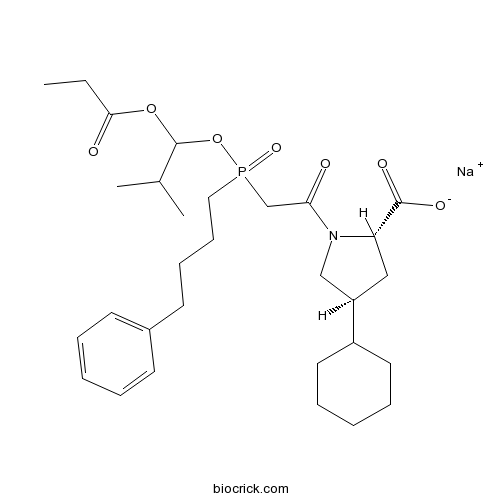
Fosinopril sodiumACE inhibitor CAS# 88889-14-9 |
- Saquinavir
Catalog No.:BCC1921
CAS No.:127779-20-8
- Saquinavir mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1922
CAS No.:149845-06-7
- Nelfinavir Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1794
CAS No.:159989-65-8
- Lopinavir
Catalog No.:BCC3621
CAS No.:192725-17-0
- Darunavir
Catalog No.:BCC3623
CAS No.:206361-99-1
- BMS-626529
Catalog No.:BCC1427
CAS No.:701213-36-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 88889-14-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23681451 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H45NNaO7P | M.Wt | 585.64 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (56.91 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 1 mg/mL (1.71 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;(2S,4S)-4-cyclohexyl-1-[2-[(2-methyl-1-propanoyloxypropoxy)-(4-phenylbutyl)phosphoryl]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CCC(=O)OC(C(C)C)OP(=O)(CCCCC1=CC=CC=C1)CC(=O)N2CC(CC2C(=O)[O-])C3CCCCC3.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TVTJZMHAIQQZTL-HREVRLCXSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H46NO7P.Na/c1-4-28(33)37-30(22(2)3)38-39(36,18-12-11-15-23-13-7-5-8-14-23)21-27(32)31-20-25(19-26(31)29(34)35)24-16-9-6-10-17-24;/h5,7-8,13-14,22,24-26,30H,4,6,9-12,15-21H2,1-3H3,(H,34,35);/q;+1/p-1/t25-,26+,30?,39?;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Fosinopril sodium Dilution Calculator

Fosinopril sodium Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7075 mL | 8.5377 mL | 17.0753 mL | 34.1507 mL | 42.6883 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3415 mL | 1.7075 mL | 3.4151 mL | 6.8301 mL | 8.5377 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1708 mL | 0.8538 mL | 1.7075 mL | 3.4151 mL | 4.2688 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0342 mL | 0.1708 mL | 0.3415 mL | 0.683 mL | 0.8538 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0171 mL | 0.0854 mL | 0.1708 mL | 0.3415 mL | 0.4269 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fosinopril sodium is an effective inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) with IC50 value of 9nM [1].
Fosinopril is a third type ACE inhibitor with a phosphinic acid. It binds to the active site of ACE via targeting the zinc ions with its phosphinic acid moiety. Fosinopril is an orally active prodrug which is hydrolysed and converted to its active diacid fosinoprilat after oral administration. The absorption of fosinopril ranges between 18 and 41 %. Antacids can affect the absorption of fosinopril and cause a decrease in its bioavailability by increasing the gastric pH. The pharmacokinetics assay shows fosinopril is hydrolysed completely into fosinoprilat after absorption. And fosinoprilat is slowly eliminated by renal and hepatic clearance. Fosinopril is proved to produce sustained blood pressure reduction through improving systemic and renal haemodynamics and reducing left ventricular mass [1].
References:
[1] Shionoiri H, Naruse M, Minamisawa K, Ueda S, Himeno H, Hiroto S, Takasaki I. Fosinopril. Clinical pharmacokinetics and clinical potential. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 Jun;32(6):460-80.
- Sprengerinin A
Catalog No.:BCN6658
CAS No.:88866-99-3
- Adrenorphin, Free Acid
Catalog No.:BCC1011
CAS No.:88866-92-6
- Sprengerinin C
Catalog No.:BCN6657
CAS No.:88861-91-0
- 11,12-De(methylenedioxy)danuphylline
Catalog No.:BCN4436
CAS No.:888482-17-5
- Ganetespib (STA-9090)
Catalog No.:BCC2336
CAS No.:888216-25-9
- Galanin (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5960
CAS No.:88813-36-9
- Gambogoic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN7936
CAS No.:887923-50-4
- Isogambogenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3076
CAS No.:887923-47-9
- Gaudichaudic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3071
CAS No.:887923-46-8
- Bafetinib (INNO-406)
Catalog No.:BCC4036
CAS No.:887650-05-7
- (-)-Holostyligone
Catalog No.:BCN2863
CAS No.:887501-28-2
- Fmoc-Arg(Mts)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3075
CAS No.:88743-97-9
- Inulanolide A
Catalog No.:BCN3705
CAS No.:888941-86-4
- Atrial natriuretic factor (1-28) (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5843
CAS No.:88898-17-3
- Bafilomycin A1
Catalog No.:BCC3914
CAS No.:88899-55-2
- Mogroside V
Catalog No.:BCN1036
CAS No.:88901-36-4
- Mogroside IIIe
Catalog No.:BCN7924
CAS No.:88901-37-5
- Mogroside IIe
Catalog No.:BCN3168
CAS No.:88901-38-6
- Mogroside IVa
Catalog No.:BCN3165
CAS No.:88901-41-1
- Mogroside III-A1
Catalog No.:BCN3170
CAS No.:88901-42-2
- Mogroside III-A2
Catalog No.:BCN7925
CAS No.:88901-43-3
- Mogroside II-A1
Catalog No.:BCN7926
CAS No.:88901-44-4
- Mogroside II-A2
Catalog No.:BCN3180
CAS No.:88901-45-5
- (-)-Xestospongin C
Catalog No.:BCC7002
CAS No.:88903-69-9
Monitoring of fosinopril sodium impurities by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry including the neural networks in method evaluation.[Pubmed:18154978]
J Chromatogr A. 2008 May 2;1189(1-2):366-73.
In this paper, the mass spectrometry (MS) detection has been applied for screening of Fosinopril sodium impurities which arise during forced stress study. Before MS analysis, liquid chromatographic method with suitable mobile phase composition was developed. The separation was done on SunFire 100 mm x 4.6 mm 3.5 microm particle size column. The mobile phases which consisted of methanol-ammonium acetate buffer-acetic acid, in different ratios, were used in a preliminary study. Flow rate was 0.3 mL min(-1). Under these conditions, percent of methanol, concentration of ammonium acetate buffer and acetic acid content were tested simultaneously applying central composite design (CCD) and artificial neural network (ANN). The combinations of experimental design (ED) and ANN present powerful technique in method optimization. Input and output variables from CCD were used for network training, verification and testing. Multiple layer perceptron (MLP) with back propagation (BP) algorithm was chosen for network training. When the optimal neural topology was selected, network was trained by adjusting strength of connections between neurons in order to adapt the outputs of whole network to be closer to the desired outputs, or to minimize the sum of the squared errors. From the method optimization the following mobile phase composition was selected as appropriate: methanol-10 mM ammonium acetate buffer-acidic acid (80:19.5:0.5 v/v/v). This mobile phase was used as inlet for MS. According to molecular structure and literature data, electrospray positive ion mode was applied for analysis of Fosinopril sodium and its impurities. The proposed method could be used for screening of Fosinopril sodium impurities in bulk and pharmaceuticals, as well as for tracking the degradation under stress conditions.
Microemulsion liquid chromatographic method for characterisation of fosinopril sodium and fosinoprilat separation with chemometrical support.[Pubmed:16195875]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005 Oct;383(4):687-94.
The properties of the eluent are the essential factors governing the efficiency in the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. A novel approach in retention modelling in the liquid chromatographic separation of Fosinopril sodium and its degradation product, fosinoprilat, applying a microemulsion as the mobile phase, was used. The modifications of the mobile phase included the changes to the type of the lipophilic phase, the type and concentration of co-surfactant and surfactant, as well as the pH of the mobile phase. In this study, a full factorial 2(3) design, as the optimal method for screening of the experiment, was applied for selecting factors which had an influence on separation. Optimisation was done by a central composite design. An appropriate resolution with reasonable retention times was obtained with a microemulsion containing 0.9% w/w of cyclohexane, 2.2% w/w of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), 8.0% w/w of n-butanol and 88.9% of aqueous 25 mM disodium phosphate, the pH of which was adjusted to 2.8 with 85% orthophosphoric acid. Separations were performed on an X-Terra 50-mmx4.6-mm, 3.5-mum particle size column at 30 degrees C. UV detection was performed at 220 nm and with a flow rate of 0.3 mL min(-1). The established method was validated and applied for analysis of appropriate tablets. The proposed chromatographic procedure for the separation of Fosinopril sodium and its degradation product is less expensive compared with the conventional reversed-phase HPLC method, as well as being simple and rapid. The optimised and validated method can be used for separation, identification and simultaneous determination of Fosinopril sodium and fosinoprilat in bulk drug and in pharmaceutical dose forms.
A new treatment forInterdialytic hyperkalemia - the use of fosinopril sodium.[Pubmed:10393377]
Am J Nephrol. 1999;19(3):395-9.
Fosinopril sodium is the first of the phosphinic acid class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI). It is used as an antihypertensive agent, but differs from other ACEI in its dual routes of excretion (liver and kidney), and less incidence of hyperkalemia and cough. We conducted a study in known chronic hemodialysis patients who developed interdialytic hyperkalemia in spite of other treatments to control hyperkalemia. We used fosinopril in this group of patients to assess the effect of fosinopril on serum potassium (K) levels. Twenty-four patients were given fosinopril 10 mg at 18:00 h daily for 8 weeks. K levels were measured before and after each dialysis treatment. Interdialytic weight gains were recorded. The average pretrial potassium level was 6.57 mmol/l (+/- 0.47), and the posttrial level was 5.34 (+/- 0.76); p
[Protective effect of fosinopril sodium pretreatment combined with ischemic postconditioning on rat heart underwent myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury].[Pubmed:21055289]
Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Jul;38(7):633-7.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of Fosinopril sodium pre-treatment combined with ischemic postconditioning on rat serum and myocardial oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines post ischemia/reperfusion. METHODS: Sixty Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into sham group (n = 15), ischemia/reperfusion group (30 minutes in situ occlusion of the left anterior descending artery followed by 1 hour reperfusion, n = 15), IPoC group (30 minutes occlusion of the left anterior descending artery followed by 3 cycles of 10 seconds of reperfusion/10 seconds of ischemia before 1 hour reperfusion, n = 15) and Fosinopril sodium group [pretreated with Fosinopril sodium (0.9 mgxkg(-1)xd(-1) for 14 days) followed by IPoC protocol at 2 h after the last gavage, n = 15]. The arterial blood and heart samples were extracted after 1 hour reperfusion. Serum CK-MB and cTnT levels were detected by colorimetric method, myocardial infarction size was measured by nitrotetrazolium blue chloride staining, SOD content was examined by colorimetric method, MDA content was detected using thiobarbituric acid method, serum levels of Interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha), Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were examined by radioimmunoassay, IL-1alpha, IL-6 and TNF-alpha levels of myocardial tissue were detected by ELISA. RESULTS: Compared with I/R group, myocardial enzymes and infarction size were significantly decreased (P < 0.05, P < 0.01), serum SOD content was increased and MDA content was decreased (all P < 0.01), serum and myocardial levels of IL-1alpha, IL-6 and TNF-alpha were significantly reduced (P < 0.05, P < 0.05, P < 0.01) in IPoC group. Compared with IPoC group, Fosinopril sodium pretreatment further reduced infarction size and myocardial enzyme CK-MB (P < 0.05), increased SOD content (P < 0.05) while reduced serum IL-6 and myocardial tissue TNF-alpha (P < 0.05, P < 0.01). CONCLUSION: Pretreatment with Fosinopril sodium enhanced the protective effect of IPoC on rat myocardium underwent I/R injury, possibly by reducing oxidative stress and early inflammatory reaction.


