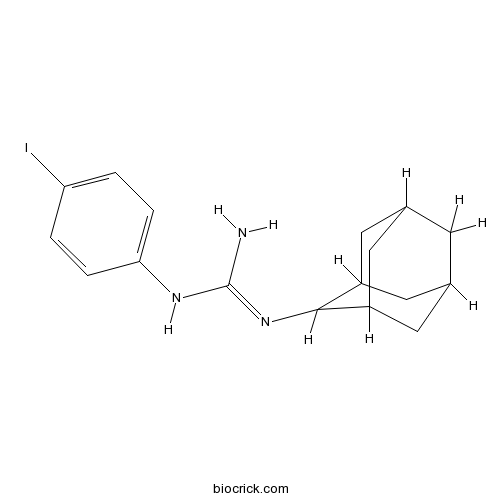
IPAGCAS# 193527-91-2 |
- FRAX597
Catalog No.:BCC4172
CAS No.:1286739-19-2
- PF-3758309
Catalog No.:BCC1853
CAS No.:898044-15-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 193527-91-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4239764 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H22IN3 | M.Wt | 395.29 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in ethanol and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-adamantyl)-1-(4-iodophenyl)guanidine | ||
| SMILES | C1C2CC3CC1CC(C2)C3N=C(N)NC4=CC=C(C=C4)I | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UUKPIWYXWLJPJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H22IN3/c18-14-1-3-15(4-2-14)20-17(19)21-16-12-6-10-5-11(8-12)9-13(16)7-10/h1-4,10-13,16H,5-9H2,(H3,19,20,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent σ-receptor antagonist. |

IPAG Dilution Calculator

IPAG Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5298 mL | 12.6489 mL | 25.2979 mL | 50.5958 mL | 63.2447 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.506 mL | 2.5298 mL | 5.0596 mL | 10.1192 mL | 12.6489 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.253 mL | 1.2649 mL | 2.5298 mL | 5.0596 mL | 6.3245 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0506 mL | 0.253 mL | 0.506 mL | 1.0119 mL | 1.2649 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0253 mL | 0.1265 mL | 0.253 mL | 0.506 mL | 0.6324 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Mulberroside F
Catalog No.:BCN2908
CAS No.:193483-95-3
- Fmoc-Glu(Edans)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3491
CAS No.:193475-66-0
- Zeylenone
Catalog No.:BCC8268
CAS No.:193410-84-3
- Tartrazine
Catalog No.:BCN2217
CAS No.:1934-21-0
- Co 101244 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7369
CAS No.:193356-17-1
- 5-Aminoindazole
Catalog No.:BCC8734
CAS No.:19335-11-6
- Lonafarnib
Catalog No.:BCC2331
CAS No.:193275-84-2
- 1-O-Acetyl-6alpha-O-(2-methylbutyryl)britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN7747
CAS No.:1932687-71-2
- cis-Moschamine
Catalog No.:BCN3901
CAS No.:193224-24-7
- Otamixaban
Catalog No.:BCC1827
CAS No.:193153-04-7
- Cardamonin
Catalog No.:BCN1184
CAS No.:19309-14-9
- CTS-1027
Catalog No.:BCC1502
CAS No.:193022-04-7
- SB 239063
Catalog No.:BCC1923
CAS No.:193551-21-2
- Calcifediol
Catalog No.:BCC4949
CAS No.:19356-17-3
- GB 1b
Catalog No.:BCN7385
CAS No.:19360-72-6
- Terrestrosin K
Catalog No.:BCN2935
CAS No.:193605-07-1
- SB 216641 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6987
CAS No.:193611-67-5
- BRL-15572
Catalog No.:BCC5065
CAS No.:193611-72-2
- TAS 301
Catalog No.:BCC6214
CAS No.:193620-69-8
- Methyl 4-hydroxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN4014
CAS No.:19367-38-5
- 8beta-Methoxyatractylenolide I
Catalog No.:BCN7594
CAS No.:193694-24-5
- Aminoguanidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6795
CAS No.:1937-19-5
- SB 242235
Catalog No.:BCC4171
CAS No.:193746-75-7
- Cortistatin 14
Catalog No.:BCC6010
CAS No.:193829-96-8
A combination of the IPAG questionnaire and PiKo-6(R) flow meter is a valuable screening tool for COPD in the primary care setting.[Pubmed:21597666]
Prim Care Respir J. 2011 Jun;20(2):184-9, 1 p following 189.
AIMS: To investigate the validity of the International Primary Care Airways Guidelines (IPAG) questionnaire and PiKo-6(R) (Ferraris Respiratory Europe Ltd.) flow meter as screening tools for diagnosing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the primary care setting. METHODS: The first 50 patients in 25 general practice offices completed the IPAG questionnaire and underwent spirometry with the handheld PiKo-6(R) flow meter. The results were compared with official spirometry parameters after bronchodilation. All participants had no previous medical diagnosis of respiratory diseases. RESULTS: Data from 1,078 out of 1,250 subjects (462 males, mean age 65.3 +/- 11.4 years) were analysed. The percentage of smokers was 48.4% (38 +/- 29 pack-years). COPD was diagnosed in 111 (10.3%) patients. In the subgroup of smokers the sensitivity and specificity for COPD diagnosis were 91% and 49%, respectively, for the IPAG questionnaire; 80% and 95% respectively for the PiKo-6(R) spirometer; and 72% and 97% for their combination. The negative predictive value of the questionnaire was 97%, whereas the positive predictive value of the questionnaire/ PiKo-6(R) combination was 82%. Using a cut-off score of 19 points for the IPAG questionnaire, we calculated the best combination of sensitivity (75%) and specificity (72%). CONCLUSIONS: The IPAG questionnaire and the hand-held PiKo-6(R) spirometer can be used in combination to increase the possibility of an early and accurate diagnosis of COPD in the primary care setting.
Antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by sigma site ligands: potency, subtype-selectivity and mechanisms of inhibition.[Pubmed:9223571]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jul;282(1):326-38.
Recent studies propose that sigma site ligands antagonize N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors by either direct, or indirect mechanisms of inhibition. To investigate this question further we used electrical recordings to assay actions of seventeen structurally diverse sigma site ligands on three diheteromeric subunit combinations of cloned rat NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: NR1a coexpressed with either NR2A, 2B or 2C. The sigma site ligands had a wide range of potency for antagonizing NMDA receptor currents. Steady-state IC50 values ranged between approximately 0.1 to >100 microM. In all cases inhibition was non-competitive with respect to glycine and glutamate. Five structurally related sigma ligands [eliprodil, haloperidol, ifenprodil, 4-phenyl-1-(4-phenylbutyl)-piperidine and trifluperidol] were strongly selective for NR1a/2B receptors. The other drugs were weakly selective or nonselective inhibitors. There was no correlation between sigma site affinity and potency of NMDA receptor antagonism for any subunit combination. Inhibition of NR1a/2B receptors by the selective antagonists was independent of voltage whereas inhibition by the weakly selective antagonists was voltage dependent. Potency of 10 sigma ligands was cross-checked on NMDA currents in cultured rat cortical neurons. There was close correspondence between the two assay systems. Our results argue that antagonism of NMDA receptor currents by the sigma ligands tested is due to direct effects on the receptor channel complex as opposed to indirect effects mediated by sigma receptors. Inhibition occurs via sites in the NMDA receptor channel pore, or via allosteric modulatory sites associated with the NR2B subunit.
Radiosynthesis of sigma receptor ligands for positron emission tomography: 11C- and 18F-labeled guanidines.[Pubmed:1648140]
J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1867-70.
A series of analogues of the potent and selective sigma receptor ligand 1,3-ditolylguanidine (DTG) were synthesized and demonstrated to have high affinity for the sigma receptor as measured by in vitro [3H]DTG displacement studies using guinea pig brain tissue. Three of these 1-aryl-3-(1-adamantyl)guanidines were radiolabeled--two with carbon-11 and one with fluorine-18. Radiochemical yields and specific activities were sufficient for these radiotracers to be used in positron emission tomography imaging of the haloperidol-sensitive sigma receptor.


