4499 mL | 2.2494 mL | 4.4988 mL | 8.9977 mL | 11.2471 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2249 mL | 1.1247 mL | 2.2494 mL | 4.4988 mL | 5.6235 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.045 mL | 0.2249 mL | 0.4499 mL | 0.8998 mL | 1.1247 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0225 mL | 0.1125 mL | 0.2249 mL | 0.4499 mL | 0.5624 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bufotalin is a cardiotoxic bufanolide steroid, cardiac glycoside analogue, secreted by a number of toad species; a novel anti-osteoblastoma agent. IC50 value: Target: in vitro: bufotalin induced osteoblastoma cell death and apoptosis in dose- and time-dependent manners. Further, bufotalin induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress activation in osteoblastoma cells, the latter was detected by the induction of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), phosphorylation of inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) and PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), as well as caspase-12 activation [1]. Bufotalin was the most potent active compound among these four bufadienolides, and it exerted stronger inhibitory effect on the viability of doxorubicin-induced multidrug resistant liver cancer cells (R-HepG2) than that of their parent cells HepG2. bufotalin treatment induced cell cycle arrest at G(2)/M phase through down-regulation of Aurora A, CDC25, CDK1, cyclin A and cyclin B1, as well as up-regulation of p53 and p21. Bufotalin treatment also induced apoptosis which was accompanied by decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, increases in intracellular calcium level and reactive oxygen species production, activations of caspase-9 and -3, cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) as well as changes in the expressions of bcl-2 and bax [2]. Bufotalin promoted death receptor-mediated cell death, especially TRAIL-induced apoptosis, through activation of caspase-3 and PARP-1. Cotreatment of bufotalin with TRAIL resulted in the downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins, including Bcl-XL, Mcl-1, survivin and XIAP, and the up-regulation of MAPKs and TRAIL receptor DR5. In addition, phosphorylation of STAT1 was strongly inhibited by bufotalin [3]. externalization of phosphatidylserine, accumulation of sub-G(1) cells, fragmentation of DNA, and formation of apoptotic bodies were observed in bufotalin-treated Hep 3B cells [4].
References:
[1]. Zhu YR, et al. Bufotalin-induced apoptosis in osteoblastoma cells is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Aug 15;451(1):112-8.
[2]. Zhang DM, et al. Bufotalin from Venenum Bufonis inhibits growth of multidrug resistant HepG2 cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 5;692(1-3):19-28.
[3]. Waiwut P, et al. Bufotalin sensitizes death receptor-induced apoptosis via Bid- and STAT1-dependent pathways. Int J Oncol. 2012 Jan;40(1):203-8.
[4]. Su CL, et al. Involvement of caspases and apoptosis-inducing factor in bufotalin-induced apoptosis of Hep 3B cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jan 14;57(1):55-61.
- Stachydrine
Catalog No.:BCN8384
CAS No.:471-87-4
- (-)-Steviol
Catalog No.:BCN8358
CAS No.:471-80-7
- Dipterocarpol
Catalog No.:BCN5523
CAS No.:471-69-2
- alpha-Boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5522
CAS No.:471-66-9
- Isocolumbin
Catalog No.:BCN5361
CAS No.:471-54-5
- Glycyrrhetinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5942
CAS No.:471-53-4
- 8-Amino-7-oxononanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1778
CAS No.:4707-58-8
- Atraric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5521
CAS No.:4707-47-5
- alpha-Lapachone
Catalog No.:BCN5520
CAS No.:4707-33-9
- Beta-Lapachone
Catalog No.:BCC5088
CAS No.:4707-32-8
- Benzoyl-DL-methionine
Catalog No.:BCC8863
CAS No.:4703-38-2
- Cineole
Catalog No.:BCN2686
CAS No.:470-82-6
- (E)-Aldosecologanin
Catalog No.:BCN4631
CAS No.:471271-55-3
- Boc-D-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3448
CAS No.:47173-80-8
- MK-0752
Catalog No.:BCC2090
CAS No.:471905-41-6
- Ruscogenin
Catalog No.:BCN6287
CAS No.:472-11-7
- Betulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5524
CAS No.:472-15-1
- Telocinobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN2359
CAS No.:472-26-4
- Butyrospermol
Catalog No.:BCN3340
CAS No.:472-28-6
- Masticadienolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5525
CAS No.:472-30-0
- Astaxanthin
Catalog No.:BCN2248
CAS No.:472-61-7
- H-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3031
CAS No.:4726-96-9
- Kartogenin
Catalog No.:BCC6211
CAS No.:4727-31-5
- 1-Benzyl-4-hydroxypiperidine
Catalog No.:BCC8459
CAS No.:4727-72-4
Involvement of caspases and apoptosis-inducing factor in bufotalin-induced apoptosis of Hep 3B cells.[Pubmed:19055367]
J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jan 14;57(1):55-61.
Bufotalin is one of the bufadienolides isolated from Formosan Ch'an Su, which is made of the skin and parotid glands of toads. Ingestion of toad venom results in severe morbidity and high mortality. Although Ch'an Su is clinically toxic, it has been used as an important traditional Chinese medicine for heart failure and pains. In this study, bufotalin-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep 3B cells was investigated. The results indicate that externalization of phosphatidylserine, accumulation of sub-G(1) cells, fragmentation of DNA, and formation of apoptotic bodies were observed in bufotalin-treated Hep 3B cells. The signaling pathway might be via the activation of caspase-8, increase in mitochondrial tBid, disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, and translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Active caspase-8 might activate caspase-9 and caspase-3 leading to the cleavage of nuclear PARP. Presence of AIF and cleaved PARP in the nuclei might lead to DNA fragmentation. Caspase-8 inhibitor (Z-IETD) or wide-ranging caspase inhibitor (Z-VAD) significantly suppressed the bufotalin-induced apoptosis, while the anti-Fas neutralization antibody had no effect. These data suggest that bufotalin-induced apoptosis in Hep 3B cells might involve caspases and AIF.
Bufotalin from Venenum Bufonis inhibits growth of multidrug resistant HepG2 cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.[Pubmed:22841670]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 5;692(1-3):19-28.
Venenum Bufonis, a traditional Chinese medicine, is widely used in the treatment of liver cancer in modern Chinese medical practices. In our search for anti-hepatoma constituents in Venenum Bufonis, bufotalin, bufalin, telocinobufagin and cinobufagin were obtained. Bufotalin was the most potent active compound among these four bufadienolides, and it exerted stronger inhibitory effect on the viability of doxorubicin-induced multidrug resistant liver cancer cells (R-HepG2) than that of their parent cells HepG2. Structure-activity relationship analysis indicated that the acetyl group linked to C-16 of bufadienolides might be useful for increasing anti-hepatoma activity. Further mechanistic studies revealed that bufotalin treatment induced cell cycle arrest at G(2)/M phase through down-regulation of Aurora A, CDC25, CDK1, cyclin A and cyclin B1, as well as up-regulation of p53 and p21. Bufotalin treatment also induced apoptosis which was accompanied by decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential, increases in intracellular calcium level and reactive oxygen species production, activations of caspase-9 and -3, cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) as well as changes in the expressions of bcl-2 and bax. It was also found that the inhibition of Akt expression and phosphorylation was involved in apoptosis induction, and specific Akt inhibitor LY294002 or siRNA targeting Akt can synergistically enhanced bufotalin-induced apoptosis. In vivo study showed that bufotalin significantly inhibited the growth of xenografted R-HepG2 cells, without body weight loss or marked toxicity towards the spleen. These results indicate that bufotalin has a promising potential to become a novel anti-cancer agent for the treatment of liver cancer with multidrug resistance.
Bufotalin sensitizes death receptor-induced apoptosis via Bid- and STAT1-dependent pathways.[Pubmed:21887462]
Int J Oncol. 2012 Jan;40(1):203-8.
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) are apoptosis-inducing ligands that stimulate death receptors. In this study, we investigated the effects of bufotalin, a major compound in toad venom, on sensitizing TNF-alpha and TRAIL-induced apoptosis of HeLa cells. Bufotalin promoted death receptor-mediated cell death, especially TRAIL-induced apoptosis, through activation of caspase-3 and PARP-1. Mitochondrial Bid-dependent pathway was activated in TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Cotreatment of bufotalin with TRAIL resulted in the downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins, including Bcl-XL, Mcl-1, survivin and XIAP, and the up-regulation of MAPKs and TRAIL receptor DR5. In addition, phosphorylation of STAT1 was strongly inhibited by bufotalin. Moreover, DR5 expression was induced by knocking down the STAT1 expression. Moreover, the TRAIL-induced apoptotic response was promoted by STAT1 siRNA. Our results demonstrated that bufotalin is a powerful sensitizer of death receptor-induced apoptosis in cancer cells.


