CGP 42112Selective, high affinity AT2 ligand CAS# 127060-75-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 127060-75-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 123794 | Appearance | Powder |
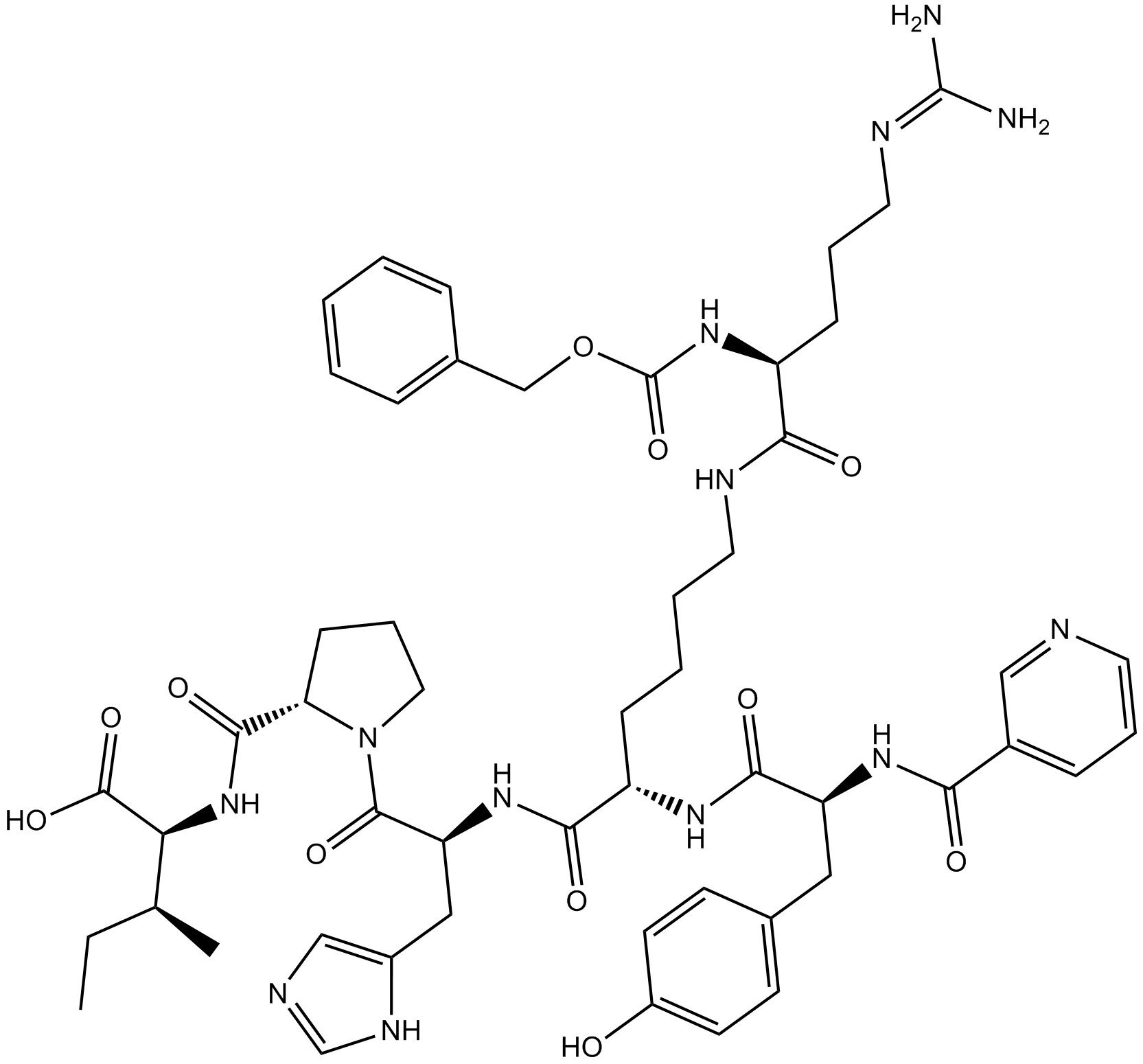
| Formula | C52H69N13O11 | M.Wt | 1052.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CGP42112A | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 350 mg/mL (332.64 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Sequence | YKHPI (Modifications: Tyr-1 = N-α-Nicotinoyl, Lys-2 = Lys-(N-α-Z-Arg)) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-[[(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)pentanoyl]amino]-2-[[(2S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(pyridine-3-carbonylamino)propanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)O)NC(=O)C1CCCN1C(=O)C(CC2=CN=CN2)NC(=O)C(CCCCNC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)OCC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C5=CN=CC=C5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UXGNARZDONUMMK-LRMQDCNJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C52H69N13O11/c1-3-32(2)43(50(73)74)64-48(71)42-17-11-25-65(42)49(72)41(27-36-29-56-31-59-36)62-46(69)39(60-47(70)40(26-33-18-20-37(66)21-19-33)61-44(67)35-14-9-22-55-28-35)15-7-8-23-57-45(68)38(16-10-24-58-51(53)54)63-52(75)76-30-34-12-5-4-6-13-34/h4-6,9,12-14,18-22,28-29,31-32,38-43,66H,3,7-8,10-11,15-17,23-27,30H2,1-2H3,(H,56,59)(H,57,68)(H,60,70)(H,61,67)(H,62,69)(H,63,75)(H,64,71)(H,73,74)(H4,53,54,58)/t32-,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, high affinity angiotensin AT2 receptor ligand (Ki = 0.24 nM). Displays agonistic properties at proximal tubule AT2 receptors, causes Na+, K+-ATPase inhibition and sodium excretion. Antagonizes Ang-II induced contractions in rabbit aortic rings (IC50 = 1850 nM). |

CGP 42112 Dilution Calculator

CGP 42112 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CGP-42112(CGP-42112A) is a potent Angiotensin-II subtype 2 receptor(AT2 R) agonist. IC50 value: Target: AT2 R agonist in vitro: CGP42112 (>==1 nM) significantly inhibited cGMP production from the basal value. CGP42112 (>==1 nM) significantly inhibited TH-enzyme activity from the basal value. These inhibitory effects of CGP42112 on TH-enzyme activity and-cGMP production were abolished by PD123319 (AT(2)-R antagonist) while CV-11974 (AT(1)-R antagonist) was ineffective [1]. [125I]CGP 42112 bound selectively to the AT2 angiotensin II receptor subtype. [125I]CGP 42112 bound with higher affinity in the brain than in the adrenal. beta-Mercaptoethanol enhanced [125I]CGP 42112 binding in the brain, but did not alter its binding in the adrenal [2]. [125I]CGP 42112 bound with high affinity (Kd = 0.07-0.3 nM, depending on the area studied). [125I]CGP 42112 binding was selective for AT2 receptors, as determined by lack of competition with the AT1 ligand losartan, and competition by the AT2 ligands PD 123177 and unlabeled CGP 42112 and the non-selective peptides Ang II and angiotensin III (Ang III) [4]. in vivo: Intravenous infusions of CGP 42112 (0.1 and 1 mg kg-1 min-1) and PD 123319 (0.36 and 1 mg kg-1 min-1) shifted the upper limit of CBF autoregulation toward higher blood pressures without affecting baseline CBF [3].
References:
[1]. Takekoshi K, et al. Angiotensin-II subtype 2 receptor agonist (CGP-42112) inhibits catecholamine biosynthesis in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jun 7;272(2):544-50.
[2]. Speth RC. [125I]CGP 42112 binding reveals differences between rat brain and adrenal AT2 receptor binding sites. Regul Pept. 1993 Mar 19;44(2):189-97.
[3]. Naveri L, et al. Angiotensin II AT2 receptor stimulation extends the upper limit of cerebral blood flow autoregulation: agonist effects of CGP 42112 and PD 123319. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Jan;14(1):38-44.
[4]. Heemskerk FM, et al. Quantitative autoradiography of angiotensin II AT2 receptors with [125I]CGP 42112. Brain Res. 1995 Apr 17;677(1):29-38.
- 4,9-Dimethoxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3107
CAS No.:1270001-72-3
- Beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8302
CAS No.:127-91-3
- Sulfamerazine
Catalog No.:BCC4854
CAS No.:127-79-7
- Sulfisoxazole
Catalog No.:BCC4860
CAS No.:127-69-5
- Sulfamerazine sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5205
CAS No.:127-58-2
- Sulfacetamide Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4383
CAS No.:127-56-0
- 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-isopropylphenyl)propane
Catalog No.:BCC8494
CAS No.:127-54-8
- Vitamin A Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4748
CAS No.:127-47-9
- Lutein
Catalog No.:BCN6151
CAS No.:127-40-2
- Lasiocarpine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2002
CAS No.:127-30-0
- Pimaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN6149
CAS No.:127-27-5
- Taraxerol
Catalog No.:BCN6148
CAS No.:127-22-0
- Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3578
CAS No.:127062-22-0
- Glyceryl hexacosanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8991
CAS No.:127098-14-0
- BMS-911543
Catalog No.:BCC2204
CAS No.:1271022-90-2
- MI-3
Catalog No.:BCC1747
CAS No.:1271738-59-0
- MI-2
Catalog No.:BCC1746
CAS No.:1271738-62-5
- 4-O-Demethylkadsurenin D
Catalog No.:BCN6649
CAS No.:127179-70-8
- 7-(2'-Deoxyadenosin-N6-yl)aristolactam I
Catalog No.:BCN2559
CAS No.:127191-86-0
- KN-62
Catalog No.:BCC3602
CAS No.:127191-97-3
- (3S,4S)-3-(Boc-amino)-4-methylpyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCC4015
CAS No.:127199-54-6
- Bisacurone C
Catalog No.:BCN7316
CAS No.:127214-86-2
- Intermedin B
Catalog No.:BCN7317
CAS No.:127214-87-3
- Sitafloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC5164
CAS No.:127254-12-0
Angiotensin-II subtype 2 receptor agonist (CGP-42112) inhibits catecholamine biosynthesis in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells.[Pubmed:10833449]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jun 7;272(2):544-50.
Angiotensin II subtype 2 receptor (AT(2)-R) is abundantly expressed in adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. However, the physiological roles of AT(2)-R in chromaffin cells remain to be clarified. Therefore, we investigated the effects of CGP42112 (AT(2)-R agonist) on catecholamine biosynthesis in cultured porcine adrenal medullary cells. We initially confirmed AT(2)-R was predominantly expressed in porcine adrenal medullary cells by [(125)I]-Ang II binding studies. CGP42112 (>==1 nM) significantly inhibited cGMP production from the basal value. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthesis of catecholamine, and its activity is regulated by both TH-enzyme activity and TH-synthesis. CGP42112 (>==1 nM) significantly inhibited TH-enzyme activity from the basal value. These inhibitory effects of CGP42112 on TH-enzyme activity and-cGMP production were abolished by PD123319 (AT(2)-R antagonist) while CV-11974 (AT(1)-R antagonist) was ineffective. We also tested whether decrease of cGMP is involved in the inhibitory effect of CGP42112 on TH-enzyme activity. Pretreatment of 8-Br-cGMP (membrane-permeable cGMP analogue) prevented the inhibitory effect of CGP 42112 on TH-enzyme activity. Similar to that of TH-enzyme activity, CGP42112 (>==1 nM) significantly reduced TH-mRNA and TH-protein level from the basal value, and these inhibitory effects were abolished by PD123319 but not CV-11974. These findings demonstrate that CGP 42112 reduces both TH-enzyme activity and TH-synthesis and that these inhibitory effects could be mediated by decrease of cGMP production.
CGP-42112 partially activates human monocytes and reduces their stimulation by lipopolysaccharides.[Pubmed:9316402]
Am J Physiol. 1997 Sep;273(3 Pt 1):C826-33.
CGP 42112, a high-affinity ligand for angiotensin II AT2 receptors, binds to rat macrophage/microglia lacking AT2 receptors. Here we report that CGP-42112 binds to human monocytes and exerts specific effects. Binding studies revealed a single site, highly specific for CGP-42112, not displaceable by angiotensin II, angiotensin fragments, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin (IL)-4, IL-10, transforming growth factor-beta, or lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Incubation of purified human monocytes in serum-free medium with CGP-42112 enhanced, in a dose-dependent manner, cell attachment to fibronectin and collagen-coated dishes as well as matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion. CGP-42112 did not promote cytokine secretion. In contrast, when added in the presence of low doses of LPS, CGP-42112 reduced the LPS-stimulated secretion of TNF-alpha, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 without affecting IL-10 and decreased the LPS-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity. Additionally, CGP-42112 inhibited the increase in protein kinase A activity produced by LPS. Our results indicate that CGP-42112 may modulate monocyte activation through binding to a novel receptor.
Increased non-angiotensin II [125I]CGP 42112 binding in rat carotid artery after balloon injury.[Pubmed:8804082]
Peptides. 1996;17(4):695-9.
In this study, [125I]CGP 42112, a ligand of high affinity and selectivity for the angiotensin II AT2 receptor, was used to detect and quantify a non-angiotensin II binding site in the balloon-injured carotid artery of the rat. The amount of [125I]CGP 42112 binding was significantly enhanced in the adventitia of the injured arteries. Localization of the binding site using emulsion autoradiography and immunocytochemistry suggests that the binding sites may be expressed by macrophages in the inflamed tissue surrounding the injured artery.
Expression of non-angiotensin II -125I-CGP 42112 binding sites on activated microglia after kainic acid induced neurodegeneration.[Pubmed:8846070]
Brain Res. 1995 Dec 8;702(1-2):153-61.
[125I]CGP 42112, first developed to identify angiotensin II receptor subtype 2 (AT2), was recently shown to bind to a novel non-angiotensin binding site in injured rat brain tissue. We addressed the question whether non-angiotensin [125I]CGP 42112 binding appears after kainic acid induced hippocampal neurodegeneration, a process of neuronal cell death at a distance from the toxin injection site. After intraventricular kainic acid injection, we found non-angiotensin [125I]CGP 42112 binding in the hippocampal areas CA3 (4 and 14 days after injection), CA1 and CA4 and the subiculum (14 days after injection). In addition, 14 days after kainic acid injection, [125I]CGP 42112 binding was found in 50% of the animals, in the thalamus, amygdala and piriform cortex, areas receiving projections from the hippocampus and suffering kainic acid induced delayed neurodegeneration. The loss of neurons in these regions was accompanied by an accumulation of activated microglia as demonstrated by immunostaining with the specific antibodies OX-42 and ED1. The time course and regional pattern of OX-42/ED1 positive immunostaining was identical with the appearance and distribution of the non-angiotensin [125I]CGP 42112 binding site. The non-angiotensin [125I]CGP 42112 binding was not detected in brain regions unaffected by kainic acid injection. Our findings indicate the expression of a novel [125I]CGP 42112 binding site on activated microglia. This site appears at a distance from the lesion and may be of importance in the process of neuronal death and brain tissue repair.
Angiotensin II AT2 receptors inhibit proximal tubular Na+-K+-ATPase activity via a NO/cGMP-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:16380464]
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Jun;290(6):F1430-6.
Angiotensin II AT2 receptors act as a functional antagonist for the AT1 receptors in various tissues. We previously reported that activation of the renal AT2 receptors promotes natriuresis and diuresis; however, the mechanism is not known. The present study was designed to investigate whether activation of AT2 receptors affects the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase (NKA), an active tubular sodium transporter, in the proximal tubules isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats. The AT2 receptor agonist CGP-42112 (10(-10)-10(-7) M) produced a dose-dependent inhibition of NKA activity (9-38%); the inhibition was attenuated by the presence of the AT2 receptor antagonist PD-123319 (1 microM), suggesting the involvement of the AT2 receptors. The AT1 receptor antagonist losartan (1 microM) did not affect the CGP-42112 (100 nM)-induced inhibition of NKA activity. The presence of guanylyl cyclase inhibitor ODQ (10 microM) and the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; 100 microM) abolished the CGP-42112 (100 nM)-induced NKA inhibition. ANG II (100 nM), in the presence of losartan, significantly inhibited NKA activity; the inhibition was attenuated by PD-123319. CGP-42112 also, in a dose-dependent manner, stimulated NO production (approximately 0-230%) and cGMP accumulation (approximately 25-100%). The CGP-42112 (100 nM)-induced NO and cGMP increases were abolished by the AT2 receptor antagonist PD-123319, ODQ, and L-NAME. The data suggest that the activation of the AT2 receptor via stimulation of the NO/cGMP pathway causes inhibition of NKA activity in the proximal tubules. This phenomenon provides a plausible mechanism responsible for the AT2 receptor-mediated natriuresis-diuresis in rodents.
The role of angiotensin receptor subtypes in cerebrovascular regulation in the rat.[Pubmed:8610501]
Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1995;630:1-48.
The present studies were conducted to examine the roles of angiotensin II, angiotensin IV, and the angiotensin receptor subtypes in the cerebral circulation. The effects of angiotensin II, the selective AT1 receptor antagonist losartan, and the selective AT2 receptor ligands, PD 123319 and CGP 42112, on cerebral blood flow autoregulation, were studied during increases and decreases in blood pressure in normotensive rats. Cerebrocortical blood flow was measured by laser-Doppler flowmetry, while systemic blood pressure was either increased by phenylephrine infusion, or decreased by controlled haemorrhage. The effects of angiotensin II, and AT1 and AT2 receptor ligands on the contractility of rat anterior cerebral artery in vitro, were studied using cannulated, perfused vessel segments. The effect of angiotensin IV on cerebral blood flow after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage, and possible involvement of nitric oxide, was studied in rat. Subarachnoid haemorrhage was simulated by injecting 0.3 ml arterial blood into the cisterna magna, while cerebral blood flow was measured by laser-Doppler flowmetry. The main findings in the present studies were that angiotensin II, the AT1 antagonist losartan, and the AT2 ligands PD 123319 and CGP 42112, shifted the cerebral blood flow autoregulatory range towards higher blood pressures. PD 123319 and CGP 42112 acted as AT2 receptor agonists. In vitro, angiotensin II elicited an AT1 receptor mediated contraction of rat anterior cerebral artery. Angiotensin IV was able to reverse the acute CBF reduction after subarachnoid haemorrhage. No evidence was found to support the involvement of nitric oxide in this response. In conclusion, there is strong evidence supporting a role for the AT2 receptor in the regulation of cerebral circulation. The role of the AT1 receptor is questionable, and the losartan induced autoregulatory shift is possibly mediated indirectly through AT2 receptor stimulation. Although AT1 receptors mediate the angiotensin II induced contraction of rat anterior cerebral artery in vitro, this effect does not explain the effect of losartan on CBF autoregulation. Angiotensin IV increases cerebral blood flow after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage possibly by dilating cerebral vessels through stimulation of the AT4 receptor.


