DihydroseselinCAS# 2221-66-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2221-66-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 797506 | Appearance | Powder |
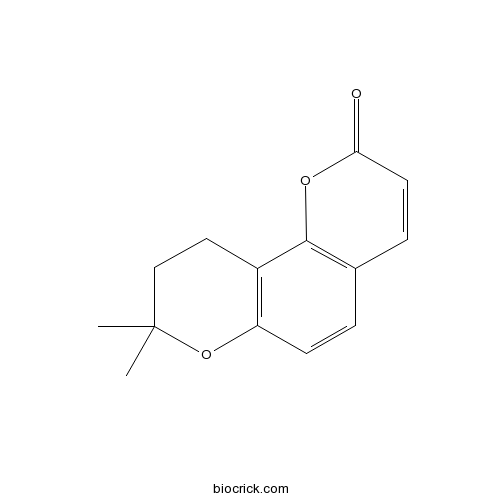
| Formula | C14H14O3 | M.Wt | 230.3 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 8,8-dimethyl-9,10-dihydropyrano[2,3-h]chromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC(=O)C=C3)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GXOXLDJHMAATRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14O3/c1-14(2)8-7-10-11(17-14)5-3-9-4-6-12(15)16-13(9)10/h3-6H,7-8H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Dihydroseselin type of pyranocoumarin possessing a 4'-isovaleryl group is important to suksdorfin's enhanced anti-HIV activity. |
| Targets | HIV |

Dihydroseselin Dilution Calculator

Dihydroseselin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3422 mL | 21.7108 mL | 43.4216 mL | 86.8432 mL | 108.5541 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8684 mL | 4.3422 mL | 8.6843 mL | 17.3686 mL | 21.7108 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4342 mL | 2.1711 mL | 4.3422 mL | 8.6843 mL | 10.8554 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0868 mL | 0.4342 mL | 0.8684 mL | 1.7369 mL | 2.1711 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2171 mL | 0.4342 mL | 0.8684 mL | 1.0855 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Naproxen
Catalog No.:BCC9091
CAS No.:22204-53-1
- Pyrantel Pamoate
Catalog No.:BCC4958
CAS No.:22204-24-6
- Lyn peptide inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC5895
CAS No.:222018-18-0
- L-Canavanine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6746
CAS No.:2219-31-0
- Macrocarpal N
Catalog No.:BCN5811
CAS No.:221899-21-4
- Zotarolimus(ABT-578)
Catalog No.:BCC5481
CAS No.:221877-54-9
- Methylswertianin
Catalog No.:BCN8505
CAS No.:22172-17-4
- Conocarpan
Catalog No.:BCN5053
CAS No.:221666-27-9
- OBAA
Catalog No.:BCC6716
CAS No.:221632-26-4
- L-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4971
CAS No.:2216-51-5
- Boron tributoxide
Catalog No.:BCN8281
CAS No.:688-74-4
- 2,6-Dimethoxy-1-acetonylquinol
Catalog No.:BCN5052
CAS No.:2215-96-5
- Dehydroglaucine
Catalog No.:BCN2548
CAS No.:22212-26-6
- Cucurbitacin I
Catalog No.:BCC2439
CAS No.:2222-07-3
- Thalrugosaminine
Catalog No.:BCN7745
CAS No.:22226-73-9
- Fern-7-en-19-one
Catalog No.:BCN6443
CAS No.:222294-61-3
- 7-Amino-3-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8776
CAS No.:22252-43-3
- Ipratropium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC3795
CAS No.:22254-24-6
- Methyl 6-hydroxyangolensate
Catalog No.:BCN5054
CAS No.:22255-07-8
- alpha-Amyrin palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN5055
CAS No.:22255-10-3
- Guaijaverin
Catalog No.:BCN5056
CAS No.:22255-13-6
- Trimethoxystilbene
Catalog No.:BCN6762
CAS No.:22255-22-7
- Lucidin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8249
CAS No.:22255-29-4
- Loganic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5057
CAS No.:22255-40-9
[Chemical constituents from fruits of Vitex trifolia var. simplicifolia].[Pubmed:30384535]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Sep;43(18):3694-3700.
The present study is to investigate the chemical constituents from the dried ripe fruits of Vitex trifolia var. simplicifolia The compounds were isolated by using a variety of chromatographic methods including silicagel, ODS, Sephadex LH-20, reversed-phase HPLC, and other methods. Their structures were identified by NMR, and MS date. As a result, 18 compounds were isolated and identified as ent-2-oxo15,16,19-trihydroxypimar-8(14)-ene (1), chrysosplenol D (2), casticin (3), luteolin (4), eupatrin (5), apigenin (6), 5,4'-dihydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxyflavone (7), luteolin-4'-O-glucoside (8), hypolaetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (9), swertisin (10), agestricin D (11), 5,3'-dihydroxy-6,7,4'-trimethoxyflavanone (12), tomentic acid (13), 2alpha,3beta,23-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (14), 3'-acetoxy-4'-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (15), dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol (16), 3,5'-dimethoxy-4',7-epoxy-8,3'-neolignane-5,9,9'-triol (17) and salicifoliol (18). Among them, compounds 1, 2, 5-15, 17 and 18 were obtained from V. trifolia var. simplicifolia Cham for the first time and compounds 1, 5, 7-11, 15, 17 and 18 were isolated from thegenus Vitex for the first time.
[Chemical constituents from root of Angelica decursiva].[Pubmed:29139270]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Aug;42(15):2999-3003.
The compounds were isolated and purified by HP20 macroporous adsorption resin, ODS, silica gel, and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, as well as semi-preparative HPLC chromatography from the 80% ethanol extract of the root of Angelica decursiva, and their structures were identified based on their physiochemical properties and spectroscopic data. Twelve compounds were structures were identified as (9R,10R)-9-acetoxy-8,8-dimethyl-9,10-dihydro-2H,8H-benzo[1,2-b3,4-b']dipyran-2-on e-10-yl ester (1), bakuchicin (2), (3', S,4'S)-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (3), (3'R,4'R)-3'-angeloyloxy-4'-senecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselincalipteryxin (4), (+)-8,9-dihydro-8-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-oxo-2H-furo[2,3h]chromen-9-yl-3-methyl but-2-enoate (5), libanoridin (6), selinidin (7), suberosin (8), crocatone (9), peujaponisinol B (10), peujaponisinol A (11), and ostenol (12), respectively. Compounds 1-5 were isolated from the plants of Angelica genus for the first time. Compounds 7-12 were isolated from A. decursiva for the first time.
Improved Biological Activities of Isoepoxypteryxin by Biotransformation.[Pubmed:27449560]
Chem Biodivers. 2016 Oct;13(10):1307-1315.
Isoepoxypteryxin is the major coumarin of a Japanese medicinal plant Angelica shikokiana. This research was designed to study the effect of structural changes through fungal biotransformation on the reported biological activities of isoepoxypteryxin. Among the tested microorganisms, only Cordyceps sinensis had enzymes that could catalyze the ester hydrolysis and the reductive cleavage of the epoxide ring of isoepoxypteryxin, separately, to give two more polar metabolites (+)-cis-khellactone (P1) and a new coumarin derivative (+)-cis-3'-[(2-methyl-3-hydroxybutanoyl)oxy]-4'-acetoxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (P2), respectively. The polar metabolite P2 showed stronger cytotoxicity and higher selectivity than isoepoxypteryxin. On the molecular level, P2 showed more in vitro inhibition of both tubulin polymerization and histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8). Similarly, P2 showed more neuroprotection against amyloid beta fragment 1 - 42 (Abeta1 - 42 )-induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y) and exhibited more inhibition of the in vitro aggregation of Abeta1 - 42 . Both metabolites showed stronger antiplatelet aggregation by increased inhibition of thromboxane-A2 synthase (TXS) activity and thromboxane-A2 (TXA2) production. This study is the first to describe the improved cytotoxic, neuroprotective, and antiplatelet aggregation activities of isoepoxypteryxin through its biotransformation by C. sinensis.
[Chemical constituents from ethyl acetate exaction of root of Paeonia lactiflora].[Pubmed:28901069]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;41(12):2255-2260.
Two new phenylpropanoids(1 and 2), together with thirteen known compounds(3-15), have been isolated from the root of Paeonia lactiflora by using various chromatographic techniques. Their structures were identified by spectroscopic data analysis(MS,IR,1D and 2D NMR)as(+)-(7R,8R)-1-guaiacyl-1,2-propanediolacetonide(1),(-)-(7R,8S)-1-guaiacyl-1 ,2-propanediolacetonide(2),O-senecioyllomatin(3),O-angeloyllomatin(4),(+)-cis-3'- senecioyloxy-4'-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin(5),columbianadin(6), benzyl 2,5-dihydroxybenzoate(7),3,6-dimethyl-5-hydroxyBenzo-furan(8),(S)-evofolin-A(9),2 ,3-dihydroxy-4-methoxyacetophenone(10), 2,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxyacetophenone(11), 2,5-dihydroxy-4-methyl acetophenone(12),ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate(13), vanillic acid(14),and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde(15).Compounds 1 and 2 were new compounds,and compounds 3-9 were obtained from the genus Paeonia for the first time.
Anti-inflammatory Actions of (+)-3'alpha-Angeloxy-4'-keto-3',4'-dihydroseselin (Pd-Ib) against Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in C57BL/6 Mice.[Pubmed:26905227]
J Nat Prod. 2016 Apr 22;79(4):1056-62.
The immunoregulatory protective properties of (+)-3'alpha-angeloxy-4'-keto-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (Pd-Ib) isolated from Bupleurum malconense has not been reported. In the present study, the therapeutic effect of Pd-Ib (30, 60, and 120 mg/kg/day) was examined in a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute colitis. Administration of Pd-Ib significantly reduced the disease activity index, inhibited the shortening of colon length, reduced colonic tissue damage, and suppressed colonic myeloperoxidase activity and nitric oxide levels in mice with DSS-induced colitis. Moreover, Pd-Ib greatly suppressed the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-17A while enhancing the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4. The protein levels of phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) and phosphorylated p38 (p-p38) were down-regulated in the colonic tissues of DSS-treated mice. Importantly, the anti-inflammatory effect of Pd-Ib against acute colitis was comparable to the anti-inflammatory sulfa drug sulfasalazine (300 mg/kg). Furthermore, the in vitro study showed that the inhibitory effect of Pd-Ib on p-STAT3 and IL-6 protein levels was accompanied by the reduction of MAPKs (JNK and p38). In conclusion, this study suggested that Pd-Ib attenuated DSS-induced acute colitis via the regulation of interleukins principally through the STAT3 and MAPK pathways.
A novel coumarin, (+)-3'-angeloxyloxy-4'-keto-3',4'-dihydroseselin, isolated from Bupleurum malconense (Chaihu) inhibited NF-kappaB activity.[Pubmed:26877763]
Chin Med. 2016 Feb 13;11:5.
BACKGROUND: This study aims to identify the major anti-inflammatory components in the petroleum ether extract of Bupleurum malconense (Chaihu), by bioassay-guided fractionation, and to investigate the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of active components in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine macrophage RAW-Blue cells. METHODS: A QUANTI-Blue assay was used to guide fractionation of B. malconense root extract. The petroleum ether extract which exerted significant secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) inhibition effect was purified by silica gel column chromatography and assisted with reverse phase HPLC. The major bioactive compound which significantly inhibited SEAP activity was obtained and its anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced RAW-Blue cells were measured by the overproduction of NO (Griess method), gene expression of Il-1beta, Tnf-alpha and iNos (real-time PCR). In parallel, protein expressions of COX-2, iNOS and IkappaB-alpha were determined by western blot. RESULTS: In bioassay-guided fractionation using LPS-stimulated mouse macrophage RAW-Blue cells, (+)-3'-angeloxyloxy-4'-keto-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (Pd-Ib) was identified by MS and NMR spectral analyses. Pd-Ib (5, 10, 20 mug/mL) suppressed the gene expression of Il-1beta (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001 for three respective concentrations), Tnf-alpha (P = 0.006, P = 0.001, P < 0.0001 for three respective concentrations) and iNos (P = 0.009, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001 for three respective concentrations) in LPS-stimulated macrophages. The production of cyclooxygenase-2 (P = 0.019, P = 0.002, P < 0.0001), iNOS (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001 for three respective concentrations) and NO (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001 for three respective concentrations) significantly decreased when macrophages were treated with Pd-Ib (5, 10, 20 mug/mL) in the presence of LPS. Pd-Ib (5, 10, 20 mug/mL) suppressed the nuclear activation of NF-kappaB while it up-regulated the IkappaB-alpha level (P = 0.028, P = 0.013, P = 0.005 for three respective concentrations) in LPS-stimulated macrophages. CONCLUSIONS: Pd-Ib isolated from B. malconense suppressed LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages by inhibiting NF-kappaB activity and reducing the expression of iNOS, COX-2 as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Pharmacological mechanism underlying anti-inflammatory properties of two structurally divergent coumarins through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes and cytokines.[Pubmed:26221081]
J Inflamm (Lond). 2015 Jul 29;12:47.
BACKGROUND: The aim of the present study is to investigate the effects of two structurally divergent coumarins, calipteryxin (1) and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (2) from Seseli recinosum, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine macrophages. METHODS: The nitrite production was evaluated using Griess reagent. The protein and mRNA expression levels were investigated through Western blot and quantitative real time-PCR analyses. The NF-kappaB and AP-1 DNA-binding activities were assessed using an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. The docking studies were performed with Glide XP in Schrodinger suite (version 2013). RESULTS: The results of the present study revealed that calipteryxin (1) and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (2) treatment showed potent inhibitory effects on pro-inflammatory enzymes and cytokines associated with molecular signaling pathways. Treatment with calipteryxin and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin also decreased the production of nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta) in a dose-dependent manner. Additionally, both coumarins inhibited the LPS-induced protein and mRNA expression levels of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in RAW264.7 cells. To explore the potential mechanisms underlying the inhibitory activity of coumarin derivatives, the protein signaling pathways for NF-kappaB, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt were examined. Calipteryxin and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin markedly reduced the LPS-stimulated phosphorylation of IKKalpha/beta, p-IkappaBalpha and IkappaBalpha degradation as well as the nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit of pro-inflammatory transcription factor NF-kappaB. In addition, calipteryxin and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin) considerably inhibited the LPS-induced expression of ERK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 and Akt proteins. Furthermore, both coumarins significantly inhibited c-Jun expression in the nucleus. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, these results support the therapeutic potential and molecular mechanism of calipteryxin and (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin associated with inflammatory diseases.
Enantiomeric separation of angular-type pyranocoumarins from Peucedani Radix using AD-RH chiral column.[Pubmed:24502289]
Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(8):545-50.
Enantiomers and diastereoisomers of angular-type pyranocoumarins (APs) are abundant in Peucedani Radix (Chinese name: Qian-hu), eliciting distinct activities in vitro and in vivo. Our ongoing investigation on APs yielded eight pairs of enantiomers (1a and 1b, 2a and 2b, 3a and 3b, 4a and 4b, 5a and 5b, 6a and 6b, 7a and 7b and 8a and 8b) via enantiomeric separation of trans-3'-angeloylkhellactone (1), trans-3'-acetyl-4'-isobutyrylkhellactone (2), trans-3'-acetyl-4'-angeloyl-khellactone (3), 3'-angeloyloxy-4'-oxo-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (4), cis-3'-acetyl-4'-angeloylkhellactone (5), cis-3'-isovaleryl-4'-acetylkhellactone (6), cis-3'-angeloyl-4'-isovalerylkhellactone (7) and cis-3',4'-diisovalerylkhellactone (8), respectively, using semi-preparative AD-RH chiral column. All the compounds (1-8) were enantioseparated for the first time, while the absolute configurations of 2a, 2b, 6a and 8b were reported first.
Application of stepwise gradients in counter-current chromatography: a rapid and economical strategy for the one-step separation of eight coumarins from Seseli resinosum.[Pubmed:23992840]
J Chromatogr A. 2013 Oct 4;1310:66-73.
The targeted purification of compounds with a broad polarity range from traditional medicinal plants is a big challenge for counter-current chromatography (CCC). Gradient elution was introduced in CCC to address this problem. However, once a suitable solvent system is selected, the separation process requires optimization of operational parameters. The present study was conducted to optimize various operational parameters to integrate the flow rate and solvent gradients for the rapid isolation of eight coumarins from Seseli resinosum in a single run. An increase in the system temperature from 15 degrees C to 35 degrees C increased the stationary phase retention and solubility of the sample, whereas the operation time and viscosity of the system were decreased. The high purity of each compound was ensured by collecting the fractions from the main peaks while all the shoulder peaks were mixed and separated under the same conditions with semi-preparative CCC. GC-FID was used to analyze the components of each phase, which was prepared without presaturation to save the time and solvent consumption. Finally, eight coumarins were purified, including (1) d-laserpitin, (2) (3'S,4'S)-3'-angeloyloxy-4'-hydroxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin, (3) (+)-samidin, (4) (3'S,4'S)-3'-acetoxy-4'-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin, (5) deltoin (6), calipteryxin, (7) (3'S,4'S)-3',4'-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin, and (8) (-)-anomalin. The present technique has successfully accomplished the goal of one-step separation of these compounds with high purity and recovery in an economic and time efficient manner.
Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of coumarins from Seseli gummiferum subsp. corymbosum (Apiaceae).[Pubmed:19323267]
Z Naturforsch C. 2009 Jan-Feb;64(1-2):56-62.
n-Hexane and ethyl acetate extracts as well as coumarin derivatives obtained from the n-hexane extract of the aerial parts of Seseli gummiferum Pall. ex Sm. subsp. corymbosum (Boiss. & Heldr.) P.H. Davis (Apiaceae) were evaluated in vivo for their anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities. The n-hexane and ethyl acetate extracts of the species were shown to possess significant inhibitory activity against the carrageenan-induced hind paw edema and p-benzoquinone-induced writhing models in mice. Among the isolated coumarin derivatives; (-)-(3'S,4'S)-3'-acetoxy-4'-isovaleryloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (1), (-)-(3'S,4'S)-3'-acetoxy-4'-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (2), (+)-(3'S,4'S)-3'-hydroxy-4'-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (D-laserpitin) (3), (-)-(3'S,4'S)-3'-angeloyloxy-4'-hydroxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (4), and osthole (5), only the 3'-acetoxy derivatives 1 and 2 were found to possess potent antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities, per os, without inducing any apparent acute toxicity as well as gastric damage, while all other compounds and extracts were found to be ineffective in the TPA-induced mouse ear edema model assay.
Isolation of coumarins and ferulate from the roots of Angelica purpuraefolia and the antitumor activity of khellactone.[Pubmed:17236175]
Phytother Res. 2007 May;21(5):406-9.
A new coumarin, hydroxylomatin (1), was isolated from the CHCl(3)-soluble fraction of the roots of Angelica purpuraefolia, along with one ferulate (2) and three other known coumarins (3-5) including khellactone (3). The structure of hydroxylomatin (1) was determined to be 3'beta,5'-dihydroxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin (1) by spectroscopic means including 2D-NMR. The modified Mosher's method was used to determine the chiral center at C-1 of compound 2. Khellactone (3) is a major compound of the roots of A. purpuraefolia. This study also examined the antitumor activity of khellactone (3) using a LLC mouse lung carcinoma in the BDF-1 mice and a NCI-H460 human lung carcinoma in a human tumor xenograft model in nude mice. This compound (3) inhibited LLC tumor growth with a T/C (mean value of treated group/mean value of control group) value of 12.9% at a dose of 5 mg/kg and 33.2% at a dose of 10 mg/kg, respectively, in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, it suppressed the growth of NCI-H460 tumor cells, accounting for 81.4% at a dose of 10 mg/kg in nude mice.
Chemical constituents of Selinum cryptotaenium.[Pubmed:16864434]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2006 Apr-May;8(3):273-5.
A new pyranocoumarin, named secryptotaenin A, determined as 3'(S)-angeloyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin, was isolated from the roots of Selinum cryptotaenium, along with thirteen known compounds, umbelliferone, osthol, coumurrayin, (+)-heraclenol, longshengensin A, anomalin, ferulic acid, galactitol, stearic acid, melissic acid, lignoceric acid, beta-sitosterol and daucosterol. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic methods.
Coumarins from Peucedanum wulongense.[Pubmed:12931850]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2003 Sep;5(3):183-7.
A new angular dihydropyrancoumarin named wulongensin A, along with five known coumarins, (-)-anomalin, umbelliferone, (-)-smyrinol, 3'(S),4'(S)-disenecioyloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin, (+)-trans-khellactone, was isolated from the root of Peucedanum wulongense. The structure of wulongensin A was established as 3'(R)-angeloyloxy-4'(R)-isovaleryloxy-3',4'-Dihydroseselin by spectroscopic methods and the absolute configurations were deduced by chemical correlations with known compounds.


