Eburicoic acidCAS# 560-66-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 560-66-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 237891 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C31H50O3 | M.Wt | 470.73 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
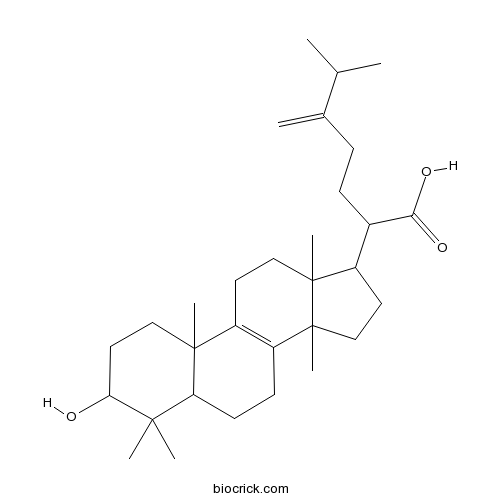
| Chemical Name | 2-(3-hydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,11,12,15,16,17-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)-6-methyl-5-methylideneheptanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(=C)CCC(C1CCC2(C1(CCC3=C2CCC4C3(CCC(C4(C)C)O)C)C)C)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UGMQOYZVOPASJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H50O3/c1-19(2)20(3)9-10-21(27(33)34)22-13-17-31(8)24-11-12-25-28(4,5)26(32)15-16-29(25,6)23(24)14-18-30(22,31)7/h19,21-22,25-26,32H,3,9-18H2,1-2,4-8H3,(H,33,34) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Eburicoic acid has significant anti-liver cancer effects and more distinctive mechanisms. 2. Eburicoic acid and TR2 protect the liver from CCl4-induced hepatic damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. 3. Eburicoic acid and TR2 have anti-inflammatory activity, the mechanism is related to the decrease of inflammatory cytokines and an increase of antioxidant enzyme activity. |
| Targets | SOD | NO | TNF-α | NOS | COX | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | IL Receptor |

Eburicoic acid Dilution Calculator

Eburicoic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1244 mL | 10.6218 mL | 21.2436 mL | 42.4872 mL | 53.109 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4249 mL | 2.1244 mL | 4.2487 mL | 8.4974 mL | 10.6218 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2124 mL | 1.0622 mL | 2.1244 mL | 4.2487 mL | 5.3109 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0425 mL | 0.2124 mL | 0.4249 mL | 0.8497 mL | 1.0622 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0212 mL | 0.1062 mL | 0.2124 mL | 0.4249 mL | 0.5311 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 9-Hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8802
CAS No.:560-62-3
- Chlorhexidine acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8912
CAS No.:56-95-1
- Histamine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4530
CAS No.:56-92-8
- (H-Cys-OH)2
Catalog No.:BCC2915
CAS No.:56-89-3
- L-lysine
Catalog No.:BCN7157
CAS No.:56-87-1
- L-Glutamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3809
CAS No.:56-86-0
- L-Glutamine
Catalog No.:BCC3803
CAS No.:56-85-9
- H-Asp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2881
CAS No.:56-84-8
- Glycerol
Catalog No.:BCC8990
CAS No.:56-81-5
- Chloramphenicol
Catalog No.:BCC1201
CAS No.:56-75-7
- DL-5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCN1232
CAS No.:56-69-9
- Quinidine
Catalog No.:BCC7863
CAS No.:56-54-2
- Sucralose
Catalog No.:BCC4725
CAS No.:56038-13-2
- Hispidin
Catalog No.:BCN3567
CAS No.:56070-89-4
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- 3-Methoxyshancigusin I
Catalog No.:BCC9002
CAS No.:
- Ionomycin free acid
Catalog No.:BCC7261
CAS No.:56092-81-0
- Ionomycin calcium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5805
CAS No.:56092-82-1
- Securinine
Catalog No.:BCN6988
CAS No.:5610-40-2
- Parisaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN2835
CAS No.:561007-63-4
- Asperglaucide
Catalog No.:BCN5748
CAS No.:56121-42-7
- 4-O-Methylhelichrysetin
Catalog No.:BCN3986
CAS No.:56121-44-9
- Valrubicin
Catalog No.:BCC5219
CAS No.:56124-62-0
- H-Sar-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3336
CAS No.:5616-81-9
Eburicoic Acid, an Active Triterpenoid from the Fruiting Bodies of Basswood Cultivated Antrodia cinnamomea, Induces ER Stress-Mediated Autophagy in Human Hepatoma Cells.[Pubmed:24716146]
J Tradit Complement Med. 2012 Oct;2(4):312-22.
Antrodia cinnamomea, a Taiwan-specific medicinal mushroom, can manipulate biological activities, including hepatoprotection, anti-inflammation, anti-hepatitis B virus activity, anticancer activity, etc. In this study, the anti-liver cancer activity and molecular mechanisms of Eburicoic acid, the second most abundant triterpenoid from the fruiting bodies of basswood cultivated Antrodia cinnamomea was investigated using the human hepatoma Hep 3B cells. The results show that Eburicoic acid effectively reduced Hep 3B cell viability within 24 hours, and the IC50 was 18.4 muM, which was equivalent to 8.7 mug/mL. Besides, Eburicoic acid induced conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II and a large number of autophagosomes/autolysosomes formation. In depth investigation for the molecular mechanisms, revealed that Eburicoic acid firstly promoted reactive oxygen species generation and ATP depletion, leading to endoplasmic reticulum stress, followed by elevated cytosolic calcium ion concentration and BiP expression, downregulated phosphorylation of DAPK, upregulated phosphorylation of Beclin-1, JNK, and Bcl-2, and finally induced autophagy in Hep 3B cells. These results indicate that Eburicoic acid has significant anti-liver cancer effects and more distinctive mechanisms.
Hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury.[Pubmed:23871054]
Food Chem. 2013 Dec 1;141(3):3020-7.
The hepatoprotective effects of Eburicoic acid (TR1) and dehydroEburicoic acid (TR2) from Antrodia camphorata (AC) against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage were investigated in mice. TR1 and TR2 was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) for 7 days prior to the administration of CCl4. Pretreatment with TR1 and TR2 prevented the elevation of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and liver lipid peroxides in CCl4-treated mice. The activities of antioxidant enzymes [catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)], nitric oxide (NO) production, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were decreased after the treatment with TR1 and TR2 in CCl4-treated mice. Western blotting revealed that TR1 and TR2 significantly decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expressions and increased the expression of cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) in CCl4-treated mice. Therefore, we speculate that TR1 and TR2 protect the liver from CCl4-induced hepatic damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory bioactivities of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid isolated from Antrodia camphorata on the inflammatory mediator expression in mice.[Pubmed:23495748]
J Agric Food Chem. 2013 May 29;61(21):5064-71.
Eburicoic acid (TR1) and dehydroEburicoic acid (TR2), an active ingredient from Antrodia camphorata (AC) solid-state culture, were evaluated for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Treatment with TR1 and TR2 significantly inhibited a number of acetic acid-induced writhing responses and formalin-induced pain in the late phase. In the anti-inflammatory test, TR1 and TR2 decreased paw edema at the fourth and fifth hour after lambda-carrageenan (Carr) administration and increased the activities of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the paw edema tissue. We also demonstrated that TR1 and TR2 significantly attenuated the malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) levels in either edema paw or serum at the fifth hour after Carr injection. Western blotting revealed that TR1 and TR2 decreased Carr-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cycloxyclase (COX-2) expressions at the fifth hour in paw edema. Treatment with TR1 and TR2 also diminished neutrophil infiltration into the paw edema at the fifth hour. The present study suggests that the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of TR1 and TR2 might be related to the decrease of inflammatory cytokines and an increase of antioxidant enzyme activity.


