Co 101244 hydrochlorideCAS# 193356-17-1 |
- PF-4708671
Catalog No.:BCC5031
CAS No.:1255517-76-0
- BIX 02565
Catalog No.:BCC4303
CAS No.:1311367-27-7
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1580
CAS No.:821794-92-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 193356-17-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6918426 | Appearance | Powder |
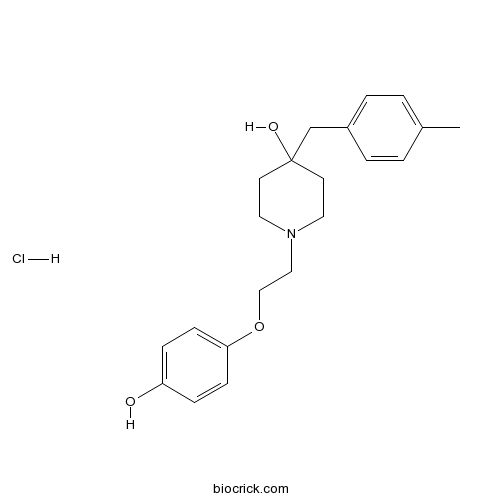
| Formula | C21H28ClNO3 | M.Wt | 377.91 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PD 174494, Ro 63-1908 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-[2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)ethyl]-4-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-ol;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2(CCN(CC2)CCOC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WFFZHKKSIDENAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H27NO3.ClH/c1-17-2-4-18(5-3-17)16-21(24)10-12-22(13-11-21)14-15-25-20-8-6-19(23)7-9-20;/h2-9,23-24H,10-16H2,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Novel, potent and selective antagonist of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors (IC50 values are 0.043, > 100 and > 100 μM for NR1A/2B, NR1A/2A and NR1A/2C subunit combinations respectively). Displays neuroprotective effects in vivo and in vitro. |

Co 101244 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Co 101244 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6461 mL | 13.2307 mL | 26.4613 mL | 52.9227 mL | 66.1533 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5292 mL | 2.6461 mL | 5.2923 mL | 10.5845 mL | 13.2307 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2646 mL | 1.3231 mL | 2.6461 mL | 5.2923 mL | 6.6153 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0529 mL | 0.2646 mL | 0.5292 mL | 1.0585 mL | 1.3231 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0265 mL | 0.1323 mL | 0.2646 mL | 0.5292 mL | 0.6615 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5-Aminoindazole
Catalog No.:BCC8734
CAS No.:19335-11-6
- Lonafarnib
Catalog No.:BCC2331
CAS No.:193275-84-2
- 1-O-Acetyl-6alpha-O-(2-methylbutyryl)britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN7747
CAS No.:1932687-71-2
- cis-Moschamine
Catalog No.:BCN3901
CAS No.:193224-24-7
- Otamixaban
Catalog No.:BCC1827
CAS No.:193153-04-7
- Cardamonin
Catalog No.:BCN1184
CAS No.:19309-14-9
- CTS-1027
Catalog No.:BCC1502
CAS No.:193022-04-7
- ZM323881
Catalog No.:BCC2073
CAS No.:193001-14-8
- ZM 323881 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5098
CAS No.:193000-39-4
- Ximelagatran
Catalog No.:BCC6382
CAS No.:192939-46-1
- LY310762
Catalog No.:BCC5052
CAS No.:192927-92-7
- 2-Amino-2'-nitrodiphenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8522
CAS No.:19284-81-2
- Tartrazine
Catalog No.:BCN2217
CAS No.:1934-21-0
- Zeylenone
Catalog No.:BCC8268
CAS No.:193410-84-3
- Fmoc-Glu(Edans)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3491
CAS No.:193475-66-0
- Mulberroside F
Catalog No.:BCN2908
CAS No.:193483-95-3
- IPAG
Catalog No.:BCC5662
CAS No.:193527-91-2
- SB 239063
Catalog No.:BCC1923
CAS No.:193551-21-2
- Calcifediol
Catalog No.:BCC4949
CAS No.:19356-17-3
- GB 1b
Catalog No.:BCN7385
CAS No.:19360-72-6
- Terrestrosin K
Catalog No.:BCN2935
CAS No.:193605-07-1
- SB 216641 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6987
CAS No.:193611-67-5
- BRL-15572
Catalog No.:BCC5065
CAS No.:193611-72-2
- TAS 301
Catalog No.:BCC6214
CAS No.:193620-69-8
Development of Poly(lactide-co-glicolide) Nanoparticles Incorporating Morphine Hydrochloride to Prolong its Circulation in Blood.[Pubmed:27908267]
Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(13):2015-2025.
BACKGROUND: Formulations incorporating nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used to prolong drug release. In this regard, poly(lactide-co-glicolide) (PLGA) is often used in their preparation due to its high degree of biocompatibility and biodegradability. In the present study, morphine HCl is incorporated in PLGA-NPs and different preparation alternatives are evaluated for their effects on the properties, stability and capacity of encapsulation. METHODS: NPs were prepared by a double emulsion solvent diffusion-ammonium loading (DESD-AL) or double emulsion solvent diffusion-traditional (DESD-T) technique. NP morphology, size, zeta potential and encapsulation efficiency were investigated. In vitro studies were performed in phosphate buffer pH 7.4 at 37 masculineC and deionized water at 4 masculineC. Adult male Swiss mice were used to study the pharmacokinetic behavior in vivo. RESULTS: Our results show that DESD-AL provides a higher level of morphine entrapment and that increasing the sonication time reduces the size but does not appreciably reduce the entrapment percentage. It was also observed that NP stability was greater when Pluronic F68 was used rather than PVA, and that in vitro assays provided better results with low concentrations of both stabilizers. Lyophilized NPs, after rehydration showed properties that were only slightly different from those of the untreated ones, with no sign of precipitation or aggregation. Finally, the obtained NPs enhanced morphine bioavailability. CONCLUSIONS: In conclusion, a useful method for encapsulating morphine in order to obtain an extended delivery period is described and its effects are compared with those of the free drug.
Co-amorphous Formation Induced by Combination of Tranilast and Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride.[Pubmed:27539557]
J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jan;106(1):123-128.
In this study, we investigated the formation of a co-amorphous system of tranilast (TRL) and diphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH), which are drugs used for treating allergies and inflammation. The crystallization from undercooled melts of the drugs and drug mixtures was evaluated by thermal analysis. Both drugs in the amorphous state underwent crystallization on heating, although the mixture remained in the amorphous state, indicating the formation of a co-amorphous system. The physicochemical properties of co-amorphous TRL-DPH prepared by the melting-cooling process were studied. The glass transition temperature of co-amorphous TRL-DPH deviated from the theoretical value. The enthalpy relaxation rate of the amorphous drugs, which reflected the molecular mobility, was reduced by the formation of a co-amorphous system. The intermolecular interactions between TRL and DPH in the co-amorphous system were measured by the change in the IR spectra. These results were consistent with the high physical stability. The co-amorphous sample remained in the amorphous state for over 30 days at 40 degrees C, whereas the amorphous drugs showed rapid crystallization. Our findings demonstrate that TRL and DPH form a co-amorphous system, which dramatically decreases their crystallization without an excipient.
Multilayer micro-dispersing system as oral carriers for co-delivery of doxorubicin hydrochloride and P-gp inhibitor.[Pubmed:27720963]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Jan;94(Pt A):170-180.
The primary constraints for efficient oral delivery of anticancer drugs include the efflux pump function of the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) for anticancer drugs and the barriers to drug absorption in gastrointestinal (GI) tract. To improve bypassing P-gp drug efflux pumps and oral bioavailability of doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX), Multilayer micro-dispersing system (MMS) was constructed by co-immobilization of DOX loaded chitosan/carboxymethyl chitosan nanogels (DOX:CS/CMCS-NGs), along with quercetin (Qu) in the core of multilayer sodium alginate beads (DOX:NGs/Qu-M-ALG-Beads). The obtained DOX:NGs/Qu-M-ALG-Beads possessed layer-by-layer structure and porous core with many nanoscale particles. The swelling characteristic and drug release results indicated that DOX:NGs/Qu-M-ALG-Beads exhibited favorable gastric acid tolerance and targeting release of intact DOX:CS/CMCS-NGs and Qu in small intestine. After oral administration of DOX:NGs/Qu-M-ALG-Beads in rats, DOX was effectively delivered into systemic circulation due to P-gp inhibitory properties of Qu. The absolute bioavailability reached 55.75%, about 18.65 folds higher than oral DOX. Tissue distribution results showed that the liver exhibited the highest DOX level, followed by kidney, heart, lung, and spleen. These results implied that DOX:NGs/Qu-M-ALG-Beads had great potential to be applied as dual drug delivery for oral chemotherapy.
Formulation and dissolution kinetics study of hydrophilic matrix tablets with tramadol hydrochloride and different co-processed dry binders.[Pubmed:27496049]
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016 Dec 1;95:36-45.
The aim of this study is to present the possibility of using of co-processed dry binders for formulation of matrix tablets with drug controlled release. Hydrophilic matrix tablets with tramadol hydrochloride, hypromellose and different co-processed dry binders were prepared by direct compression method. Hypromelloses Methocel K4M Premium CR or Methocel K100M Premium CR were used as controlled release agents and Prosolv(R) SMCC 90 or Disintequik MCC 25 were used as co-processed dry binders. Homogeneity of the tablets was evaluated using scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis. The release of tramadol hydrochloride from prepared formulations was studied by dissolution test method. The dissolution profiles obtained were evaluated by non-linear regression analysis, release rate constants and other kinetic parameters were determined. It was found that matrix tablets based on Prosolv(R) SMCC 90 and Methocel Premium CR cannot control the tramadol release effectively for >12h and tablets containing Disintequik MCC 25 and Methocel Premium CR >8h.
Pharmacological characterization of Ro 63-1908 (1-[2-(4-hydroxy-phenoxy)-ethyl]-4-(4-methyl-benzyl)-piperidin-4-ol), a novel subtype-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist.[Pubmed:12183650]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Sep;302(3):940-8.
Ro 63-1908, 1-[2-(4-hydroxy-phenoxy)-ethyl]-4-(4-methyl-benzyl)-piperidin-4-ol, is a novel subtype-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist that has been characterized in vitro and in vivo. Ro 63-1908 inhibited [(3)H]dizocilpine ((3)H-MK-801) binding in a biphasic manner with IC(50) values of 0.002 and 97 microM for the high- and low-affinity sites, respectively. Ro 63-1908 selectively blocked recombinant receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes containing NR1C + NR2B subunits with an IC(50) of 0.003 microM and those containing NR1C + NR2A subunits with an IC(50) of >100 microM, thus demonstrating greater than 20,000-fold selectivity for the recombinant receptors expressing NR1C + NR2B. Ro 63-1908 blocked these NMDA NR2B-subtype receptors in an activity-dependent manner. Ro 63-1908 was neuroprotective against glutamate-induced toxicity and against oxygen/glucose deprivation-induced toxicity in vitro with IC(50) values of 0.68 and 0.06 microM, respectively. Thus, the in vitro pharmacological characterization demonstrated that Ro 63-1908 was a potent and highly selective antagonist of the NR2B subtype of NMDA receptors. Ro 63-1908 was active against sound-induced seizures (ED(50) = 4.5 mg/kg i.p. when administered 30 min beforehand) in DBA/2 mice. The dose required to give a full anticonvulsant effect did not produce a deficit in the Rotarod test. NMDA-induced seizures were also inhibited by Ro 63-1908 with an ED(50) of 2.31 mg/kg i.v. when administered 15 min before testing. Ro 63-1908 gave a dose-related neuroprotective effect against cortical damage in a model of permanent focal ischemia. Maximum protection of 39% was seen at a plasma concentration of 450 ng/ml. There were, however, no adverse cardiovascular or CNS side-effects seen at this dosing level.
4-Hydroxy-1-[2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)ethyl]-4-(4-methylbenzyl)piperidine: a novel, potent, and selective NR1/2B NMDA receptor antagonist.[Pubmed:10425109]
J Med Chem. 1999 Jul 29;42(15):2993-3000.
A structure-based search and screen of our compound library identified N-(2-phenoxyethyl)-4-benzylpiperidine (8) as a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist that has high selectivity for the NR1/2B subunit combination (IC(50) = 0.63 microM). We report on the optimization of this lead compound in terms of potency, side effect liability, and in vivo activity. Potency was assayed by electrical recordings in Xenopus oocytes expressing cloned rat NMDA receptors. Side effect liability was assessed by measuring affinity for alpha(1)-adrenergic receptors and inhibition of neuronal K(+) channels. Central bioavailability was gauged indirectly by determining anticonvulsant activity in a mouse maximal electroshock (MES) assay. Making progressive modifications to 8, a hydroxyl substituent on the phenyl ring para to the oxyethyl tether (10a) resulted in a approximately 25-fold increase in NR1A/2B potency (IC(50) = 0.025 microM). p-Methyl substitution on the benzyl ring (10b) produced a approximately 3-fold increase in MES activity (ED(50) = 0.7 mg/kg iv). Introduction of a second hydroxyl group into the C-4 position on the piperidine ring (10e) resulted in a substantial decrease in affinity for alpha(1) receptors and reduction in inhibition of K(+) channels with only a modest decrease in NR1A/2B and MES potencies. Among the compounds described, 10e (4-hydroxy-N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)ethyl]-4-(4-methylbenzyl)piperid ine, Co 101244/PD 174494) had the optimum pharmacological profile and was selected for further biological evaluation.


