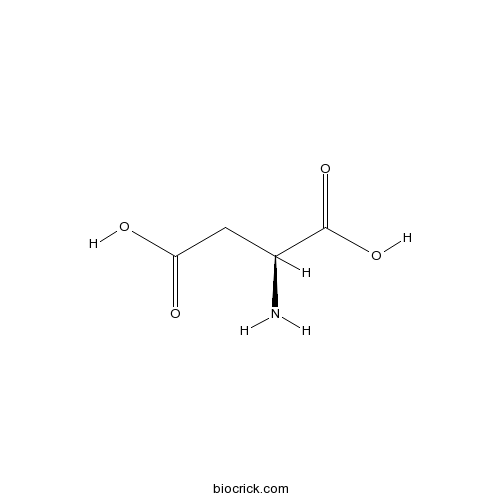
H-Asp-OHCAS# 56-84-8 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 56-84-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5960 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C4H7NO4 | M.Wt | 133.1 |
| Type of Compound | Nitrogen-containing Compounds | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | L-Asparagic acid; L-Asparaginic acid | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 8.33 mg/mL (62.58 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-aminobutanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Endogenous NMDA receptor agonist. |

H-Asp-OH Dilution Calculator

H-Asp-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.5131 mL | 37.5657 mL | 75.1315 mL | 150.263 mL | 187.8287 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.5026 mL | 7.5131 mL | 15.0263 mL | 30.0526 mL | 37.5657 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7513 mL | 3.7566 mL | 7.5131 mL | 15.0263 mL | 18.7829 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1503 mL | 0.7513 mL | 1.5026 mL | 3.0053 mL | 3.7566 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0751 mL | 0.3757 mL | 0.7513 mL | 1.5026 mL | 1.8783 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H-Asp-OH
- Glycerol
Catalog No.:BCC8990
CAS No.:56-81-5
- Chloramphenicol
Catalog No.:BCC1201
CAS No.:56-75-7
- DL-5-Hydroxytryptophan
Catalog No.:BCN1232
CAS No.:56-69-9
- Quinidine
Catalog No.:BCC7863
CAS No.:56-54-2
- Diethylstilbestrol
Catalog No.:BCC4900
CAS No.:56-53-1
- Deoxycorticosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4655
CAS No.:56-47-3
- H-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3028
CAS No.:56-45-1
- H-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3190
CAS No.:56-41-7
- H-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2946
CAS No.:56-40-6
- Tetraethylammonium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7554
CAS No.:56-34-8
- Cantharidin
Catalog No.:BCN1280
CAS No.:56-25-7
- Cystamine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6344
CAS No.:56-17-7
- L-Glutamine
Catalog No.:BCC3803
CAS No.:56-85-9
- L-Glutamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3809
CAS No.:56-86-0
- L-lysine
Catalog No.:BCN7157
CAS No.:56-87-1
- (H-Cys-OH)2
Catalog No.:BCC2915
CAS No.:56-89-3
- Histamine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4530
CAS No.:56-92-8
- Chlorhexidine acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8912
CAS No.:56-95-1
- 9-Hydroxy-4-androstene-3,17-dione
Catalog No.:BCC8802
CAS No.:560-62-3
- Eburicoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2556
CAS No.:560-66-7
- Sucralose
Catalog No.:BCC4725
CAS No.:56038-13-2
- Hispidin
Catalog No.:BCN3567
CAS No.:56070-89-4
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- 3-Methoxyshancigusin I
Catalog No.:BCC9002
CAS No.:
Structure/activity relations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands as studied by their inhibition of [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid binding in rat brain membranes.[Pubmed:2901691]
Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):17-31.
Structure/activity relations of agonists and antagonists for the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor have been investigated by measuring the ability of a large range of substances to inhibit binding of [3H]2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate to rat brain membranes. A major difference between optimum structures for agonist and antagonist activity lay in the differential effectiveness of sulphonic and phosphonic acid groups as the omega-acidic terminal in these two types of compound. The sulphonic acid moiety was an effective omega-acidic terminal in short chain agonists, but not in longer chain antagonists, while the phosphonic acid group was the most effective omega-acidic terminal in longer chain antagonists, but was only very weakly active in short chain agonists. It is proposed that the binding site of the omega-acidic terminal of antagonists is different from that for the omega-acidic group of agonists. Other structural features conducive to effective interaction of ligands with the receptor are discussed.


