Lyn peptide inhibitorInhibits Lyn activation via hematopoietin βc receptor; cell-permeable CAS# 222018-18-0 |
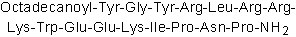
- Ampalex
Catalog No.:BCC1359
CAS No.:154235-83-3
- Tezampanel
Catalog No.:BCC1993
CAS No.:154652-83-2
- Noopept
Catalog No.:BCC1804
CAS No.:157115-85-0
- Perampanel
Catalog No.:BCC1847
CAS No.:380917-97-5
- Aniracetam
Catalog No.:BCC4219
CAS No.:72432-10-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 222018-18-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102586615 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C115H184N30O24 | M.Wt | 2370.91 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | YGYRLRRKWEEKIPNP (Modifications: Tyr-1 = Octadecanoyl-Tyr, Pro-16 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC=C43)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)N5CCCC5C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)N6CCCC6C(=O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MITSVNFZLBORMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C115H184N30O24/c1-6-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-42-93(149)131-86(63-71-43-47-74(146)48-44-71)99(156)130-68-94(150)132-87(64-72-45-49-75(147)50-46-72)108(165)137-82(39-30-59-128-115(124)125)103(160)140-85(62-69(3)4)107(164)136-81(38-29-58-127-114(122)123)101(158)135-80(37-28-57-126-113(120)121)100(157)133-78(35-24-26-55-116)102(159)141-88(65-73-67-129-77-34-23-22-33-76(73)77)109(166)139-84(52-54-96(153)154)105(162)138-83(51-53-95(151)152)104(161)134-79(36-25-27-56-117)106(163)143-97(70(5)7-2)112(169)145-61-32-41-91(145)110(167)142-89(66-92(118)148)111(168)144-60-31-40-90(144)98(119)155/h22-23,33-34,43-50,67,69-70,78-91,97,129,146-147H,6-21,24-32,35-42,51-66,68,116-117H2,1-5H3,(H2,118,148)(H2,119,155)(H,130,156)(H,131,149)(H,132,150)(H,133,157)(H,134,161)(H,135,158)(H,136,164)(H,137,165)(H,138,162)(H,139,166)(H,140,160)(H,141,159)(H,142,167)(H,143,163)(H,151,152)(H,153,154)(H4,120,121,126)(H4,122,123,127)(H4,124,125,128) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cell-permeable inhibitor of Lyn-dependent effects of the IL-5 receptor. Blocks binding of Lyn tyrosine kinase to βc subunit of IL-3/GM-CSF/IL-5 receptors, blocking Lyn activation. Inhibits IL-5 receptor-mediated eosinophil differentiation and survival in vitro. Inhibits airway eosinophilic inflammation in mouse model of asthma. |

Lyn peptide inhibitor Dilution Calculator

Lyn peptide inhibitor Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- L-Canavanine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6746
CAS No.:2219-31-0
- Macrocarpal N
Catalog No.:BCN5811
CAS No.:221899-21-4
- Zotarolimus(ABT-578)
Catalog No.:BCC5481
CAS No.:221877-54-9
- Methylswertianin
Catalog No.:BCN8505
CAS No.:22172-17-4
- Conocarpan
Catalog No.:BCN5053
CAS No.:221666-27-9
- OBAA
Catalog No.:BCC6716
CAS No.:221632-26-4
- L-Menthol
Catalog No.:BCN4971
CAS No.:2216-51-5
- Boron tributoxide
Catalog No.:BCN8281
CAS No.:688-74-4
- 2,6-Dimethoxy-1-acetonylquinol
Catalog No.:BCN5052
CAS No.:2215-96-5
- 1-Benzyl-1H-indazol-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8458
CAS No.:2215-63-6
- Stigmastane-3,6-dione
Catalog No.:BCN5051
CAS No.:22149-69-5
- Hopane-3beta,22-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4852
CAS No.:22149-65-1
- Pyrantel Pamoate
Catalog No.:BCC4958
CAS No.:22204-24-6
- Naproxen
Catalog No.:BCC9091
CAS No.:22204-53-1
- Dihydroseselin
Catalog No.:BCN8258
CAS No.:2221-66-1
- Dehydroglaucine
Catalog No.:BCN2548
CAS No.:22212-26-6
- Cucurbitacin I
Catalog No.:BCC2439
CAS No.:2222-07-3
- Thalrugosaminine
Catalog No.:BCN7745
CAS No.:22226-73-9
- Fern-7-en-19-one
Catalog No.:BCN6443
CAS No.:222294-61-3
- 7-Amino-3-methyl-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8776
CAS No.:22252-43-3
- Ipratropium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC3795
CAS No.:22254-24-6
- Methyl 6-hydroxyangolensate
Catalog No.:BCN5054
CAS No.:22255-07-8
- alpha-Amyrin palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN5055
CAS No.:22255-10-3
- Guaijaverin
Catalog No.:BCN5056
CAS No.:22255-13-6
A novel Lyn-binding peptide inhibitor blocks eosinophil differentiation, survival, and airway eosinophilic inflammation.[Pubmed:10395690]
J Immunol. 1999 Jul 15;163(2):939-46.
Receptor antagonists block all receptor-coupled signaling pathways indiscriminately. We introduce a novel class of peptide inhibitors that is designed to block a specific signal from a receptor while keeping other signals intact. This concept was tested in the model of IL-5 signaling via Lyn kinase. We have previously mapped the Lyn-binding site of the IL-5/GM-CSF receptor common beta (beta c) subunit. In the present study, we designed a peptide inhibitor using the Lyn-binding sequence. The peptide was N-stearated to enable cellular internalization. The stearated peptide blocked the binding of Lyn to the beta c receptor and the activation of Lyn. The lipopeptide did not affect the activation of Janus kinase 2 or its association with beta c. The inhibitor blocked the Lyn-dependent functions of IL-5 in vitro (e.g., eosinophil differentiation from stem cells and eosinophil survival). It did not affect eosinophil degranulation. When applied in vivo, the Lyn-binding peptide significantly inhibited airway eosinophil influx in a mouse model of asthma. The lipopeptide had no effect on basophil histamine release or on the proliferation of B cells and T cells. To our knowledge, this is the first report on an inhibitor of IL-5 that blocks eosinophil differentiation, survival, and airway eosinophilic inflammation. This novel strategy to develop peptide inhibitors can be applied to other receptors.
The mapping of the Lyn kinase binding site of the common beta subunit of IL-3/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor/IL-5 receptor.[Pubmed:9973406]
J Immunol. 1999 Feb 1;162(3):1496-501.
It has been shown that a membrane-proximal region within common beta (betac) receptor of IL-3/granulocyte-macrophage CSF/IL-5 (amino acids 450-517) is important for Lyn binding. We have shown previously that Lyn kinase is physically associated with the IL-5R betac subunit in unstimulated cells. The result suggests that this association involves binding modules that are not activation or phosphorylation dependent. The objective of this study was to map the exact Lyn binding site on betac. Using overlapping and/or sequential peptides derived from betac 450-517, we narrowed down the Lyn binding site to nine amino acid residues, betac 457-465. The P-->A mutation in this region abrogated the binding to Lyn, indicating a critical role of proline residues. We created a cell-permeable Lyn-binding peptide by N-stearation. This cell-permeable peptide blocked the association of Lyn, but not Jak2 with betac in situ. We also investigated the betac binding site of Lyn kinase. Our results suggest that the N-terminal unique domain of Lyn kinase is important for binding to betac receptor. To our knowledge, this is the first molecular identification of the Lyn binding site of betac receptor. This finding may help develop specific inhibitors of Lyn-coupled signaling pathways.


