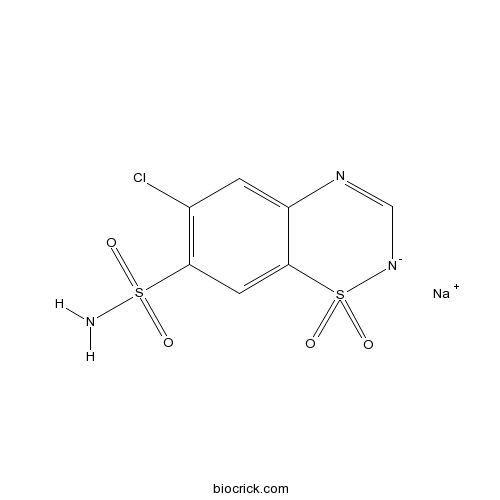
Chlorothiazide SodiumCAS# 7085-44-1 |
- Etomoxir
Catalog No.:BCC1564
CAS No.:124083-20-1
- Verteporfin
Catalog No.:BCC3690
CAS No.:129497-78-5
- Elacridar
Catalog No.:BCC1546
CAS No.:143664-11-3
- Etofenamate
Catalog No.:BCC1563
CAS No.:30544-47-9
- Etifoxine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1561
CAS No.:56776-32-0
- Etimizol
Catalog No.:BCC1562
CAS No.:64-99-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7085-44-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23675744 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H5ClN3NaO4S2 | M.Wt | 317.71 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >31.8mg/mL in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazin-2-ide-7-sulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=C2C(=CC(=C1Cl)S(=O)(=O)N)S(=O)(=O)[N-]C=N2.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CPIWHAFLBZQYLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H5ClN3O4S2.Na/c8-4-1-5-7(2-6(4)16(9,12)13)17(14,15)11-3-10-5;/h1-3H,(H2-,9,10,11,12,13);/q-1;+1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Chlorothiazide Sodium Dilution Calculator

Chlorothiazide Sodium Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1475 mL | 15.7376 mL | 31.4752 mL | 62.9505 mL | 78.6881 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6295 mL | 3.1475 mL | 6.295 mL | 12.5901 mL | 15.7376 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3148 mL | 1.5738 mL | 3.1475 mL | 6.295 mL | 7.8688 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.063 mL | 0.3148 mL | 0.6295 mL | 1.259 mL | 1.5738 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0315 mL | 0.1574 mL | 0.3148 mL | 0.6295 mL | 0.7869 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN1230
CAS No.:7084-24-4
- Chicoric acid
Catalog No.:BCN1215
CAS No.:70831-56-0
- JNJ 10397049
Catalog No.:BCC6139
CAS No.:708275-58-5
- Panaxydiol
Catalog No.:BCN3702
CAS No.:708257-91-4
- FPH1 (BRD-6125)
Catalog No.:BCC5342
CAS No.:708219-39-0
- Doxapram hydrochloride monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8953
CAS No.:7081-53-0
- 2',3'-Dihydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN7168
CAS No.:708-53-2
- Flurofamide
Catalog No.:BCC5660
CAS No.:70788-28-2
- H-D-Ala(3-pyridyl)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3323
CAS No.:70702-47-5
- 3-Chlorotyrosine
Catalog No.:BCC2639
CAS No.:70680-93-2
- Pimavanserin
Catalog No.:BCC8065
CAS No.:706779-91-1
- Canniprene
Catalog No.:BCN4271
CAS No.:70677-47-3
- Troxerutin
Catalog No.:BCN3828
CAS No.:7085-55-4
- (2S)-Isoxanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN2892
CAS No.:70872-29-6
- Dihydrocitflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6873
CAS No.:70897-14-2
- SirReal2
Catalog No.:BCC6513
CAS No.:709002-46-0
- 2-(5-Chloro-2-phenoxyphenyl)acetic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8481
CAS No.:70958-20-2
- 7,3',4'-Tri-O-methyleriodictyol
Catalog No.:BCN7766
CAS No.:70987-96-1
- H-His-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2954
CAS No.:71-00-1
- Cytosine
Catalog No.:BCN8533
CAS No.:71-30-7
- butanol
Catalog No.:BCN4976
CAS No.:71-36-3
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4485
CAS No.:71-58-9
- Veratridine
Catalog No.:BCC7515
CAS No.:71-62-5
- Digitoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5358
CAS No.:71-63-6
Effect of chlorothiazide on serial measurements of exchangeable sodium and blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats.[Pubmed:4053506]
Clin Sci (Lond). 1985 Nov;69(5):511-5.
Chlorothiazide (100 mg/kg body weight) was given by gavage daily to spontaneously hypertensive rats for 4 weeks. Another group of spontaneously hypertensive rats was given only tap water and served as control. Measurements of total exchangeable sodium, blood pressure and weight were performed for 2 weeks before and for 4 weeks during treatment. Before treatment, exchangeable sodium, blood pressure and weight were similar in the two groups of rats. Chlorothiazide significantly attenuated the blood pressure increase in spontaneously hypertensive rats, the effect being most marked during the first 2 1/2 weeks of treatment and less thereafter. Rats in the chlorothiazide-treated group gained weight more slowly than did those of the control group. Exchangeable sodium, expressed as mmol/kg body weight, did not differ significantly between the two groups at any stage. When exchangeable sodium was expressed as mmol/rat, there was a more gradual rise in the chlorothiazide-treated animals, in accordance with their slower gain in weight. There was no temporal association between the antihypertensive effect of chlorothiazide and changes in exchangeable sodium. Thus whereas chlorothiazide treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats slows the increase of both weight and exchangeable sodium, other mechanisms are apparently responsible for the antihypertensive action of the drug.
Stability of chlorothiazide sodium in polypropylene syringes.[Pubmed:26195655]
Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015 Aug 1;72(15):1292-7.
PURPOSE: The stability of a solution of chlorothiazide injection diluted with sterile water and stored in polypropylene syringes under refrigerated conditions was investigated. METHODS: Chlorothiazide solutions were compounded by adding 20 mL of sterile water for injection to a 500-mg vial of Chlorothiazide Sodium for injection. Six batches of chlorothiazide solution (25 mg/mL) were compounded; 0.5-mL portions were transferred to 1-mL polypropylene syringes, which were sealed with a Luer tip cap and stored at refrigeration temperatures (2-8 degrees C) protected from light. Three batches were potency tested by stability-indicating high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) assay using a 0.5-mL sample from each batch at designated time points. Visual and pH testing were performed using the three remaining batches; the contents of two syringes per batch were combined and visually inspected for container integrity and solution color and clarity, with duplicate pH testing performed at each time point. RESULTS: HPLC analyses showed that the remaining percentage of the initial chlorothiazide content declined at an average daily rate of 1.4%, decreasing to 93% by day 6. All samples remained intact, clear, and colorless, with no visible particulate matter or precipitation observed throughout the study period. For all samples of chlorothiazide solution, pH values remained within the range of 9.2-10.0 throughout the 10-day study period. CONCLUSION: When packaged in 1-mL polypropylene syringes and stored protected from light at refrigerated conditions, a solution of Chlorothiazide Sodium injection in water was stable for six days.
Preparation and solid state characterisation of chlorothiazide sodium intermolecular self-assembly suprastructure.[Pubmed:20816757]
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010 Dec 23;41(5):603-11.
Chlorothiazide (CTZ), unlike other thiazide diuretics, can form salts. An injectable formulation containing the sodium salt is available; however neither the physicochemical characteristics of the salt nor its solid state form have been previously reported. This work reports on the crystal structure of Chlorothiazide Sodium. The structure was investigated by single crystal X-ray and nuclear magnetic spectroscopy (NMR) analyses and compared to chlorothiazide, while the solid state characteristics were assessed by thermal analysis, powder X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy, dynamic moisture sorption and solubility analysis. The crystal structure of Chlorothiazide Sodium was determined to be triclinic; the crystal space group type was P-1. Chlorothiazide Sodium presented a self-assembly polymeric-type suprastucture, where the unit cell comprised two chlorothiazide molecules bonded together with sodium cations through the water bridges. The coordinate centre comprised the following: (CTZ)(3).(H(2)O).Na(H(2)O)(2)Na.(H(2)O).(CTZ)(3). The crystalline material was determined to be a monosodium dihydrate, stable in the range of 10-90% relative humidity (RH) at 25 degrees C. Additional processing of the salt resulted in a crystalline anhydrous form which was stable in the range 0-20% RH at 25 degrees C. The aqueous solubility of the Chlorothiazide Sodium dihydrate at 37 degrees C was found to be approximately 400-fold higher than that of chlorothiazide, which may present biopharmaceutical advantages for the salt compared to the non-salt form.


