CatalpalactoneCAS# 1585-68-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1585-68-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3014018 | Appearance | Powder |
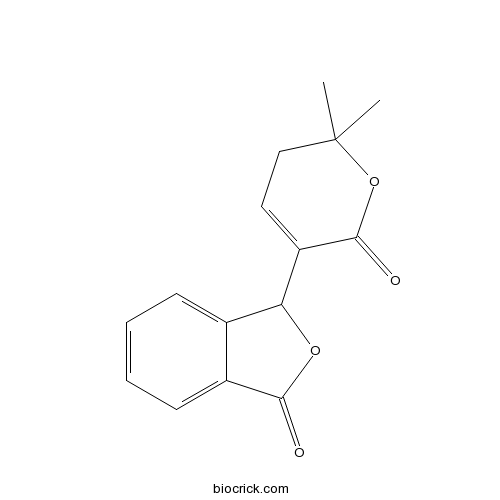
| Formula | C15H14O4 | M.Wt | 258.3 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-(2,2-dimethyl-6-oxo-3H-pyran-5-yl)-3H-2-benzofuran-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CC=C(C(=O)O1)C2C3=CC=CC=C3C(=O)O2)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GFYSRANGENPXDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14O4/c1-15(2)8-7-11(14(17)19-15)12-9-5-3-4-6-10(9)13(16)18-12/h3-7,12H,8H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Catalpalactone can inhibit dopamine biosynthesis by reducing tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and aromatic-l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) activities and enhance L-DOPA- induced cytotoxiciy in PC12 cells. 2. Catalpalactone displays good cytotoxicity activities against two human tumor cell lines(MCF-7,BxPC3). 3. Catalpalactone exhibits significant inhibitory activity against 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-induced Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation in Raji cells. 4. Catapalactone exhibits potent inhibitory effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced NO synthesis in RAW 264.7 cells , with IC50 values of 9.80 microM. 5. Catalpalactone exhibits high antitermitic activity. |
| Targets | cAMP | NO |

Catalpalactone Dilution Calculator

Catalpalactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8715 mL | 19.3573 mL | 38.7147 mL | 77.4293 mL | 96.7867 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7743 mL | 3.8715 mL | 7.7429 mL | 15.4859 mL | 19.3573 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3871 mL | 1.9357 mL | 3.8715 mL | 7.7429 mL | 9.6787 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0774 mL | 0.3871 mL | 0.7743 mL | 1.5486 mL | 1.9357 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0387 mL | 0.1936 mL | 0.3871 mL | 0.7743 mL | 0.9679 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- ω-Agatoxin TK
Catalog No.:BCC7489
CAS No.:158484-42-5
- BMS-983970
Catalog No.:BCC5509
CAS No.:1584713-87-0
- PSI
Catalog No.:BCC1124
CAS No.:158442-41-2
- Demethyl calyciphylline A
Catalog No.:BCN7040
CAS No.:1584236-34-9
- Pyraclonil
Catalog No.:BCC8073
CAS No.:158353-15-2
- Methyl 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propanoate
Catalog No.:BCN4051
CAS No.:15823-04-8
- Naringenin-7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCC8215
CAS No.:158196-34-0
- Fmoc-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3543
CAS No.:158171-14-3
- 21-O-Tigloylgymnemagenin
Catalog No.:BCN7854
CAS No.:1581276-63-2
- 5-Hydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN7470
CAS No.:1581248-32-9
- para-iodoHoechst 33258
Catalog No.:BCC1838
CAS No.:158013-43-5
- meta-iodoHoechst 33258
Catalog No.:BCC1739
CAS No.:158013-42-4
- Cnidioside B methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1707
CAS No.:158500-59-5
- Eclalbasaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN8244
CAS No.:158511-59-2
- Ombuin 3-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4055
CAS No.:158642-42-3
- Rimonabant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1898
CAS No.:158681-13-1
- Dihydrexidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5681
CAS No.:158704-02-0
- 2-Naphthyl N-benzoylphenylalaninate
Catalog No.:BCC8583
CAS No.:15873-25-3
- Aescin IIA
Catalog No.:BCN6551
CAS No.:158732-55-9
- Salvianolic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN2924
CAS No.:158732-59-3
- Escin IIB
Catalog No.:BCN8127
CAS No.:158800-83-0
- GR 159897
Catalog No.:BCC7001
CAS No.:158848-32-9
- 3-O-(2'E ,4'Z-decadienoyl)-20-O-acetylingenol
Catalog No.:BCN1550
CAS No.:158850-76-1
- Boc-ß-HoAla-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3224
CAS No.:158851-30-0
Antitumor-promoting naphthoquinones from Catalpa ovata.[Pubmed:9599262]
J Nat Prod. 1998 May;61(5):629-32.
Bioassay-directed fractionation of an extract of the stem-bark of Catalpa ovata led to the isolation of three new naphthoquinones: 8-methoxydehydroiso-alpha-lapachone (1), 9-methoxy-4-oxo-alpha-lapachone (2), and (4S,4aR,10R,10aR)-4, 10-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,4,4alpha,10, 10alpha-hexahydrobenzo[g]chromen-5-one (3), which is a 1,4-reductive form of 6. The known compounds 3-hydroxydehydroiso-alpha-lapachone (4), 4,9-dihydroxy-alpha-lapachone (5), 4-hydroxy-alpha-lapachone (6), and 9-methoxy-alpha-lapachone (7), and Catalpalactone (8) were also isolated. Their structures were elucidated by spectral methods. These compounds all exhibited significant inhibitory activity against 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-induced Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) activation in Raji cells.
Major antitermitic components of the heartwood of southern catalpa.[Pubmed:24254942]
J Chem Ecol. 1992 Mar;18(3):359-69.
The heartwood of southern catalpa,Catalpa bignonioides Walt., is resistant to attack by the eastern subterranean termiteReticulitermes flavipes (Kollar), but extraction with a ternary solvent mixture of acetone-hexanewater (54ratio44ratio2) by volume removed the antitermitic characteristics from the heartwood. Four compounds comprised approximately 98% of the antitermitic fraction of the extract: the sesquiterpene alcohol, catalponol (67%); its epimer, epicatalponol (5%); a structurally related ketone, catalponone (1%); and the phthalide, Catalpalactone (25%). Pure compounds were isolated by semipreparative scale reversed-phase HPLC and identified by GC-MS and UV spectroscopy. The structure of catalponol was further confirmed by the formation of derivatives. Bioassays indicated that catalponol had the greatest toxicity in cellulose pad tests, but in tests using vacuum impregnation of these compounds into termite-susceptible wood blocks at levels approximating those found in catalpa heartwood, Catalpalactone exhibited the highest antitermitic activity.
Naphthoquinones from Catalpa ovata and their inhibitory effects on the production of nitric oxide.[Pubmed:20361302]
Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Mar;33(3):381-5.
Bioassay-guided fractionation of a CH2Cl2-soluble fraction of the stems of Catalpa ovata led to isolation of a new naphthoquinone, 4-hydroxy-2-(2-methoxy-3-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-1-enyl)-4-hydro-1H-naphthalen-1-one (10), together with nine known compounds, catalponol (1), catalponone (2), Catalpalactone (3), alpha-lapachone (4), 9-hydroxy-alpha-lapachone (5), 4,9-dihydroxy-alpha-lapachone (6), 9-methoxy-alpha-lapachone (7), 4-oxo-alpha-lapachone (8), and 9-methoxy-4-oxo-alpha-lapachone (9). The structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analyses. The inhibitory effects of these isolates on lipopolysaccharide-induced NO synthesis in RAW 264.7 cells were evaluated. Among them, catapalactone (3), 9-hydroxy-alpha-lapachone (5) and 4,9-dihydroxy-alpha-lapachone (6) exhibited potent inhibitory effects, with IC(50) values of 9.80, 4.64 and 2.73 microM, respectively.
Effects of catalpalactone on dopamine biosynthesis and L-DOPA-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells.[Pubmed:21783893]
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;26(1):86-91.
The effects of Catalpalactone on dopamine biosynthesis and L-DOPA-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells were investigated. Catalpalactone at 5-30muM decreased intracellular dopamine content with the IC(50) value of 22.1muM. Catalpalactone at 5-20muM, but not 30muM, did not alter cell viability. Catalpalactone at 20muM inhibited tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and aromatic-l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) activities. Catalpalactone also decreased cyclic AMP levels and inhibited TH phosphorylation. In addition, Catalpalactone at 20muM reduced the increases in dopamine levels induced by L-DOPA (20-50muM). Catalpalactone (5-30muM) associated with L-DOPA (50-100muM) enhanced L-DOPA-induced cytotoxicity at 48h, which was prevented by N-acetyl-l-cysteine. These results suggest that Catalpalactone inhibited dopamine biosynthesis by reducing TH and AADC activities and enhanced L-DOPA-induced cytotoxiciy in PC12 cells.


