COG 133ApoE mimetic peptide CAS# 514200-66-9 |
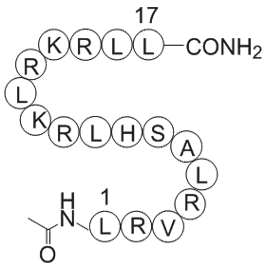
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
- Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pig
Catalog No.:BCC1020
CAS No.:98474-59-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 514200-66-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71464403 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C97H181N37O19 | M.Wt | 2169.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AM024761 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL (Modifications: Leu-1 = N-terminal Ac, Leu-17 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC1=CN=CN1)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QTWXJKVJIKDSLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C97H181N37O19/c1-50(2)40-67(76(100)137)127-89(150)72(45-55(11)12)130-82(143)64(30-23-37-114-95(105)106)122-78(139)60(26-17-19-33-98)120-79(140)62(28-21-35-112-93(101)102)123-87(148)70(43-53(7)8)129-81(142)61(27-18-20-34-99)121-80(141)63(29-22-36-113-94(103)104)124-88(149)71(44-54(9)10)131-90(151)73(46-59-47-111-49-117-59)132-91(152)74(48-135)133-77(138)57(15)118-85(146)69(42-52(5)6)128-83(144)65(31-24-38-115-96(107)108)126-92(153)75(56(13)14)134-84(145)66(32-25-39-116-97(109)110)125-86(147)68(41-51(3)4)119-58(16)136/h47,49-57,60-75,135H,17-46,48,98-99H2,1-16H3,(H2,100,137)(H,111,117)(H,118,146)(H,119,136)(H,120,140)(H,121,141)(H,122,139)(H,123,148)(H,124,149)(H,125,147)(H,126,153)(H,127,150)(H,128,144)(H,129,142)(H,130,143)(H,131,151)(H,132,152)(H,133,138)(H,134,145)(H4,101,102,112)(H4,103,104,113)(H4,105,106,114)(H4,107,108,115)(H4,109,110,116) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Apolipoprotein (ApoE) peptide fragment that functions via the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Substantially reduces the symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a model of human multiple sclerosis, and suppresses inflammation, demyelination and infiltration of cells into the spinal cord. Also acts as a non-competitive antagonist at α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (IC50 = 445 nM).#&α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors#&445 nM |

COG 133 Dilution Calculator

COG 133 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
COG 133, (C97H181N37O19), a peptide with the sequence Ac-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Leu-Ala-Ser-His-Leu-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg-Lys-Arg-Leu-Leu-amide,MW= 2169.73.Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is 299 amino acids long and transports lipoproteins(1), fat-soluble vitamins, and cholesterol into the lymph system and then into the blood. It is synthesized principally in the liver, but has also been found in other tissues such as the brain, kidneys, and spleen. In the nervous system, non-neuronal cell types, most notably astroglia and microglia, are the primary producers of APOE, while neurons preferentially express the receptors for APOE. There are seven currently identified mammalian receptors for APOE which belong to the evolutionarily conserved low density lipoprotein receptor gene family.APOE was initially recognized for its importance in lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular disease(2). Defects in APOE result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia aka type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron, VLDL and LDL remnants[citation needed]. More recently, it has been studied for its role in several biological processes not directly related to lipoprotein transport, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), immunoregulation, and cognition(3).
Figure1 the structures of Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) COG 133
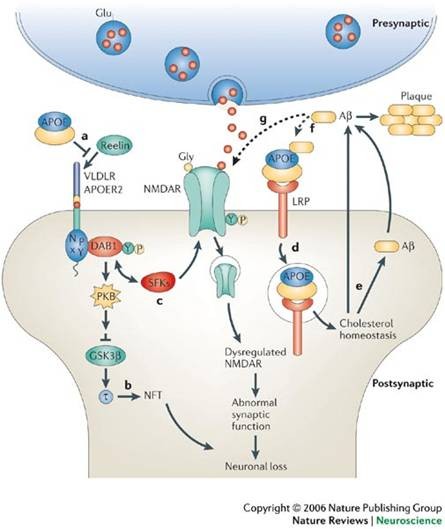
Figure2 Potential roles of APOE in neurons and Alzheimer's disease
Ref:
1. Singh PP, Singh M, Mastana SS (2002). "Genetic variation of apolipoproteins in North Indians". Hum. Biol. 74 (5): 673–82.
2. van den Elzen P, Garg S, León L, Brigl M, Leadbetter EA, Gumperz JE, Dascher CC, Cheng TY, Sacks FM, Illarionov PA, Besra GS, Kent SC, Moody DB, BrennerMB. (2005). "Apolipoprotein-mediated pathways of lipid antigen presentation.". Nature 437 (7060): 906-10.
3. Zhang HL, Wu J, Zhu J (2010). "The Role of Apolipoprotein E in Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis". J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010: 357412.
- 3-Methyladenine
Catalog No.:BCC3714
CAS No.:5142-23-4
- Odonicin
Catalog No.:BCN5637
CAS No.:51419-51-3
- Chikusetsusaponin IVa
Catalog No.:BCN3432
CAS No.:51415-02-2
- Alrestatin
Catalog No.:BCC6663
CAS No.:51411-04-2
- Canthaxanthin
Catalog No.:BCC8139
CAS No.:514-78-3
- Biperiden
Catalog No.:BCC4274
CAS No.:514-65-8
- Ferruginol
Catalog No.:BCN3155
CAS No.:514-62-5
- Euphol
Catalog No.:BCN7790
CAS No.:514-47-6
- Tirucallol
Catalog No.:BCN7787
CAS No.:514-46-5
- Parkeol
Catalog No.:BCN3728
CAS No.:514-45-4
- Periplogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2656
CAS No.:514-39-6
- Abietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2728
CAS No.:514-10-3
- Cyclo(Tyr-Phe)
Catalog No.:BCN2423
CAS No.:5147-17-1
- Deoxynivalenol
Catalog No.:BCC7832
CAS No.:51481-10-8
- Cimetidine
Catalog No.:BCC4527
CAS No.:51481-61-9
- PMX 205
Catalog No.:BCC8039
CAS No.:514814-49-4
- H-Tyr(tBu)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2672
CAS No.:51482-39-4
- Sclareol
Catalog No.:BCN2395
CAS No.:515-03-7
- (+)-Turicine
Catalog No.:BCC8361
CAS No.:515-24-2
- Cochinchinenin A
Catalog No.:BCN3496
CAS No.:221696-69-1
- Adiantulupanone
Catalog No.:BCN7360
CAS No.:51511-05-8
- GW 803430
Catalog No.:BCC7897
CAS No.:515141-51-2
- Vitexin argininate
Catalog No.:BCC8179
CAS No.:51542-56-4
- Flurizan
Catalog No.:BCC2342
CAS No.:51543-40-9
Apolipoprotein E COG 133 mimetic peptide improves 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis.[Pubmed:22524518]
BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 Jul 13;12:35.
BACKGROUND: Intestinal mucositis is one of the major troublesome side effects of anticancer chemotherapy leading to poor patient compliance. In this study we addressed the role of the novel apolipoprotein E (ApoE) COG 133 mimetic peptide in 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-challenged Swiss mice and IEC-6 cell monolayers. Experiments were also conducted in C57BL6J ApoE knock-out mice to assess the effects of apoE peptide treatment. METHODS: Experimental groups were as follows: unchallenged controls, 5-FU-challenged mice (450 mg/kg, i.p) with or without the ApoE peptide (0.3, 1, and 3 muM, given twice daily i.p. for 4 days). Mice were sacrificed 3 days after 5-FU challenge. Proximal small intestinal samples were harvested for molecular biology and histological processing. We conducted ELISA assays and RT-PCR to target IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-10, iNOS, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) to assess intestinal inflammation. Cell death and NF-kappaB assays were also conducted in apoE knock-out mice. In our in vitro models, IEC-6 cells were exposed to 1 mM of 5-FU in glutamine free media with or without the ApoE peptide (0.02, 0.2, 2, 5, 10, and 20 muM). We investigated IEC-6 cell proliferation and migration, 24 h after the 5-FU challenge. Additionally, apoptotic IEC-6 cells were measured by Tunel and flow cytometry. Equimolar doses of the ApoA-I (D4-F) peptide were also used in some experiments for comparative studies. RESULTS: Villus blunting and heavy inflammatory infiltrates were seen in the 5-FU-challenged group, findings that were partially ameliorated by the ApoE peptide. We found increased intestinal MPO and pro-inflammatory IL-1beta and TNF-alpha levels, and TNF-alpha and iNOS transcripts, and reduction of IL-10 following 5-FU treatment, each of which were partially abrogated by the peptide. Improvements were also found in IEC-6 cell apoptosis and migration following ApoE and D-4F treatment. CONCLUSION: Altogether, these findings suggest that the novel ApoE COG 133 mimetic peptide can reduce 5-FU-induced intestinal changes and potentially benefit mucositis.
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor inhibition by an apolipoprotein E-derived peptide relies on low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein.[Pubmed:18602124]
Neuropharmacology. 2008 Aug;55(2):204-14.
The effects of a synthetic apoE peptide, viz., residues 133-149 (apoE[133-149]), a mimetic that comprises the apoE receptor binding domain, on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)/glycine-induced ion flow through NMDA receptor (NMDAR) channels, have been investigated. The activity of apoE[133-149] was found to depend on the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Competition experiments with receptor-associated protein (RAP) and activated alpha(2)-macroglobulin (alpha(2)M*), two proteins that compete for apoE binding to LRP, demonstrate that apoE[133-149] inhibition of NMDAR function is mediated at a locus in LRP that overlaps with the binding sites of RAP and alpha(2)M*. A coreceptor of LRP, cell surface heparin sulfate proteoglycan, did not function in this system. Additional electrophysiology experiments demonstrated that the inhibitory potency of apoE[133-149] was threefold greater for NMDAR-transfected wild-type Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells compared with NMDAR-transfected CHO cells deficient in LRP. Studies with truncation and replacement variants of the apoE peptide demonstrated that the NMDAR inhibitory properties of these peptides correlate with their binding affinities for LRP. These novel results indicate that apoE functions as an inhibitor of NMDAR ion channels indirectly via LRP, and are suggestive of a participatory role for LRP in NMDAR-based neuropathies.
Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides block alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in xenopus oocytes.[Pubmed:16249370]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Feb;316(2):835-42.
For decades, the pathology of Alzheimer's disease has been associated with dysfunction of cholinergic signaling; however, the cellular mechanisms by which nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) function is impaired in Alzheimer's disease are as yet unknown. The most significant genetic risk factor for the development of Alzheimer's disease is inheritance of the epsilon4 allele of apolipoprotein E (apoE). Recent data have demonstrated the ability of apoE-derived peptides to inhibit nAChRs in rat hippocampus. In the current study, the functional interaction between nAChRs and apoE-derived peptides was investigated in Xenopus oocytes expressing selected nAChRs. Both a 17-amino acid peptide fragment, apoE(133-149), and an eight-amino acid peptide, apoE(141-148), were able to maximally block acetylcholine (ACh)-mediated peak current responses for homomeric alpha7 nAChRs. ApoE peptide inhibition was dose-dependent and voltage- and activity-independent. The current findings suggest that apoE peptides are noncompetitive for acetylcholine and do not block functional alpha-bungarotoxin binding. ApoE peptides had a significantly decreased ability to inhibit ACh-mediated peak current responses for alpha4beta2 and alpha2beta2 nAChRs. Amino acid substitutions in the apoE peptide sequence suggest that the arginines are critical for peptide blockade of the alpha7 nAChR. The current data suggest that apoE fragments can disrupt nAChR signaling through a direct blockade of alpha7 nAChRs. These results may be useful in elucidating the mechanisms underlying memory loss and cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer's disease as well as aid in the development of novel therapeutics using apoE-derived peptides.
Apolipoprotein E-derived peptides ameliorate clinical disability and inflammatory infiltrates into the spinal cord in a murine model of multiple sclerosis.[Pubmed:16740622]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Sep;318(3):956-65.
Apolipoprotein E (apoE), well known to play a role in lipid transport and cholesterol metabolism, also exerts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in the central nervous system. Recent clinical and genetic studies display an association between apoE genotype (APOE) and the progression and severity of multiple sclerosis, raising the possibility that modulation of apoE may be a novel treatment for multiple sclerosis. Using a murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of human multiple sclerosis, we found that a peptidomimetic of apoE protein, COG133, substantially reduces the clinical symptoms of EAE and promotes remission from the disability when administered before or after onset of disease. Most notably, fusion of COG133 to a protein transduction domain creates COG112, a modified apoE-mimetic peptide with significantly enhanced anti-inflammatory bioactivities in vitro, and improved therapeutic effects on EAE in vivo, which renders a nearly full remission from the disability. Histopathological analysis showed that COG112 and COG133 attenuated demyelination and significantly diminished the number of peripheral cells infiltrating into the spinal cord. ApoE mimetics also interfered with several mechanisms relevant to the pathogenesis of EAE and multiple sclerosis, including activation of macrophages, subsequent production of nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokines, and lymphocyte proliferation. These data suggest that apoE mimetics represent a multidimensional therapeutic for multiple sclerosis capable of inhibiting the inflammatory cascade, modulating immune cell function, and reducing clinical signs, which may have novel utility for the treatment of inflammatory autoimmune diseases.


