CGP 39551CAS# 127910-32-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 127910-32-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6372334 | Appearance | Powder |
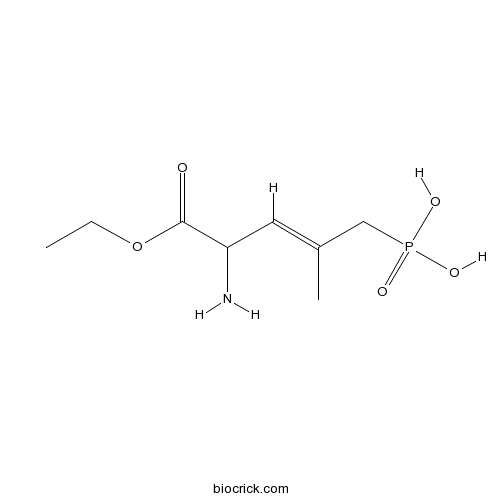
| Formula | C8H16NO5P | M.Wt | 237.19 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | [(E)-4-amino-5-ethoxy-2-methyl-5-oxopent-2-enyl]phosphonic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(C=C(C)CP(=O)(O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OKDOWCKDTWNRCB-GQCTYLIASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H16NO5P/c1-3-14-8(10)7(9)4-6(2)5-15(11,12)13/h4,7H,3,5,9H2,1-2H3,(H2,11,12,13)/b6-4+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective and competitive NMDA antagonist (Ki = 310 nM for inhibition of [3H]-CPP binding in rat brain). Centrally active upon oral administration in vivo. |

CGP 39551 Dilution Calculator

CGP 39551 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.216 mL | 21.0801 mL | 42.1603 mL | 84.3206 mL | 105.4007 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8432 mL | 4.216 mL | 8.4321 mL | 16.8641 mL | 21.0801 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4216 mL | 2.108 mL | 4.216 mL | 8.4321 mL | 10.5401 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0843 mL | 0.4216 mL | 0.8432 mL | 1.6864 mL | 2.108 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0422 mL | 0.2108 mL | 0.4216 mL | 0.8432 mL | 1.054 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- CGP 37849
Catalog No.:BCC7078
CAS No.:127910-31-0
- C-type natriuretic peptide (1-22) (human, rat, swine)
Catalog No.:BCC6033
CAS No.:127869-51-6
- Saquinavir
Catalog No.:BCC1921
CAS No.:127779-20-8
- Dryocrassin ABBA
Catalog No.:BCN6276
CAS No.:12777-70-7
- 2'-O-Methylbroussonin A
Catalog No.:BCN7318
CAS No.:127757-13-5
- SKF 97541
Catalog No.:BCC6626
CAS No.:127729-35-5
- Radicicol
Catalog No.:BCC2131
CAS No.:12772-57-5
- (2R)-5,7-Dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN7806
CAS No.:1277188-85-8
- 9alpha,11-Dihydroxydrim-7-en-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN7225
CAS No.:127681-58-7
- PF-4989216
Catalog No.:BCC6468
CAS No.:1276553-09-3
- Cadherin Peptide, avian
Catalog No.:BCC1018
CAS No.:127650-08-2
- Oleficin
Catalog No.:BCN1848
CAS No.:12764-54-4
- 24(31)-Dehydrocarboxyacetylquercinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1589
CAS No.:127970-62-1
- CU CPT 4a
Catalog No.:BCC6319
CAS No.:1279713-77-7
- Teucrin A
Catalog No.:BCC8259
CAS No.:12798-51-5
- Ursodiol
Catalog No.:BCC4945
CAS No.:128-13-2
- Pregnanolone
Catalog No.:BCC7736
CAS No.:128-20-1
- Sennoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1003
CAS No.:128-57-4
- Arvanil
Catalog No.:BCC7026
CAS No.:128007-31-8
- erythro-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1588
CAS No.:1280602-81-4
- Fmoc-D-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3548
CAS No.:128107-47-1
- Escitalopram
Catalog No.:BCC4193
CAS No.:128196-01-0
- N-ArachidonylGABA
Catalog No.:BCC7186
CAS No.:128201-89-8
- (R,R)-2,6-Bis(4-phenyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8397
CAS No.:128249-70-7
Lack of development of tolerance to anticonvulsant effects of two excitatory amino acid antagonists, CGP [corrected] 37849 and CGP 39551 in genetically epilepsy-prone rats.[Pubmed:8896813]
Brain Res. 1996 Sep 23;734(1-2):91-7.
Two selective excitatory amino acid antagonists, DL-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl- 5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid (CGP 37849) and its carboxyethylester (CGP 39551), were studied against audiogenic seizures in genetically epilepsy-prone rats following oral administration. Acute administration of CGP 37849 attenuated the clonic and tonic phases of the audiogenic seizures (109 dB, 12-16 kHz) 120 min after pretreatment (ED50 19.7 and 11.2 mumol kg-1, respectively). Similarly, CGP 39551 attenuated the clonic and tonic phases of audiogenic seizures 120 min after acute treatment with ED50 values of 17.2 and 8.8 mumol kg-1, respectively. For chronic studies animals were treated orally once daily (at 10 h) for 4 weeks with CGP 37849 (20 or 40 mumol kg-1) or CGP 39551 (15 or 30 mumol kg-1). In order to assess anticonvulsant activity, rats were subjected to auditory stimulation 120 min after drug administration on days 1, 3 and 5 and then every 3 or 4 days. Following 2 and 4 weeks of repeated drug administration with CGP 37849 (20 and 40 mumol kg-1) the ED50 values against clonic and tonic seizures were not significantly different from those observed following an acute administration. Similarly, 2 and 4 weeks after repeated treatment CGP 39551 (15 and 30 mumol kg-1) the ED50 values against clonic and tonic seizures were not significantly different from those observed following an acute administration. There was no significant difference between the ED50 values following either acute or repeated treatment of the two excitatory amino acid antagonists suggesting a lack of development tolerance. The duration of anticonvulsant activity observed between 0.5 and 24 h following administration of CGP 37849- and CGP 39551 was similar in acute and chronic treatment. The effects of CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 on motor behaviour was also evaluated following acute and repeated treatment by a rotarod apparatus 110 min following drug administration. The TD50 values for CGP 37849 and CGP 39551-induced impairment of locomotor performance recorded 2 or 4 weeks of repeated administration were not significantly different from those observed following an acute administration. The TD50 values for CGP 37849- and CGP 39551-induced impairment of locomotor performance were 87.6 and 70.8 mumol kg-1 i.p. respectively following 2 weeks treatment and 92.9 and 76.9 mumol kg-1 i.p. respectively following 4 weeks treatment. The doses of CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 required to elicit motor impairment were at least an order of magnitude above required for anticonvulsant activity. Since these compounds showed anticonvulsant properties after oral administration and lack of development of tolerance after repeated treatment, a potential use for antiepileptic therapy in man is suggested.
Adaptive changes in the NMDA receptor complex in rat hippocampus after chronic treatment with CGP 39551.[Pubmed:7698217]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec 12;271(1):93-101.
Chronic treatment of adult rats with DL-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic carboxyethylester (CGP 39551) (30 mg/kg orally for 12 days) induced a significant increase, 72 h after the last dose, in the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-sensitive [3H]glutamate binding in the hippocampal pyramidal layer (stratum oriens CA1, CA3: +51% on average; stratum radiatum CA1, CA3: +40% on average; stratum pyramidale CA1: +20%, CA3: +55%) and in the dentate gyrus (+43%) compared to vehicle-injected animals, as assessed by quantitative receptor autoradiography. Similar results were obtained using the NMDA receptor antagonist, [3H]DL-(E)-2-amino-4-propyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid (CGP 39653). Saturation experiments showed that the increase in [3H]CGP 39653 binding was due to the maximum number of receptors, without changes in affinity. The same regimen did not alter [3H]N-(1-[2-thienyl]-cyclohexyl)-3,4-piperidine (TCP) binding to the ion channel coupled to the receptor but prevented D-serine (5 microM)-induced enhancement of [3H]glutamate binding. NMDA (3-300 microM) enhanced [3H]noradrenaline release from hippocampal slices, and 7-Cl-kynurenic acid (5-100 microM) and (+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo-[a,d]cyclo-hepten-5,10-imine maleate (MK 801) (0.03-0.3 microM), antagonists at the glycine site and ion channel respectively, antagonized this effect to the same extent in CGP 39551-treated rats and controls. Chronic CGP 39551 did not affect the neurotoxic potency of quinolinic acid, a selective agonist at the NMDA receptor, injected in the hippocampus.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Excitatory amino acid antagonists and pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures during ontogenesis. IV. Effects of CGP 39551.[Pubmed:9077588]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1997 Mar;56(3):493-8.
We determined anticonvulsant effects of CGP 39551 [(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid 1-ethylester] against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in developing, 7-90 day old, rats. The rats received CGP 39551 in doses of 10, 20 or 40 mg/kg IP 30 min prior to the pentylenetetrazol administration (100 mg/kg s.c.). In addition, the 20 mg/kg dose of CGP 39551 was injected 120 min prior to pentylenetetrazol. In adult rats, all doses of CGP 39551 blocked generalized tonic-clonic pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. In younger rats, higher doses of CGP 39551 and/or a longer delay between the CGP 39551 pretreatment and pentylenetetrazol administration was necessary for similar anticonvulsant effects against tonic-clonic seizures. In contrast, there was no effect of CGP on pentylenetetrazol-induced clonic seizures. The results indicate that CGP 39551 has anticonvulsant features similar to other competitive NMDA receptor antagonists. High doses of CGP 39551 and long pretreatment latency which are necessary in young rats for anticonvulsant effects may reflect the overexpression of NMDA transmission during the second and third postnatal week of the rat. Alternatively in adult rats, we can speculate an anticonvulsant role of a CGP 39551 metabolite or maturation of brain uptake mechanism for CGP 39551.
Effects of the competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist CGP 37849 and its ethylester CGP 39551 on N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked whole-cell currents in cultured spinal neurones and on vestibular stimulation-induced seizures in EL mice.[Pubmed:9893924]
Arzneimittelforschung. 1998 Dec;48(12):1121-5.
The competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist DL-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid (CAS 127910-31-0, 4-methyl-APPA, CGP 37849) and its ethyl ester (CAS 127910-32-1, CGP 39551) potently block NMDA-evoked whole-cell current on mouse spinal neurones in primary dissociated cell cultures with IC50 (+/- SE) values of 189 +/- 9 nmol/l (CGP 37849) and 2100 +/- 220 nmol/l (CGP 39551), respectively. The compounds dose-dependently blocked vestibular stimulation-induced convulsions in EL mice, 2 h after oral administration, with ED50 (95% CI) values of 135 (78-236) mumol/kg (CGP 37849) and 65 (45-94) mumol/kg (CGP 39551). In male Swiss albino mice, performance in the step-through passive avoidance procedure was dose-dependently impaired with ED50 (95% CI) values of 85 (56-157) mumol/kg (CGP 37849) and 27 (18-42) mumol/kg (CGP 39551). In addition performance of these animals in the rotarod test of motor coordination was impaired, 2 h after oral administration of CGP 39551, with an ED50 (95% CI) of 142 (100-201) mumol/kg. These findings demonstrate anticonvulsant activity in these potent NMDA antagonists after oral administration with CGP 39551 possessing greater relative potency. However, the unfavourable ratio of therapeutic dose versus dose inducing memory or motor impairment supports the prevailing notion that such adverse effects of the presently available compounds preclude the use of NMDA antagonists as long-term therapies.
Effects of competitive NMDA receptor antagonists on excitatory amino acid-evoked currents in mouse spinal cord neurones.[Pubmed:10027090]
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1999;13(1):67-74.
The effects of CGP 37849 [DL-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoate] and its ethylester CGP 39551 on whole-cell currents evoked by the endogenous excitatory amino acids, L-glutamate and L-aspartate, were studied in cultured mouse spinal cord neurones. Although CGP 37849 was the more potent compound, both antagonists inhibited 20 microM L-aspartate or 2 microM L-glutamate currents concentration-dependently and reversibly. We calculated IC50 values of 370 +/- 180 nM for CGP 37849 and 2200 +/- 140 nM for CGP 39551 (inhibition of L-aspartate current), and 210 +/- 25 nM for CGP 37849 and 6000 +/- 4700 nM for CGP 39551 (inhibition of L-glutamate current). Both CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 selectively blocked N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-evoked inward current. Current evoked by 5 microM kainate or 5 microM alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) was unaffected by 10 microM CGP 39551. Current evoked by NMDA was concentration-dependently blocked by CGP 39551 with an IC50 of 2100 +/- 220 nM. After application of 10 microM CGP 37849, 17 +/- 6% of the current evoked by 5 microM L-glutamate remained. This residual current was due to non-NMDA receptor activation since application of 25 microM 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV) together with CGP 37849 did not significantly alter the residual current, whereas application of 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) with CGP 37849 did significantly inhibit this current. Clamping cells at potentials ranging from -80 to +60 mV showed a linear potential--current relationship for the 20 microM L-aspartate-evoked current with reversal potential around 0 mV. The proportion of the L-aspartate current antagonized by CGP 37849 or CGP 39551 appeared to be independent of clamping potential. The concentration--current relationship of L-aspartate in the absence of the antagonists showed an EC50 of 49 +/- 14 microM. Upon application of 1 microM CGP 37849 and 10 microM CGP 39551, the L-aspartate concentration--current curve shifted to higher concentrations, and resulted in a 5- and 13-fold increase in the EC50 of L-aspartate, respectively, whereas Imax was not changed by application of the antagonists. Thus, the potent NMDA antagonists CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 were shown to inhibit excitatory amino acid responses specifically by competitive binding to the neurotransmitter recognition site of the NMDA receptor. Selective, competitive antagonism of L-glutamate- and L-aspartate-evoked NMDA receptor responses probably underlies the effects of CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 such as their anticonvulsant, neuroprotectant and antidepressant actions.
Anticonvulsant and behavioral effects of two novel competitive N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonists, CGP 37849 and CGP 39551, in the kindling model of epilepsy. Comparison with MK-801 and carbamazepine.[Pubmed:1671593]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):432-40.
The orally active competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists CGP 37849 (DL-[E]-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid) and its ethyl ester CGP 39551 were evaluated in amygdala-kindled rats, a model for complex partial and secondarily generalized seizures. Anticonvulsant and behavioral effects of these novel compounds were compared with those of the noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 [(+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydroxy-5H-dibenzo(a,d)cyclohepten-5,10-imin e] and the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine, one of the major drugs for treatment of partial and generalized seizures in humans. For comparative evaluation, the compounds were injected i.p. at the following doses: 1 to 10 mg/kg (CGP 37849 or CGP 39551), 0.05 to 0.3 mg/kg (MK-801) and 20 to 40 mg/kg (carbamazepine), respectively. In contrast to carbamazepine, CGP 37849, CGP 39551 and MK-801 exerted only weak anticonvulsant effects in fully kindled rats and did not increase the focal seizure threshold. The weak anticonvulsant effects of the NMDA receptor antagonists in kindled rats were associated with profound untoward behavioral effects. The behavioral syndrome induced by the NMDA receptor antagonists in kindled rats was characterized by marked ataxia, hyperactivity and, in case of CGP 37849 and MK-801, stereotypies, such as head weaving. The low or absent effectiveness of the novel NMDA receptor antagonists against kindled seizures suggests that these compounds will not be clinically useful antiepileptics against partial and secondarily generalized seizures. Furthermore, in view of the recent clinical findings on psychotomimetic effects of MK-801 in epileptic patients, the similarities in the excitatory effects produced by CGP 39551, CGP 37849 and MK-801 in kindled rats may indicate that competitive NMDA receptor antagonists may also produce psychotomimetic effects in humans.
CGP 37849 and CGP 39551: novel and potent competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists with oral activity.[Pubmed:1972895]
Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):791-7.
1. The pharmacological properties of CGP 37849 (DL-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentenoic acid; 4-methyl-APPA) and its carboxyethylester, CGP 39551, novel unsaturated analogues of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate (AP5), were evaluated in rodent brain in vitro and in vivo. 2. Radioligand binding experiments demonstrated that CGP 37849 potently (Ki 220 nM) and competitively inhibited NMDA-sensitive L-[3H]-glutamate binding to postsynaptic density (PSD) fractions from rat brain. It inhibited the binding of the selective NMDA receptor antagonist, [3H]-((+/-)-3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonate (CPP), with a Ki of 35 nM, and was 4, 5 and 7 fold more potent than the antagonists [+/-)-cis-4-phosphonomethylpiperidine-2-carboxylic acid) (CGS 19755), CPP and D-AP5, respectively. Inhibitory activity was associated exclusively with the trans configuration of the APPA molecule and with the D-stereoisomer. CGP 39551 showed weaker activity at NMDA receptor recognition sites and both compounds were weak or inactive at 18 other receptor binding sites. 3. CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 were inactive as inhibitors of L-[3H]-glutamate uptake into rat brain synaptosomes and had no effect on the release of endogenous glutamate from rat hippocampal slices evoked by electrical field stimulation. 4. In the hippocampal slice in vitro, CGP 37849 selectively and reversibly antagonized NMDA-evoked increases in CA1 pyramidal cell firing rate. In slices bathed in medium containing low Mg2+ levels, concentrations of CGP 37849 up to 10 microM suppressed burst firing evoked in CAl neurones by stimulation of Schaffer collateral-commissural fibres without affecting the magnitude of the initial population spike; CGP 39551 exerted the same effect but was weaker. In vivo, oral administration to rats of either CGP 37849 or CGP 39551 selectively blocked firing in hippocampal neurones induced by ionophoreticallyapplied NMDA, without affecting the responses to quisqualate or kainate. 5. CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 suppressed maximal electroshock-induced seizures in mice with ED50 s of 21 and 4 mg kg'- p.o., respectively. 6. CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 are potent and competitive NMDA receptor antagonists which show significant central effects following oral administration to animals. As such, they may find value as tools to elucidate the roles of NMDA receptors in brain function, and potentially as therapeutic agents for the treatment of neurological disorders such as epilepsy and ischaemic brain damage in man.


