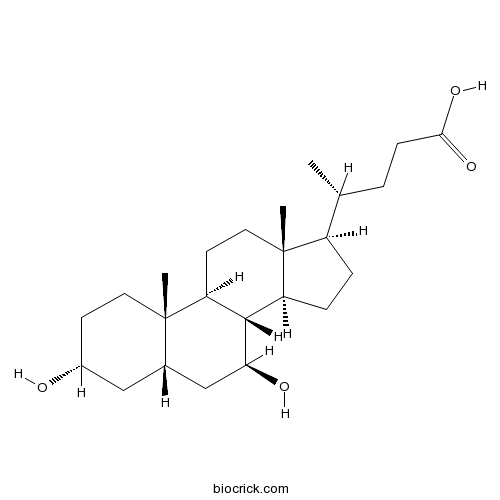
UrsodiolBile acids for PBC treatment CAS# 128-13-2 |
- CX-5461
Catalog No.:BCC3700
CAS No.:1138549-36-6
- Gemcitabine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1076
CAS No.:122111-03-9
- Fludarabine Phosphate (Fludara)
Catalog No.:BCC3681
CAS No.:75607-67-9
- Bleomycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3694
CAS No.:9041-93-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 128-13-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 31401 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H40O4 | M.Wt | 392.57 |
| Type of Compound | Steroids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ursodeoxycholic acid; UDCS | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (84.06 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,7S,8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(CCC(=O)O)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2C(CC4C3(CCC(C4)O)C)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-UZVSRGJWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ursodeoxycholic acid is a potent inhibitor of apoptosis, it prevents cytochrome c release in apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial membrane depolarization and channel formation. Ursodeoxycholic acid can ameliorate experimental ileitis counteracting intestinal barrier dysfunction and oxidative stress, it as a chemopreventive agent in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. |
| Targets | PARP | ROS | P450 (e.g. CYP17) |
| In vivo | Ursodeoxycholic acid as a chemopreventive agent in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.[Pubmed: 12671884 ]Gastroenterology. 2003 Apr;124(4):889-93.Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has shown effectiveness as a colon cancer chemopreventive agent in preclinical studies. In addition, a recent report suggests that it also may decrease the risk for developing colorectal dysplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). We sought to evaluate the effect of UDCA on colorectal neoplasia in a group of patients with UC and PSC enrolled in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates experimental ileitis counteracting intestinal barrier dysfunction and oxidative stress.[Pubmed: 15573906]Dig Dis Sci. 2004 Oct;49(10):1569-74.The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on intestinal permeability (IP) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in indomethacin-induced enteropathy, a well-known experimental model of Crohn's disease. |
| Kinase Assay | Ursodeoxycholic acid prevents cytochrome c release in apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial membrane depolarization and channel formation.[Pubmed: 10510466 ]Cell Death Differ. 1999 Sep;6(9):842-54.The hydrophilic bile salt Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a potent inhibitor of apoptosis. |
| Animal Research | Ursodeoxycholic acid aggravates bile infarcts in bile duct-ligated and Mdr2 knockout mice via disruption of cholangioles.[Pubmed: 12360485]Gastroenterology. 2002 Oct;123(4):1238-51.The effects of Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) in biliary obstruction are unclear. We aimed to determine the effects of UDCA in bile duct-ligated and in Mdr2 knockout (Mdr2(-/-)) mice with biliary strictures.
|

Ursodiol Dilution Calculator

Ursodiol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5473 mL | 12.7366 mL | 25.4732 mL | 50.9463 mL | 63.6829 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5095 mL | 2.5473 mL | 5.0946 mL | 10.1893 mL | 12.7366 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2547 mL | 1.2737 mL | 2.5473 mL | 5.0946 mL | 6.3683 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0509 mL | 0.2547 mL | 0.5095 mL | 1.0189 mL | 1.2737 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2547 mL | 0.5095 mL | 0.6368 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ursodiol (Ursodeoxycholic acid) is bile acids used in treatment of primary biliary cirrhomized (PBC) [1].
Ursodiol (Ursodeoxycholic acid) has been reported to prevent progression of PBC, and increase survival. In addition, Ursodiol has been revealed to inhibit the initiation and postinitiation phases of azoxymethane-induced colonic tumor development. Moreover, Ursodiol has been noted to dose-dependently inhibit the viability of HepG2 and BEL7402 cell lines with IC50 values of 0.92mmol/L and 0.86mmol/L, respectively. Ursodiol has also reported to dose-dependently and significantly enhance the apoptosis rates in HepG2 and BEL7402 cells. Besides, treatment of Ursodiol has shown the reduction of the ecpression of cell cycle regulating proteins (cyclinD1,cyclin D3, Cdk2 and Cdk4) in Western blot analysis [1].
References:
[1] Liu H1, Qin CY, Han GQ, Xu HW, Meng M, Yang Z. Mechanism of apoptotic effects induced selectively by ursodeoxycholic acid on human hepatoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Mar 21;13(11):1652-8.
- Teucrin A
Catalog No.:BCC8259
CAS No.:12798-51-5
- CU CPT 4a
Catalog No.:BCC6319
CAS No.:1279713-77-7
- 24(31)-Dehydrocarboxyacetylquercinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1589
CAS No.:127970-62-1
- CGP 39551
Catalog No.:BCC7053
CAS No.:127910-32-1
- CGP 37849
Catalog No.:BCC7078
CAS No.:127910-31-0
- C-type natriuretic peptide (1-22) (human, rat, swine)
Catalog No.:BCC6033
CAS No.:127869-51-6
- Saquinavir
Catalog No.:BCC1921
CAS No.:127779-20-8
- Dryocrassin ABBA
Catalog No.:BCN6276
CAS No.:12777-70-7
- 2'-O-Methylbroussonin A
Catalog No.:BCN7318
CAS No.:127757-13-5
- SKF 97541
Catalog No.:BCC6626
CAS No.:127729-35-5
- Radicicol
Catalog No.:BCC2131
CAS No.:12772-57-5
- (2R)-5,7-Dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN7806
CAS No.:1277188-85-8
- Pregnanolone
Catalog No.:BCC7736
CAS No.:128-20-1
- Sennoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1003
CAS No.:128-57-4
- Arvanil
Catalog No.:BCC7026
CAS No.:128007-31-8
- erythro-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1588
CAS No.:1280602-81-4
- Fmoc-D-Ser(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3548
CAS No.:128107-47-1
- Escitalopram
Catalog No.:BCC4193
CAS No.:128196-01-0
- N-ArachidonylGABA
Catalog No.:BCC7186
CAS No.:128201-89-8
- (R,R)-2,6-Bis(4-phenyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8397
CAS No.:128249-70-7
- GDC-0032
Catalog No.:BCC4066
CAS No.:1282512-48-4
- BAY-X 1005
Catalog No.:BCC6038
CAS No.:128253-31-6
- Pachyaximine A
Catalog No.:BCN6152
CAS No.:128255-08-3
- Axillaridine A
Catalog No.:BCN6153
CAS No.:128255-16-3
Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates experimental ileitis counteracting intestinal barrier dysfunction and oxidative stress.[Pubmed:15573906]
Dig Dis Sci. 2004 Oct;49(10):1569-74.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on intestinal permeability (IP) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in indomethacin-induced enteropathy, a well-known experimental model of Crohn's disease. Seventy-eight male Wistar rats were randomly assigned to receive indomethacin, indomethacin + UDCA, or vehicles. Indomethacin induced a significant increase in the fraction of urinary excretion of 51Cr-EDTA following oral administration (7.9 +/- 1.3 vs 2.3 +/- 0.2%; P < 0.05) and lucigenin-amplified chemiluminescence in intestinal fragments ex vivo (10.1 +/- 1.9 vs 2.6 +/- 0.4 cpm x 10(3)/mg; P < 0.05) compared to controls. UDCA significantly reversed these effects (P < 0.05), without being incorporated in biliary bile acid composition (HPLC analysis). These findings support a local protective effect of UDCA in experimental ileitis by the modulation of intestinal barrier dysfunction and oxidative stress. In short, they provide insights into mechanisms of action of UDCA in intestinal inflammation and a new perspective on the treatment of Crohn's disease.
Ursodeoxycholic acid prevents cytochrome c release in apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondrial membrane depolarization and channel formation.[Pubmed:10510466]
Cell Death Differ. 1999 Sep;6(9):842-54.
The hydrophilic bile salt ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a potent inhibitor of apoptosis. In this paper, we further characterize the mechanism by which UDCA inhibits apoptosis induced by deoxycholic acid, okadaic acid and transforming growth factor beta1 in primary rat hepatocytes. Our data indicate that coincubation of cells with UDCA and each of the apoptosis-inducing agents was associated with an approximately 80% inhibition of nuclear fragmentation (P<0.001). Moreover, UDCA prevented mitochondrial release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm by 70 - 75% (P<0.001), thereby, inhibiting subsequent activation of DEVD-specific caspases and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Each of the apoptosis-inducing agents decreased mitochondrial transmembrane potential and increased mitochondrial-associated Bax protein levels. Coincubation with UDCA was associated with significant inhibition of these mitochondrial membrane alterations. The results suggest that the mechanism by which UDCA inhibits apoptosis involves an interplay of events in which both depolarization and channel-forming activity of the mitochondrial membrane are inhibited.
Ursodeoxycholic acid as a chemopreventive agent in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.[Pubmed:12671884]
Gastroenterology. 2003 Apr;124(4):889-93.
BACKGROUND & AIMS: Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has shown effectiveness as a colon cancer chemopreventive agent in preclinical studies. In addition, a recent report suggests that it also may decrease the risk for developing colorectal dysplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). We sought to evaluate the effect of UDCA on colorectal neoplasia in a group of patients with UC and PSC enrolled in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. METHODS: From a prior, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of UDCA therapy in PSC at our center, we followed-up patients with concomitant UC to assess the effect of UDCA on the development of colorectal dysplasia and cancer as compared with placebo. RESULTS: Fifty-two subjects were followed-up for a total of 355 person-years. Those originally assigned to receive UDCA had a relative risk of 0.26 for developing colorectal dysplasia or cancer (95% confidence interval, 0.06-0.92; P = 0.034). Many of the patients originally assigned to the placebo group eventually received open-label UDCA. Assigning these patients to the UDCA group from the time they began active therapy did not change the magnitude of the protective effect (relative risk, 0.26; 95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.99; P = 0.049). CONCLUSIONS: UDCA significantly decreases the risk for developing colorectal dysplasia or cancer in patients with UC and PSC.
Ursodeoxycholic acid aggravates bile infarcts in bile duct-ligated and Mdr2 knockout mice via disruption of cholangioles.[Pubmed:12360485]
Gastroenterology. 2002 Oct;123(4):1238-51.
BACKGROUND & AIMS: The effects of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) in biliary obstruction are unclear. We aimed to determine the effects of UDCA in bile duct-ligated and in Mdr2 knockout (Mdr2(-/-)) mice with biliary strictures. METHODS: Mice fed UDCA (0.5% wt/wt) or a control diet were subjected to common bile duct ligation (CBDL), selective bile duct ligation (SBDL), or sham operation. UDCA was also fed to 2-month-old Mdr2(-/-) mice. Serum biochemistry, liver histology, and mortality rates were investigated. The biliary tract was studied by plastination, India ink injection, and electron microscopy. The effects of UDCA on biliary pressure were determined by cholangiomanometry. RESULTS: UDCA feeding in CBDL mice increased biliary pressure, with subsequent rupture of cholangioles and aggravation of hepatocyte necroses, resulting in significantly increased mortality. UDCA feeding in SBDL mice aggravated liver injury exclusively in the ligated lobe. Mdr2(-/-) mice developed liver lesions resembling sclerosing cholangitis characterized by biliary strictures and dilatations. UDCA induced bile infarcts in these animals. CONCLUSIONS: UDCA aggravates bile infarcts and hepatocyte necroses in mice with biliary obstruction via disruption of cholangioles as a result of increased biliary pressure caused by its choleretic action.


